Gibbs Free Energy Third Law of Thermodynamics Directions: Answer the following items 1. Calculate the standard free-energy changes for the following reactions at 25°C. a. CH49) + 202 - CO2@ + 2H2O b. 2MgOu) → 2Mg) + Ozg) 2. The molar heats of fusion and vaporization of benzene are 10.9 kJ/mol and 31.0 kJ/mol, respectively. Calculate the entropy changes for the solid → liquid and liquid vapor transitions for benzene. At 1 atm pressure, benzene melts at 5.5°C and boils at 80.1°C. 3. Using data listed in Table I below, calculate the equilibrium constant (K) for the following reaction at 25°C: 2H2Oa) → 2H2g) = Ozg) %3D Inorganic Substances AH°; (kJ/mol) AG°r (kJ/mol) -137.3 S° (J/K'mol) Substance CO CO22) H22) H2Ou Ozg) -110.5 197.9 -393.5 -394.4 213.6 131.0 -285.8 -237.2 69.9 205.0 Organic Substances CH4g) Mg) MgOs) Table 1. Table 1. Selected Thermodynamic Data at 1 atm and 25°C* -74.85 -50.8 186.2 32.5 -601.8 569.6 26.78 *The AH°s, AG; and S° values for ions are based on the reference states AH (H.) = 0, AGr (H.)3D0, and S (H.)%3D0.
Gibbs Free Energy Third Law of Thermodynamics Directions: Answer the following items 1. Calculate the standard free-energy changes for the following reactions at 25°C. a. CH49) + 202 - CO2@ + 2H2O b. 2MgOu) → 2Mg) + Ozg) 2. The molar heats of fusion and vaporization of benzene are 10.9 kJ/mol and 31.0 kJ/mol, respectively. Calculate the entropy changes for the solid → liquid and liquid vapor transitions for benzene. At 1 atm pressure, benzene melts at 5.5°C and boils at 80.1°C. 3. Using data listed in Table I below, calculate the equilibrium constant (K) for the following reaction at 25°C: 2H2Oa) → 2H2g) = Ozg) %3D Inorganic Substances AH°; (kJ/mol) AG°r (kJ/mol) -137.3 S° (J/K'mol) Substance CO CO22) H22) H2Ou Ozg) -110.5 197.9 -393.5 -394.4 213.6 131.0 -285.8 -237.2 69.9 205.0 Organic Substances CH4g) Mg) MgOs) Table 1. Table 1. Selected Thermodynamic Data at 1 atm and 25°C* -74.85 -50.8 186.2 32.5 -601.8 569.6 26.78 *The AH°s, AG; and S° values for ions are based on the reference states AH (H.) = 0, AGr (H.)3D0, and S (H.)%3D0.
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter10: Entropy And The Second Law Of Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10.50PAE: For the reaction NO(g)+NO2(g)N2O3(g) , use tabulated thermodynamic data to calculate H and S. Then...
