In A ABC and A DEF shown bckow, ZA ZD and B ZE. D. Which series of transformations can be used to show that A ABC- ADEF? First, translate A ABC to map point A onto point D. Next, rotate A ABOC to show that ZA ZD Finally, dilate A ABC to show ZB ZE. First, translate A ABC to mapint A onto point E. Next, rotate A ABC to show that ZA E ZE. Then, translate A ABC to map point B onto point D. Finally, rotate A ABC to show that ZB~ZD. B. Next, translate A ABC to map point C C. First, reflect A ABC across a vertical line through point C onto point E. Finally, dilate A ABC to show that ZC = ZE and ZB ZF. There is not enough information given to show that A ABC- A DEF.
In A ABC and A DEF shown bckow, ZA ZD and B ZE. D. Which series of transformations can be used to show that A ABC- ADEF? First, translate A ABC to map point A onto point D. Next, rotate A ABOC to show that ZA ZD Finally, dilate A ABC to show ZB ZE. First, translate A ABC to mapint A onto point E. Next, rotate A ABC to show that ZA E ZE. Then, translate A ABC to map point B onto point D. Finally, rotate A ABC to show that ZB~ZD. B. Next, translate A ABC to map point C C. First, reflect A ABC across a vertical line through point C onto point E. Finally, dilate A ABC to show that ZC = ZE and ZB ZF. There is not enough information given to show that A ABC- A DEF.
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter12: Angle Relationships And Transformations
Section12.6: Rotations And Symmetry
Problem 1C
Related questions
Question
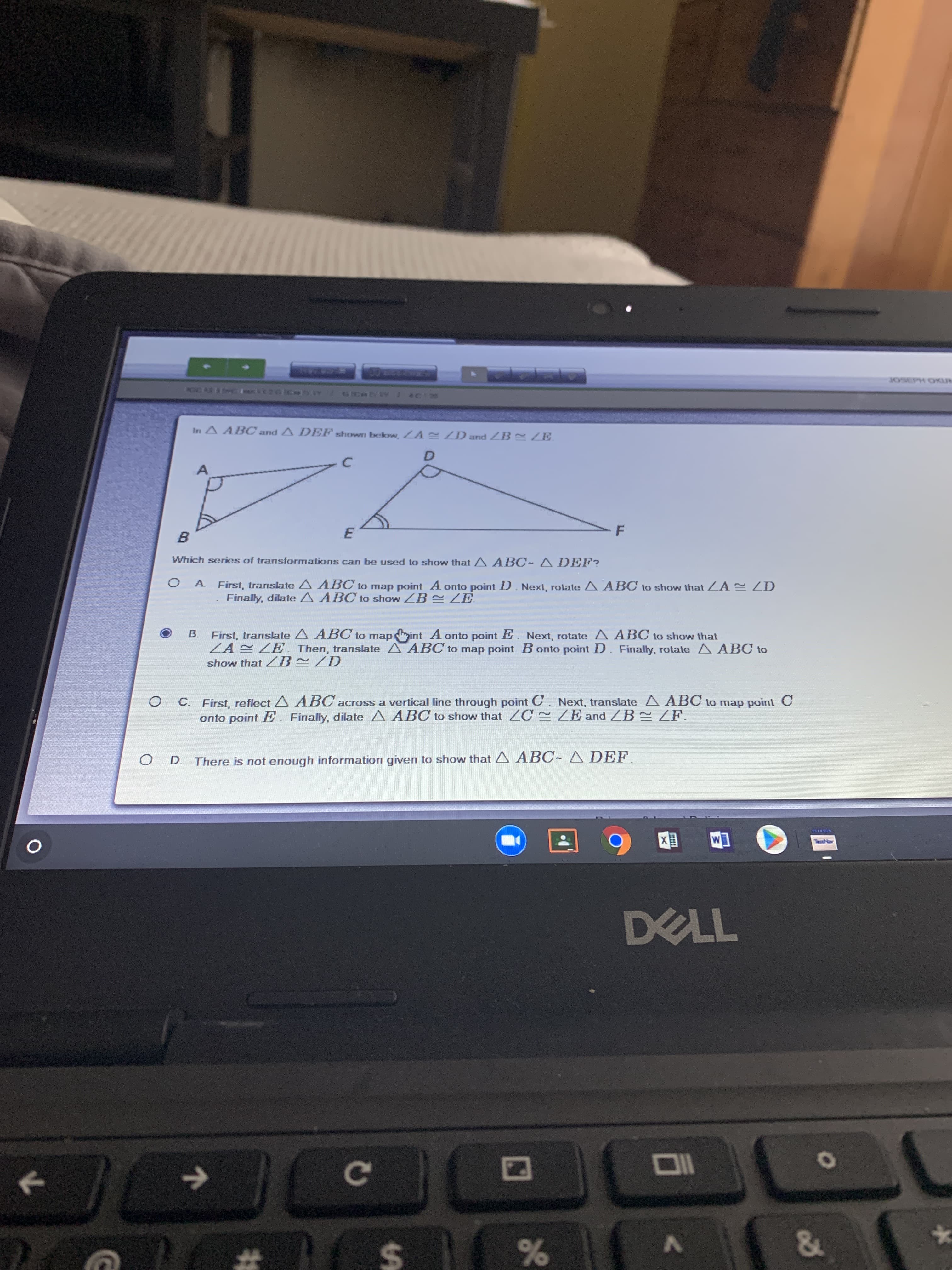
Transcribed Image Text:In A ABC and A DEF shown bckow, ZA ZD and B ZE.
D.
Which series of transformations can be used to show that A ABC- ADEF?
First, translate A ABC to map point A onto point D. Next, rotate A ABOC to show that ZA ZD
Finally, dilate A ABC to show ZB ZE.
First, translate A ABC to mapint A onto point E. Next, rotate A ABC to show that
ZA E ZE. Then, translate A ABC to map point B onto point D. Finally, rotate A ABC to
show that ZB~ZD.
B.
Next, translate A ABC to map point C
C. First, reflect A ABC across a vertical line through point C
onto point E. Finally, dilate A ABC to show that ZC = ZE and ZB ZF.
There is not enough information given to show that A ABC- A DEF.
Expert Solution
Step 1

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, geometry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning