Biology (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Chapter40: Protection, Support, And Movement
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14TYU
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Cnginu
research
hýpothesis
not supported
Hypothesis
construction
Experimental
testing
Data
analysis
Report
results
ienti
Prior
Hypothesis
supported
Exper
knowledge
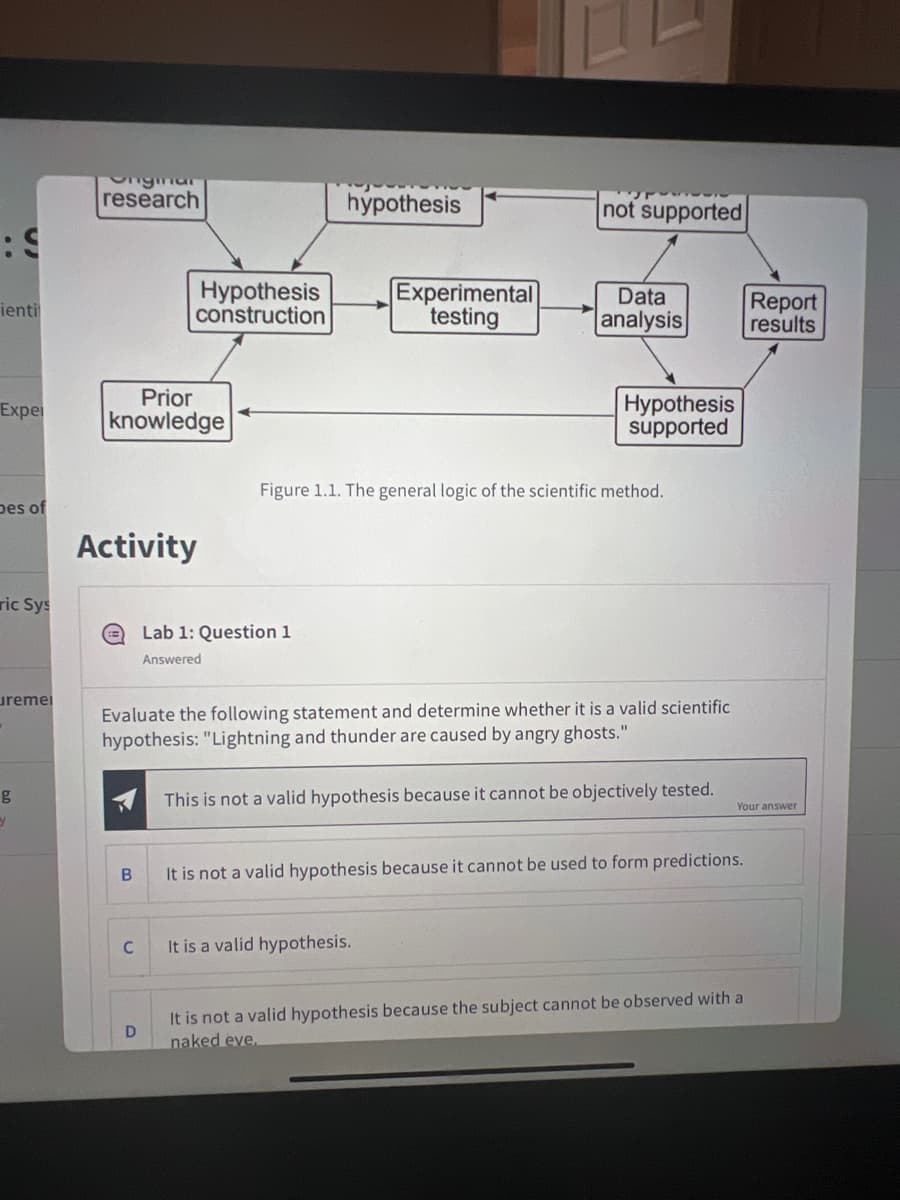
Figure 1.1. The general logic of the scientific method.
pes of
Activity
ric Sys
Lab 1: Question 1
Answered
uremei
Evaluate the following statement and determine whether it is a valid scientific
hypothesis: "Lightning and thunder are caused by angry ghosts."
This is not a valid hypothesis because it cannot be objectively tested.
Your answer
It is not a valid hypothesis because it cannot be used to form predictions.
It is a valid hypothesis.
It is not a valid hypothesis because the subject cannot be observed with a
naked eve.

Transcribed Image Text:Skill 1: Applying The Scientific Method
Science is the pursuit and application of knowledge to understanding of the natural
world by following a systematic methodology based on evidence. The scientific
method is an approach to gaining insights about the way nature works by creating and
testing scientific hypotheses. A hypothesis is a proposed testable explanation of a
natural phenomenon, usually based on prior knowledge and original observations. A
hypothesis forms a basis of predictions regarding properties or behavior of a natural
ei
system under study. Once formulated, the predictions are tested by a carefully
designed experiment, additional observations, or simulations, and the merits of the
hypothesis are evaluated in light of the data. The hypothesis is falsified when data
of
differ from the predictions and, consequently, it is either modified or rejected. The
modified hypothesis is then retested, further modified iteratively, until its predictions
Sys
are consistent with the observed phenomena (Figure 1.1). When the data agree with
the predictions and all the subsequent rigorous tests fail to falsify it, the hypothesis is
accepted as a putative explanation. It is important to recognize that a rejected
hypothesis is not a scientific failure; instead, it is a further step towards understanding
mei
a process being studied as it eliminates a false interpretation and often suggests a
direction for modifying or creating new hypotheses. Multiple corroborating hypotheses
are then used to develop broad general explanations, or scientific theories.
Original
research
Reject/revise
hypothesis
Hypothesis
not supported
Report
Data
Experimental.
Hunotheeie
1/1 answered
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781337392938
Author:
Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781337392938
Author:
Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:
Cengage Learning