If the SNR of a wireless link is 180B and the RF bandwidth is 30kHz, using Shannon's capacity formula, determine the maximum theoretical data rate that can be transmitted. (a) (b) Electro Magnetic Interference (EMI) is normally considered either conductive or radiative. For each type of interference describe at least three ways of reducing their effects. If the height of an antenna is 100 metres calculate the difference in metres between the radio and optical horizons (presume an adjustment factor of 4/3). If a correctly terminated line has a characteristic impedance of 50N and a measured (c) (d) ation of 22 x 108 m/a with uation of AdR/Arm Tf o foul+
If the SNR of a wireless link is 180B and the RF bandwidth is 30kHz, using Shannon's capacity formula, determine the maximum theoretical data rate that can be transmitted. (a) (b) Electro Magnetic Interference (EMI) is normally considered either conductive or radiative. For each type of interference describe at least three ways of reducing their effects. If the height of an antenna is 100 metres calculate the difference in metres between the radio and optical horizons (presume an adjustment factor of 4/3). If a correctly terminated line has a characteristic impedance of 50N and a measured (c) (d) ation of 22 x 108 m/a with uation of AdR/Arm Tf o foul+
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:Robert L. Boylestad
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P: Visit your local library (at school or home) and describe the extent to which it provides literature...
Related questions
Question
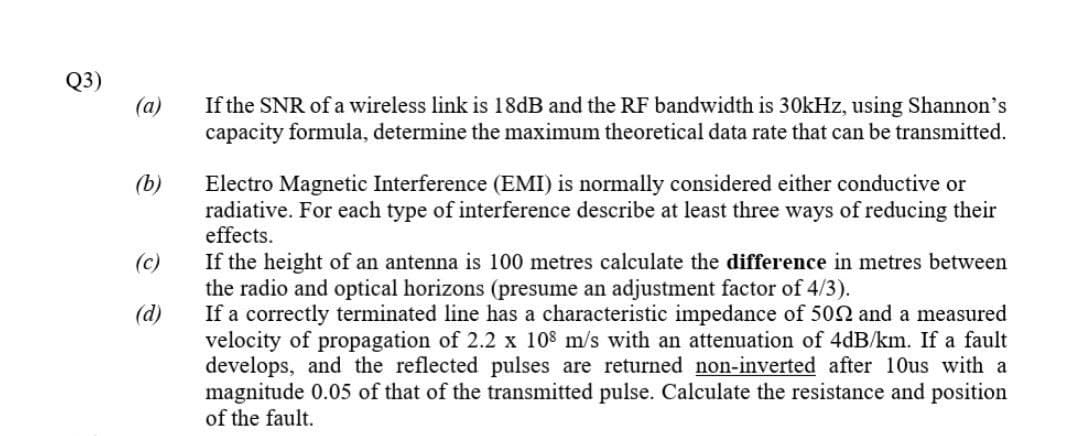
Transcribed Image Text:Q3)
(a)
If the SNR of a wireless link is 18dB and the RF bandwidth is 30kHz, using Shannon's
capacity formula, determine the maximum theoretical data rate that can be transmitted.
(b)
Electro Magnetic Interference (EMI) is normally considered either conductive or
radiative. For each type of interference describe at least three ways of reducing their
effects.
If the height of an antenna is 100 metres calculate the difference in metres between
the radio and optical horizons (presume an adjustment factor of 4/3).
If a correctly terminated line has a characteristic impedance of 502 and a measured
velocity of propagation of 2.2 x 108 m/s with an attenuation of 4dB/km. If a fault
develops, and the reflected pulses are returned non-inverted after 10us with a
magnitude 0.05 of that of the transmitted pulse. Calculate the resistance and position
of the fault.
(c)
(d)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028229
Author:
Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134746968
Author:
James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028151
Author:
Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,