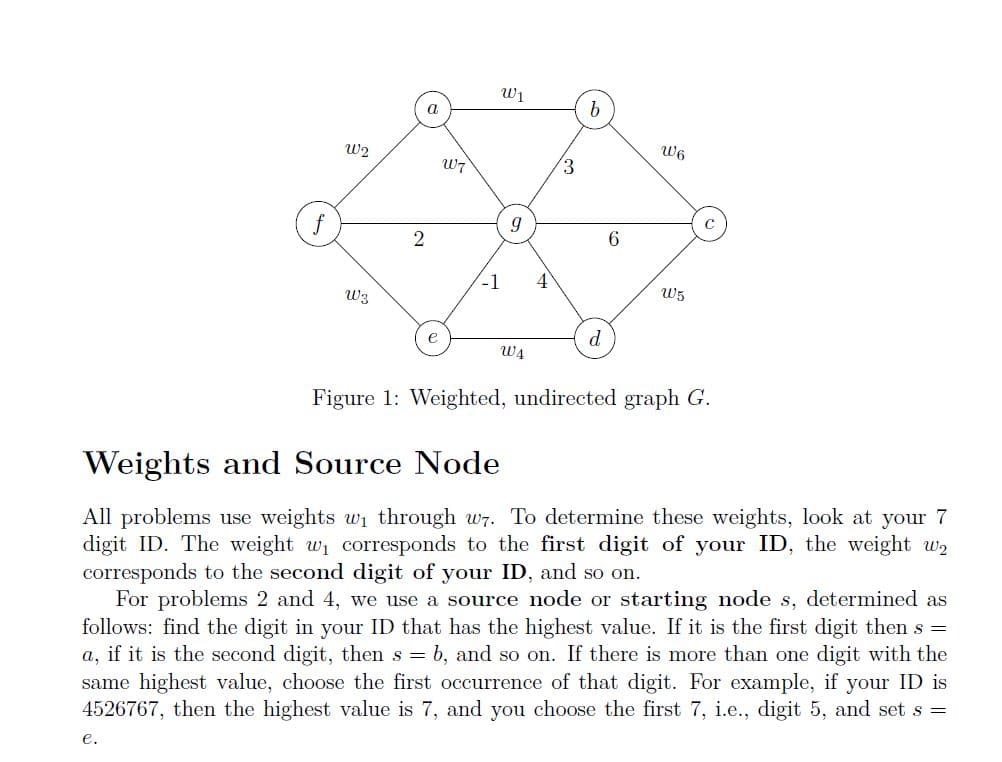
(i) Find the Shortest Paths Tree (SPT) in G starting with source vertex s using Dijkstra’s algorithm. Show the main steps of the algorithm. Note that the graph has a negative weight edge. Does Dijkstra’s algorithm still find the correct shortest paths? (ii) Find the Shortest Paths Tree (SPT) in G starting with source vertex s using Bellman-Ford’s algorithm. Show the main steps of the algorithm. (iii) Suppose we want to the shortest path distances between all pairs of nodes such that the shortest paths use intermediate vertices only from the set {a, b, g}. Use the Floyd-Warshall algorithm to compute these distances between all pairs of nodes.
ID - 1542553
Problem 2
Consider the graph from Problem 1 (Figure 1).
The goal is to find single source shortest paths (in particular, the Shortest Paths Tree) starting from source node s (see Weights and Source Node in picture).
(i) Find the Shortest Paths Tree (SPT) in G starting with source vertex s using Dijkstra’s
paths?
(ii) Find the Shortest Paths Tree (SPT) in G starting with source vertex s using Bellman-Ford’s algorithm. Show the main steps of the algorithm.
(iii) Suppose we want to the shortest path distances between all pairs of nodes such that the shortest paths use intermediate vertices only from the set {a, b, g}. Use the Floyd-Warshall algorithm to compute these distances between all pairs of nodes.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images









