Hydrogen gas filled balloons are used for survey of weather at higher altitudes. Such hydrogen balloon at Earth’s surface has a volume of 5000 mm3 on a day when the temperature is 27 ° C and the pressure is 1MPa. The balloon rises and expands as the pressure drops. What would the volume of the same number of moles of hydrogen be at an altitude of 40 km where the pressure is 0.33 MPa and the temperature is −13 ° C? If we travel from ground to sky, atmospheric pressure changes? Assess it and justify your result.
Hydrogen gas filled balloons are used for survey of weather at higher altitudes. Such hydrogen
balloon at Earth’s surface has a volume of 5000 mm3 on a day when the temperature is 27 ° C and the pressure is 1MPa. The balloon rises and expands as the pressure drops. What would the volume of the
same number of moles of hydrogen be at an altitude of 40 km where the pressure is 0.33 MPa and the
temperature is −13 ° C? If we travel from ground to sky, atmospheric pressure changes? Assess it and
justify your result.
Given data:
Initial volume (V0) = 5000 mm3
Initial temperature (T0) = 27 0C
Initial pressure (P0) = 1 MPa
Final temperature (T) = –13 0C
Initial pressure (P0) = 0.33 MPa
A balloon is filled with the hydrogen gas and is used to survey of the weather at higher altitudes.
The initial volume of the hydrogen volume (V0) = 5000 mm3
The volume of the balloon at an altitude of 40 km is calculated follows:
From the equation of state of an ideal gas
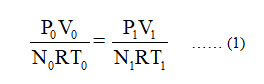
Where,
P0 represents the initial pressure.
V0 represents the initial volume.
N0 represents the initial number of moles of hydrogen gas in balloon.
P1 represents the final (at higher altitude) pressure.
V1 represents the final (at higher altitude) volume.
N1 represents the final number of moles of hydrogen gas in balloon.
R represents the universal gas constant.
It is given the number of moles of hydrogen gas remains same (V0 = V1) at an altitude of 40km, therefore, equation (1) becomes,
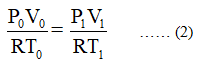
Since R is a constant term, therefore, the equation (2) becomes,
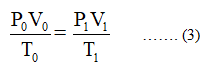
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 5 images









