H2(g) + CO2(g) H₂O(g) + CO(g) Solution First we will set up an equilibrium table. It is important to understand how to set up this table, because we will use this throughout the course. Steps to set up an equilibrium table. 1) Set up table format, it is always the same. Initial (1) Change (C) Equilibrium (E) Initial (I) Change (C) Equilibrium (E) H2(g) + CO2(g) 2) Fill in the initial concentrations from the given information in the problem. H2(g) + Ş 1M Initial (I) Change (C) Equilibrium (E) H2(g) + 1M CO2(g) IM -X 3) To determine the change, you subtract "x" multiplied by the stoichiometric coefficient from the non-zero concentrations, and add "x" multiplied by the stoichiometric coefficients to the zero concentrations. This is the procedure to use only when we have zero concentrations of products or reactants. ↓↑ CO2(g) IM H₂O(g) + CO(g) -X H₂O(g) + CO(g) 0 0 H₂O(g) + CO(g) 0 0 +x + X
H2(g) + CO2(g) H₂O(g) + CO(g) Solution First we will set up an equilibrium table. It is important to understand how to set up this table, because we will use this throughout the course. Steps to set up an equilibrium table. 1) Set up table format, it is always the same. Initial (1) Change (C) Equilibrium (E) Initial (I) Change (C) Equilibrium (E) H2(g) + CO2(g) 2) Fill in the initial concentrations from the given information in the problem. H2(g) + Ş 1M Initial (I) Change (C) Equilibrium (E) H2(g) + 1M CO2(g) IM -X 3) To determine the change, you subtract "x" multiplied by the stoichiometric coefficient from the non-zero concentrations, and add "x" multiplied by the stoichiometric coefficients to the zero concentrations. This is the procedure to use only when we have zero concentrations of products or reactants. ↓↑ CO2(g) IM H₂O(g) + CO(g) -X H₂O(g) + CO(g) 0 0 H₂O(g) + CO(g) 0 0 +x + X
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter15: Principles Of Chemical Reactivity: Equilibria
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 40GQ: Consider the following equilibrium: COBr2(g) CO(g) + Br2(g)Kc = 0.190 at 73 C (a) A 0.50 mol sample...
Related questions
Question
100%
ICE part 1,2,3 please. Tysm
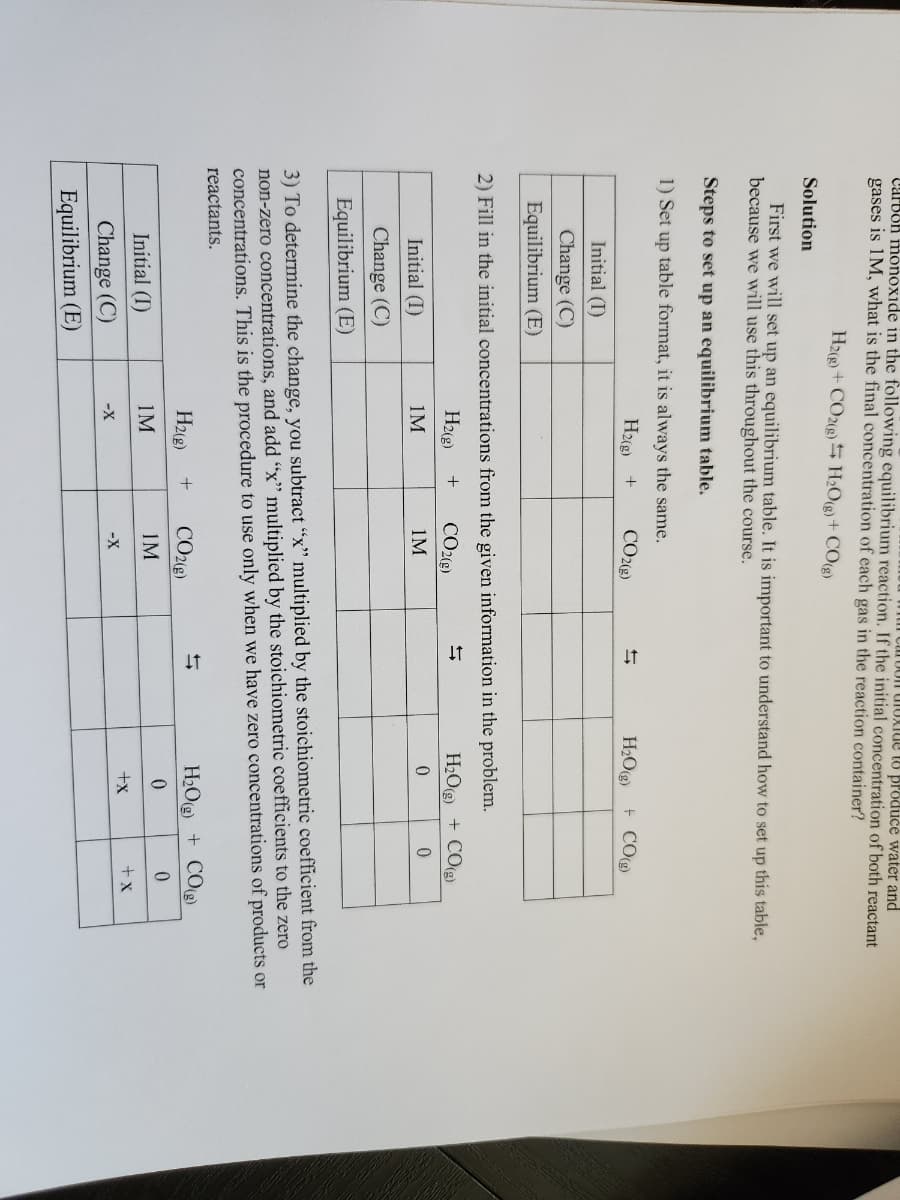
Transcribed Image Text:Carbon monoxide in the following equilibrium reaction. If the initial concentration of both reactant
carbon dioxide to produce water and
gases is 1M, what is the final concentration of each gas in the reaction container?
H2(g) + CO2(g) H₂O(g) + CO(g)
Solution
First we will set up an equilibrium table. It is important to understand how to set up this table,
because we will use this throughout the course.
Steps to set up an equilibrium table.
1) Set up table format, it is always the same.
H2(g) +
Initial (I)
Change (C)
Equilibrium (E)
Initial (I)
Change (C)
Equilibrium (E)
2) Fill in the initial concentrations from the given information in the problem.
H2(g) + CO2(g)
1M
1M
Initial (I)
Change (C)
Equilibrium (E)
CO2(g)
H2(g) +
1M
-X
3) To determine the change, you subtract "x" multiplied by the stoichiometric coefficient from the
non-zero concentrations, and add "x" multiplied by the stoichiometric coefficients to the zero
concentrations. This is the procedure to use only when we have zero concentrations of products or
reactants.
+
CO2(g)
IM
-X
H₂O(g) + CO(g)
+
H₂O(g) + CO(g)
0
0
H₂O(g) + CO(g)
0
0
+x
+ X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning