GENETICS QUESTION!! Imagine that you are a geneticist at a hospital and you are given a file for a patient whose family has a history of cancer. The patient, John Doe, is 18 years old and has had a biopsy done on a tumorous growth in his adrenal gland. He has a sister, Jane, and a brother, Bob, who are younger than he is and who are both healthy. His mother, Betty, has a diagnosis of breast cancer. John’s father, Joe, and John’s paternal grandparents have no history of cancer. Betty is one of four children. Her brother, Tom, and sister, Lucy, have never had cancer or signs of cancer. Both Tom and Lucy are older than Betty. Betty had another brother, Jake, who died very young of leukaemia. Tom has monozygotic twin daughters who are healthy. Betty’s father, Don, died of soft tissue sarcoma in his thirties. Betty’s mother is alive and healthy. Betty’s paternal grandmother, Don’s mother, died of a brain tumor in her thirties. Don had no siblings. As part of your research, you also consult the OMIM (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man) database and come up with a short list of candidate genes could mutate to cause John’s tumor. MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA, TYPE I; MEN1 OMIM #13110 • Associated with tumors of the endocrine (hormone producing) glands. Originally known as Wermer syndrome. • Most common tumors involve parathyroid gland, islet cells of the pancreas, and pituitary gland. • Other endocrine tumors include adrenal cortical tumors, carcinoid tumors and rare pheochromocytomas, as well as tumors in other parts of the digestive tract. LYNCH SYNDROME I OMIM #120435 • Also known as hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC). • Significantly increased risk of developing colorectal cancer. • Increased risk of developing other types of cancers, such as endometrial (uterine), stomach, breast, ovarian, small bowel (intestinal), pancreatic, prostate, urinary tract, liver, kidney, and bile duct cancers. LI-FRAUMENI SYNDROME; LFS OMIM #151623 • Most common types of cancer osteosarcoma (bone cancer), soft-tissue sarcoma, acute leukemia, breast cancer, brain cancer, and adrenal cortical tumors, which is an organ on the top of the kidney. • Increased risk for melanoma, Wilms' tumor, and cancers of the stomach, colon, pancreas, esophagus, lung, and gonadal germ cells (sex organs) have also been reported. CARNEY COMPLEX, TYPE 1; CNC1 OMIM #160980 • Associated with spotty skin pigmentation; myxomas, which are benign (noncancerous) connective tissue tumors. Tumors can be benign or cancerous. • Symptoms develop when a person is in his or her early 20s. • Other common features are Cushing’s syndrome and multiple thyroid nodules (tumors). Features a combination of weight gain, high blood pressure, diabetes, and easy bruising, caused by the overproduction of the hormone cortisol. NEUROBLASTOMA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO OMIM #256700 • Solid cancerous tumor that begins in the nerve cells outside the brain of infants and young children. It can start in the nerve tissue near the spine in the neck, chest, abdomen, or pelvis, but it most often begins in the adrenal glands. • Develops most often in infants and children younger than 5. VON HIPPEL-LINDAU SYNDROME; VHL OMIM #193300 • Associated with tumors arising in multiple organs. Include hemangioblastomas, spinal cord, and eye. • Increased risk of developing clear cell renal cell carcinoma, pheochromocytoma, and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. • Other features - kidney cysts, pancreatic cysts, epididymal cystadenomas, and endolymphatic sac tumors. 8. (3) Later you find out that you have access to a microarray for 10 genes that are associated with John’s type of cancer. The microarray was done comparing normal tissue (control) to cancer samples from six different patients (P1-P6). The results from the microarray are shown below. One of the patients is John. Which one of the patients is most likely John? Explain.
GENETICS QUESTION!!
Imagine that you are a geneticist at a hospital and you are given a file for a patient whose family has a history of cancer.
The patient, John Doe, is 18 years old and has had a biopsy done on a tumorous growth in his adrenal gland. He has a sister, Jane, and a brother, Bob, who are younger than he is and who are both healthy. His mother, Betty, has a diagnosis of breast cancer. John’s father, Joe, and John’s paternal grandparents have no history of cancer.
Betty is one of four children. Her brother, Tom, and sister, Lucy, have never had cancer or signs of cancer. Both Tom and Lucy are older than Betty. Betty had another brother, Jake, who died very young of leukaemia. Tom has monozygotic twin daughters who are healthy. Betty’s father, Don, died of soft tissue sarcoma in his thirties. Betty’s mother is alive and healthy. Betty’s paternal grandmother, Don’s mother, died of a brain tumor in her thirties. Don had no siblings.
As part of your research, you also consult the OMIM (Online
MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA, TYPE I; MEN1
OMIM #13110
• Associated with tumors of the endocrine (hormone producing) glands. Originally known as Wermer syndrome.
• Most common tumors involve parathyroid gland, islet cells of the pancreas, and pituitary gland.
• Other endocrine tumors include adrenal cortical tumors, carcinoid tumors and rare pheochromocytomas, as well as tumors in other parts of the digestive tract.
LYNCH SYNDROME I
OMIM #120435
• Also known as hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC).
• Significantly increased risk of developing colorectal cancer.
• Increased risk of developing other types of cancers, such as endometrial (uterine), stomach, breast, ovarian, small bowel (intestinal), pancreatic, prostate, urinary tract, liver, kidney, and bile duct cancers.
LI-FRAUMENI SYNDROME; LFS
OMIM #151623
• Most common types of cancer osteosarcoma (bone cancer), soft-tissue sarcoma, acute leukemia, breast cancer, brain cancer, and adrenal cortical tumors, which is an organ on the top of the kidney.
• Increased risk for melanoma, Wilms' tumor, and cancers of the stomach, colon, pancreas, esophagus, lung, and gonadal germ cells (sex organs) have also been reported.
CARNEY COMPLEX, TYPE 1; CNC1
OMIM #160980
• Associated with spotty skin pigmentation; myxomas, which are benign (noncancerous) connective tissue tumors. Tumors can be benign or cancerous.
• Symptoms develop when a person is in his or her early 20s.
• Other common features are Cushing’s syndrome and multiple thyroid nodules (tumors). Features a combination of weight gain, high blood pressure, diabetes, and easy bruising, caused by the overproduction of the hormone cortisol.
NEUROBLASTOMA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
OMIM #256700
• Solid cancerous tumor that begins in the nerve cells outside the brain of infants and young children. It can start in the nerve tissue near the spine in the neck, chest, abdomen, or pelvis, but it most often begins in the adrenal glands.
• Develops most often in infants and children younger than 5.
VON HIPPEL-LINDAU SYNDROME; VHL
OMIM #193300
• Associated with tumors arising in multiple organs. Include hemangioblastomas, spinal cord, and eye.
• Increased risk of developing clear cell renal cell carcinoma, pheochromocytoma, and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor.
• Other features - kidney cysts, pancreatic cysts, epididymal cystadenomas, and endolymphatic sac tumors.
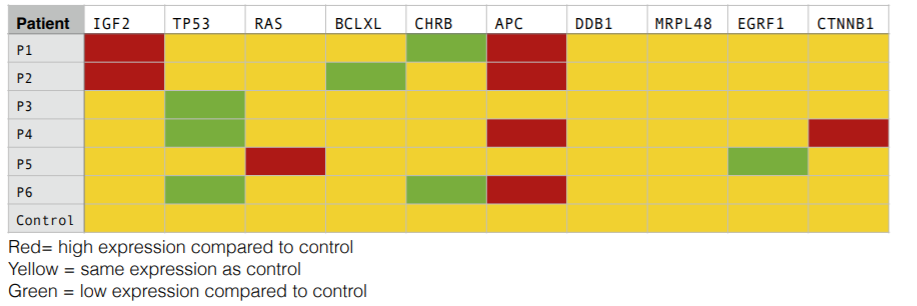
8. (3) Later you find out that you have access to a microarray for 10 genes that are associated with John’s type of cancer. The microarray was done comparing normal tissue (control) to cancer samples from six different patients (P1-P6). The results from the microarray are shown below. One of the patients is John.
Which one of the patients is most likely John? Explain.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images