Related questions
Question
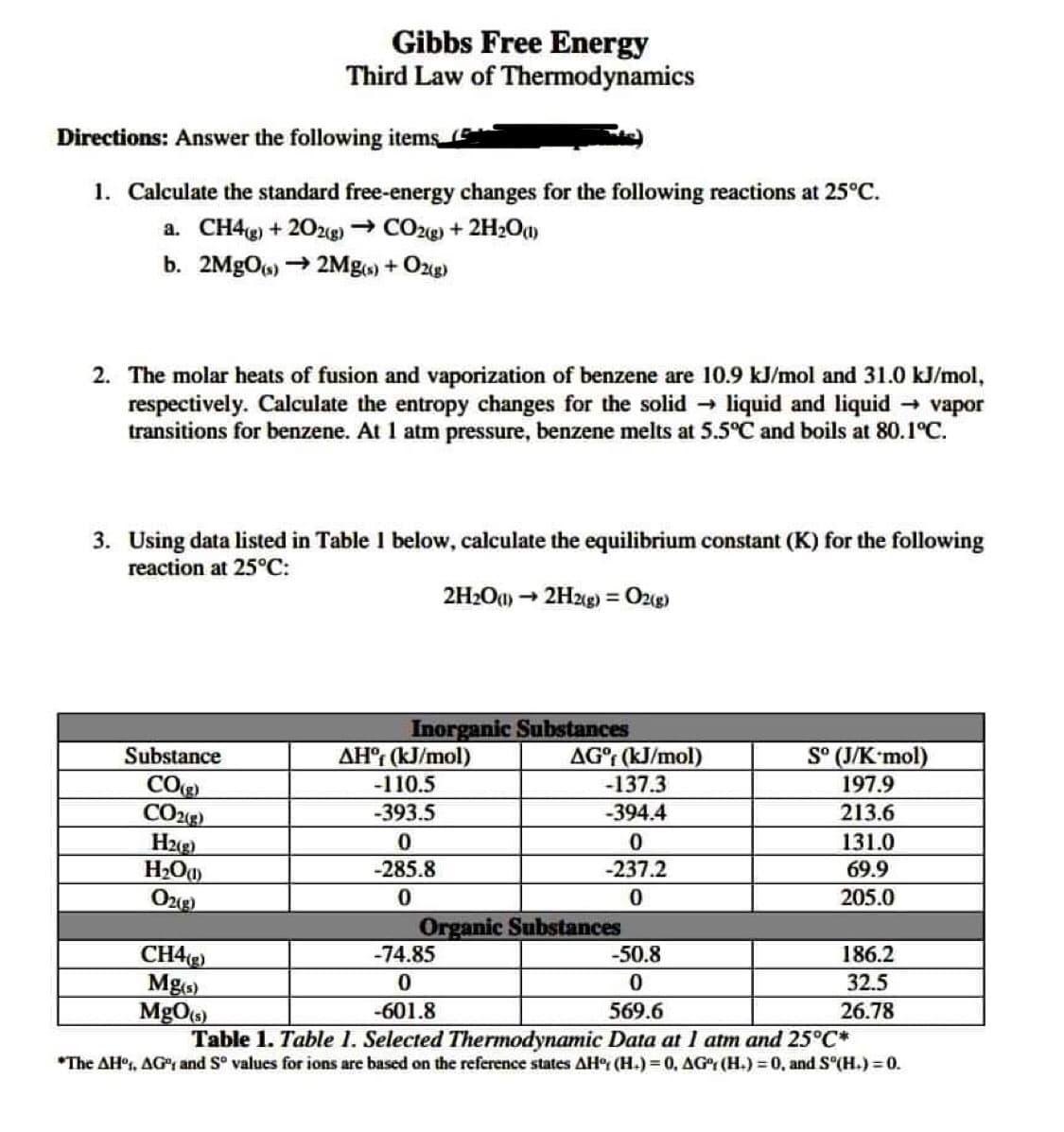
Transcribed Image Text:Gibbs Free Energy
Third Law of Thermodynamics
Directions: Answer the following items
1. Calculate the standard free-energy changes for the following reactions at 25°C.
a. CH4g + 202g) → CO2@ + 2H200
b. 2MgOs) → 2Mg) + Ozg)
2. The molar heats of fusion and vaporization of benzene are 10.9 kJ/mol and 31.0 kJ/mol,
respectively. Calculate the entropy changes for the solid → liquid and liquid vapor
transitions for benzene. At 1 atm pressure, benzene melts at 5.5°C and boils at 80.1°C.
3. Using data listed in Table I below, calculate the equilibrium constant (K) for the following
reaction at 25°C:
2H2O1) → 2Hzg) = O2g)
%3D
Inorganic Substances
AH°; (kJ/mol)
AG°r (kJ/mol)
-137.3
S° (J/K'mol)
Substance
CO
CO22)
H22)
H2Oa
Ozg)
-110.5
197.9
-393.5
-394.4
213.6
131.0
-285.8
-237.2
69.9
205.0
Organic Substances
-74.85
CH4)
Mg)
MgOs)
Table 1. Table 1. Selected Thermodynamic Data at 1 atm and 25°C*
-50.8
186.2
32.5
-601.8
569.6
26.78
*The AH°s, AG, and S° values for ions are based on the reference states AH (H.) = 0, AGr (H.)3 0, and S (H.)%3D0.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning