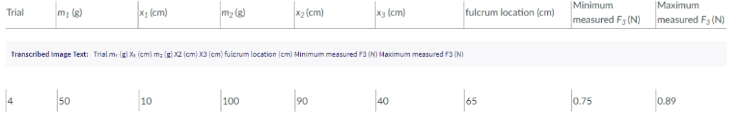
For two existing torques, what third force at a given distance from the pivot will balance them? Imagine a meter stick set up as in the figure. It hangs from a central bracket, and two hanging masses can hang from it from each of their brackets. At a third location, a force probe can either pull up or pull down on the stick, depending on what is needed to balance the stick. The mass of the meter stick is 120 g. sketch the situation (drawing r1, r2, r3, F1, F2, and F3) and determine the magnitude (value) and direction (+ or -) of each torque. Don't include the mass of a bracket that would hold the hanging mass in place; assume the mass listed is the entire mass hanging at that point. For each trial, use the principle of equilibrium (where the sum of torques is zero) to calculate the third, unknown force acting at x3
For two existing torques, what third force at a given distance from the pivot will balance them?
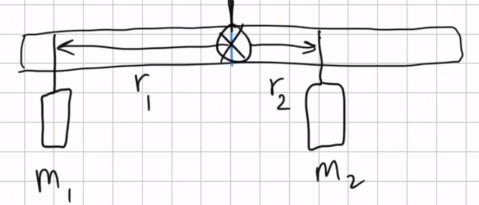
Imagine a meter stick set up as in the figure. It hangs from a central bracket, and two hanging masses can hang from it from each of their brackets. At a third location, a force probe can either pull up or pull down on the stick, depending on what is needed to balance the stick.
The mass of the meter stick is 120 g.
sketch the situation (drawing r1, r2, r3, F1, F2, and F3) and determine the magnitude (value) and direction (+ or -) of each torque. Don't include the mass of a bracket that would hold the hanging mass in place; assume the mass listed is the entire mass hanging at that point.
For each trial, use the principle of equilibrium (where the sum of torques is zero) to calculate the third, unknown force acting at x3
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 8 images









