Given: Diameter of pipe in point 1 = 3.2 Diameter of pipe in point 2 = 2.3 Specific gravity of the liquid = 0.77 h (ft) (see in figure 2) = 0.60 Pressure at point 1 = 14.6 Pressure at point 3 = 46 Combined Pump and motor efficiency = 61 Diameter of pipe in point 4 = 4.3 Diameter of pipe in point 5 = 2.2 z3 (see figure 1) = 31 With the schematic diagram of a pump, tanks, and piping determine the following: 1) The velocity of the liquid at point 5 (ft/s) 2) Pump work used by the liquid (Wpump U) (hp) 3) Electric motor power in out (kW) 4) In figure 3, the shaded (pink) in the U tube is mercury; determine y. specific gravity of mercury 13.7 5) Mass flow rate Assume the whole system is steady flow with a pipe friction loss of 2 ft of water between point 1 to point 3. Use only the following constant and conversion g= 32.2 ft/s 1 hp= 33,000 ft-lbf/min 1 hp = 0.746 kW Specific gracity of mercury 13.7 In computing for the density of mercury use the density of water =62.4 lbm/ft³ Figure 1 At point 2 Figure 2 Pressurized tank Za pump Different diameters See figure 3 See figure 2 motor Stagnation point At points 4 and 5 Figure 3 D5 D4
Given: Diameter of pipe in point 1 = 3.2 Diameter of pipe in point 2 = 2.3 Specific gravity of the liquid = 0.77 h (ft) (see in figure 2) = 0.60 Pressure at point 1 = 14.6 Pressure at point 3 = 46 Combined Pump and motor efficiency = 61 Diameter of pipe in point 4 = 4.3 Diameter of pipe in point 5 = 2.2 z3 (see figure 1) = 31 With the schematic diagram of a pump, tanks, and piping determine the following: 1) The velocity of the liquid at point 5 (ft/s) 2) Pump work used by the liquid (Wpump U) (hp) 3) Electric motor power in out (kW) 4) In figure 3, the shaded (pink) in the U tube is mercury; determine y. specific gravity of mercury 13.7 5) Mass flow rate Assume the whole system is steady flow with a pipe friction loss of 2 ft of water between point 1 to point 3. Use only the following constant and conversion g= 32.2 ft/s 1 hp= 33,000 ft-lbf/min 1 hp = 0.746 kW Specific gracity of mercury 13.7 In computing for the density of mercury use the density of water =62.4 lbm/ft³ Figure 1 At point 2 Figure 2 Pressurized tank Za pump Different diameters See figure 3 See figure 2 motor Stagnation point At points 4 and 5 Figure 3 D5 D4
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
Do not convert English units to SI units except horsepower to kW
Box final answers and round to 4 decimal numbers.
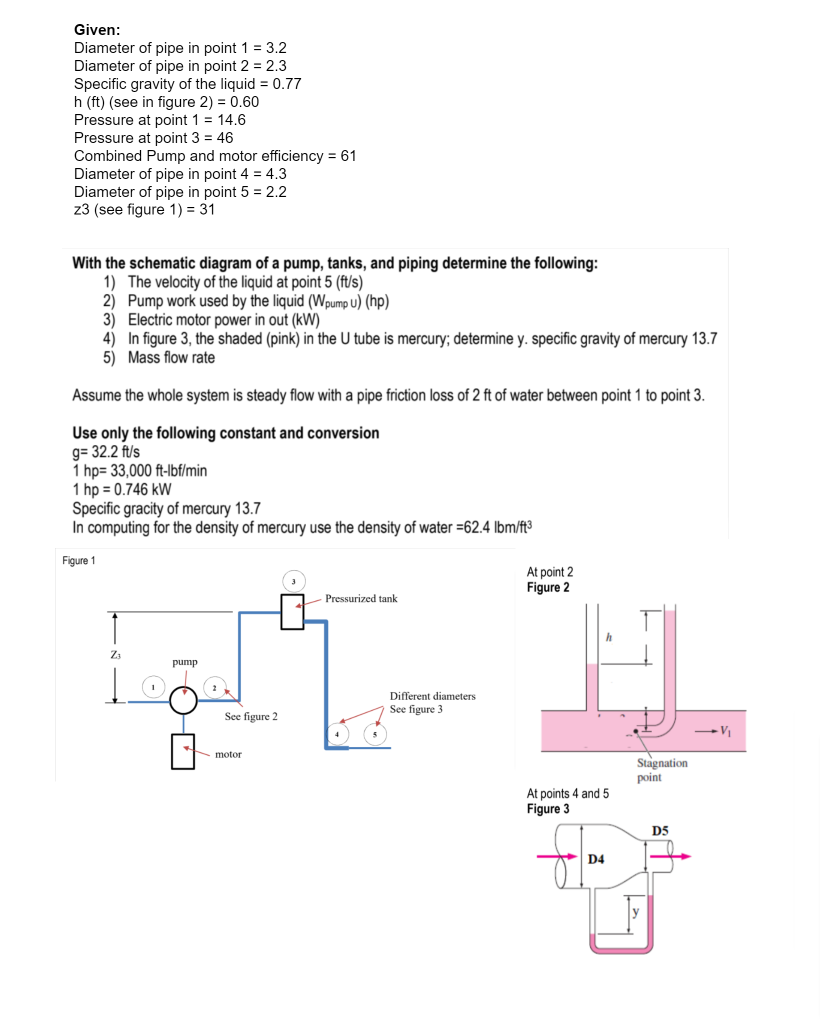
Transcribed Image Text:Given:
Diameter of pipe in point 1 = 3.2
Diameter of pipe in point 2 = 2.3
Specific gravity of the liquid = 0.77
h (ft) (see in figure 2) = 0.60
Pressure at point 1 = 14.6
Pressure at point 3 = 46
Combined Pump and motor efficiency = 61
Diameter of pipe in point 4 = 4.3
Diameter of pipe in point 5 = 2.2
z3 (see figure 1) = 31
With the schematic diagram of a pump, tanks, and piping determine the following:
1) The velocity of the liquid at point 5 (ft/s)
2) Pump work used by the liquid (Wpump U) (hp)
3) Electric motor power in out (kW)
4) In figure 3, the shaded (pink) in the U tube is mercury; determine y. specific gravity of mercury 13.7
5) Mass flow rate
Assume the whole system is steady flow with a pipe friction loss of 2 ft of water between point 1 to point 3.
Use only the following constant and conversion
g= 32.2 ft/s
1 hp= 33,000 ft-Ibf/min
1 hp = 0.746 kW
Specific gracity of mercury 13.7
In computing for the density of mercury use the density of water =62.4 lbm/ft3
Figure 1
At point 2
Figure 2
Pressurized tank
Z3
pump
Different diameters
See figure 3
See figure 2
motor
Stagnation
point
At points 4 and 5
Figure 3
D5
D4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY