For the following information, determine whether a normal sampling distribution can be used, wherep is the population proportion, a is the level of significance, p is the sample proportion, and n is the sample size. If it can be used, test the claim. Claim: p>0.57; a=0.08. Sample statistics: p=0.64, n=225 O B. The rejection region is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) OE. Anormal sampling distribution cannot be used. If a normal sampling distribution can be used, identify standardized test statistic z. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. OA 2= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) O B. Anormal sampling distribution cannot be used. If a normal sampling distribution can be used, decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis and interpret the decision. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Reject the null hypothesis. There is not enough evidence to support the claim. O B. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not enough evidence to support the claim. O C. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is enough evidence to support the claim. O D. Reject the null hypothesis. There is enough evidence to support the claim. OE. Anormal sampling distribution cannot be used.
For the following information, determine whether a normal sampling distribution can be used, wherep is the population proportion, a is the level of significance, p is the sample proportion, and n is the sample size. If it can be used, test the claim. Claim: p>0.57; a=0.08. Sample statistics: p=0.64, n=225 O B. The rejection region is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) OE. Anormal sampling distribution cannot be used. If a normal sampling distribution can be used, identify standardized test statistic z. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. OA 2= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) O B. Anormal sampling distribution cannot be used. If a normal sampling distribution can be used, decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis and interpret the decision. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Reject the null hypothesis. There is not enough evidence to support the claim. O B. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not enough evidence to support the claim. O C. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is enough evidence to support the claim. O D. Reject the null hypothesis. There is enough evidence to support the claim. OE. Anormal sampling distribution cannot be used.
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.4: Distributions Of Data
Problem 19PFA
Related questions
Question
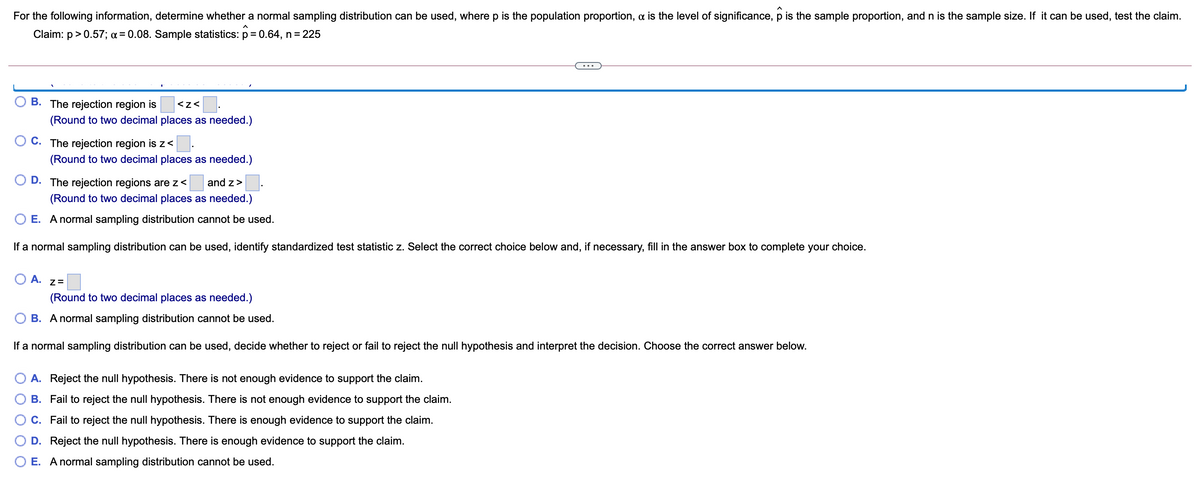
Transcribed Image Text:For the following information, determine whether a normal sampling distribution can be used, where p is the population proportion, a is the level of significance, p is the sample proportion, and n is the sample size. If it can be used, test the claim.
Claim: p> 0.57; ¤ = 0.08. Sample statistics: p 0.64, n = 225
B. The rejection region is
<z<
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
C. The rejection region is z<
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
D. The rejection regions are z<
and z>
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
O E. Anormal sampling distribution cannot be used.
If a normal sampling distribution can be used, identify standardized test statistic z. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice.
O A.
Z=
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
B. A normal sampling distribution cannot be used.
If a normal sampling distribution can be used, decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis and interpret the decision. Choose the correct answer below.
O A. Reject the null hypothesis. There is not enough evidence to support the claim.
B. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not enough evidence to support the claim.
C. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is enough evidence to support the claim.
D. Reject the null hypothesis. There is enough evidence to support the claim.
O E. A normal sampling distribution cannot be used.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill