ice water metal isolation A metal block with mass mm initially has a temperature Tm,0 (with Tm,0 > 0°C). On top of that block a beaker with water with mass m and melting ice with mass m; is placed. It has a temperature T = 0°C. Everything is isolated so that there is no heat transfer to/from the surroundings. Assume the temperature of the water is homogeneous. The heat of fusion of water is Lf. The specific heat of the metal is cm; the specific heat of water is Cw; the specific heat of ice is C₁. (a) Calculate the temperature Tm,o the metal should have to just melt all the ice. Now, suppose the initial temperature I'm,0 of the metal is AT higher than the value calculated in (a) (b) Calculate the final temperature Te of the water and the metal after thermal equilibrium has been reached.
ice water metal isolation A metal block with mass mm initially has a temperature Tm,0 (with Tm,0 > 0°C). On top of that block a beaker with water with mass m and melting ice with mass m; is placed. It has a temperature T = 0°C. Everything is isolated so that there is no heat transfer to/from the surroundings. Assume the temperature of the water is homogeneous. The heat of fusion of water is Lf. The specific heat of the metal is cm; the specific heat of water is Cw; the specific heat of ice is C₁. (a) Calculate the temperature Tm,o the metal should have to just melt all the ice. Now, suppose the initial temperature I'm,0 of the metal is AT higher than the value calculated in (a) (b) Calculate the final temperature Te of the water and the metal after thermal equilibrium has been reached.
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Chapter14: Heat And Heat Transfer Methods
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10PE: Even when shut down after a period of normal use, a large commercial nuclear reactor transfers...
Related questions
Question
Dear,
Can you please solve this for me with extra explanations and drawing to understand the answer better as I have an exam soon?
Thank you in advance and Merry Christmas!
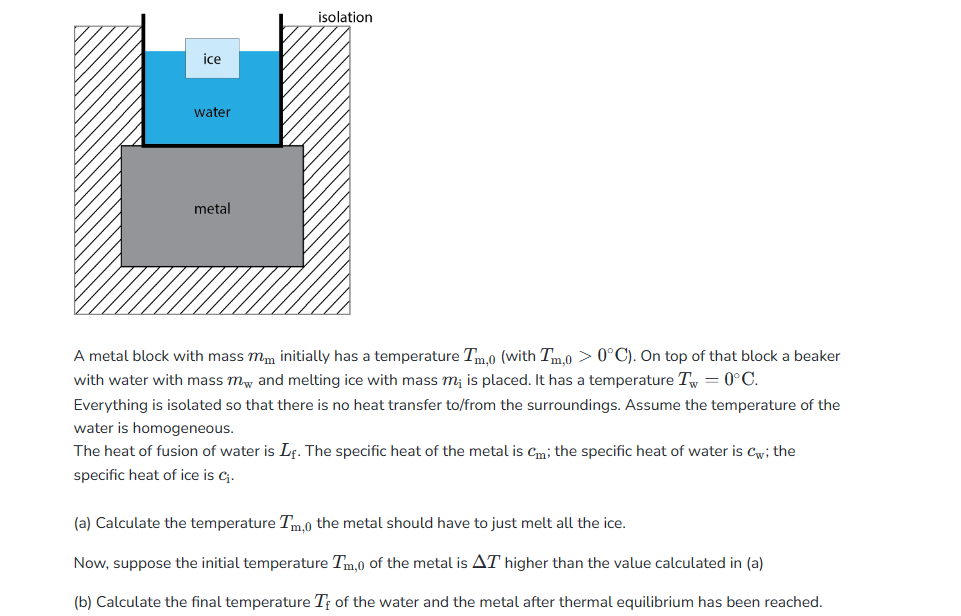
Transcribed Image Text:ice
water
metal
isolation
A metal block with mass mm initially has a temperature Tm,0 (with Tm,0 > 0°C). On top of that block a beaker
with water with mass my and melting ice with mass m; is placed. It has a temperature T = 0°C.
Everything is isolated so that there is no heat transfer to/from the surroundings. Assume the temperature of the
water is homogeneous.
The heat of fusion of water is Lf. The specific heat of the metal is Cm; the specific heat of water is Cw; the
specific heat of ice is C₁.
(a) Calculate the temperature Tm,0 the metal should have to just melt all the ice.
Now, suppose the initial temperature Tm,0 of the metal is AT higher than the value calculated in (a)
(b) Calculate the final temperature Tf of the water and the metal after thermal equilibrium has been reached.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 26 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning