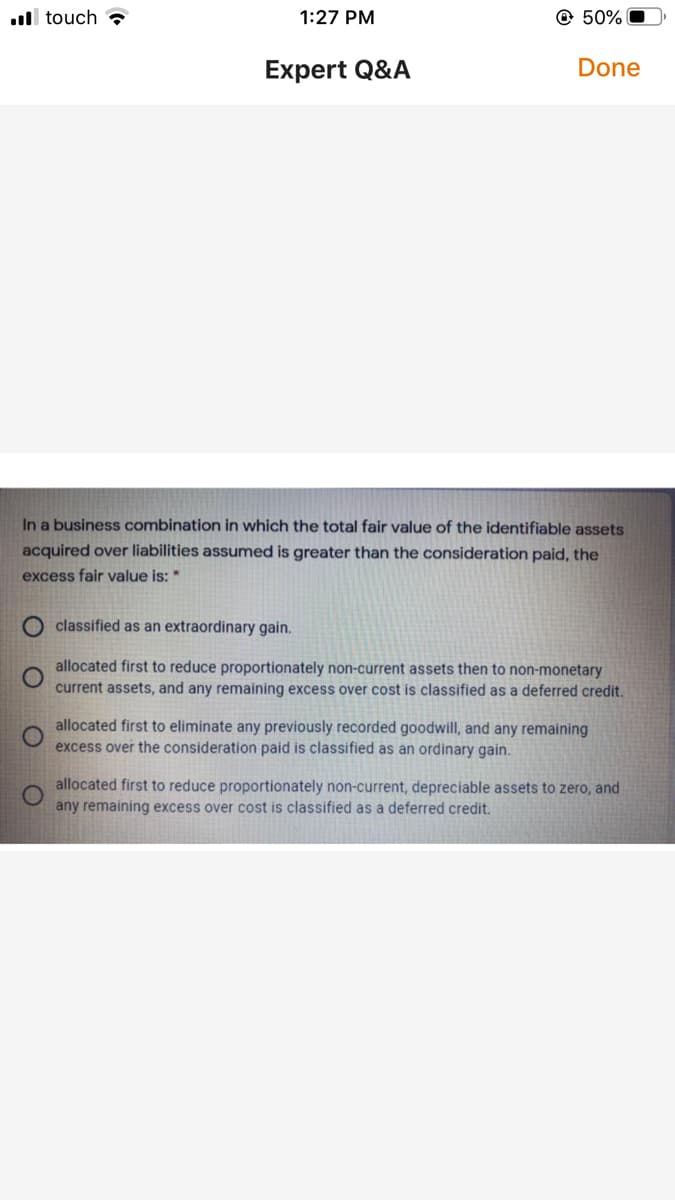
In a business combination in which the total fair value of the identifiable assets acquired over liabilities assumed is greater than the consideration paid, the excess fair value is:* O classified as an extraordinary gain. allocated first to reduce proportionately non-current assets then to non-monetary current assets, and any remaining excess over cost is classified as a deferred credit. allocated first to eliminate any previously recorded goodwill, and any remaining excess over the consideration paid is classified as an ordinary gain. allocated first to reduce proportionately non-current, depreciable assets to zero, and any remaining excess over cost is classified as a deferred credit.
In a business combination in which the total fair value of the identifiable assets acquired over liabilities assumed is greater than the consideration paid, the excess fair value is:* O classified as an extraordinary gain. allocated first to reduce proportionately non-current assets then to non-monetary current assets, and any remaining excess over cost is classified as a deferred credit. allocated first to eliminate any previously recorded goodwill, and any remaining excess over the consideration paid is classified as an ordinary gain. allocated first to reduce proportionately non-current, depreciable assets to zero, and any remaining excess over cost is classified as a deferred credit.
Chapter3: Analyzing And Recording Transactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1EA: Match the correct term with its definition. A. cost principle i. if uncertainty in a potential...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:ull touch
1:27 PM
50%
Expert Q&A
Done
In a business combination in which the total fair value of the identifiable assets
acquired over liabilities assumed is greater than the consideration paid, the
excess fair value is: *
classified as an extraordinary gain.
allocated first to reduce proportionately non-current assets then to non-monetary
current assets, and any remaining excess over cost is classified as a deferred credit.
allocated first to eliminate any previously recorded goodwill, and any remaining
excess over the consideration paid is classified as an ordinary gain.
allocated first to reduce proportionately non-current, depreciable assets to zero, and
any remaining excess over cost is classified as a deferred credit.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning