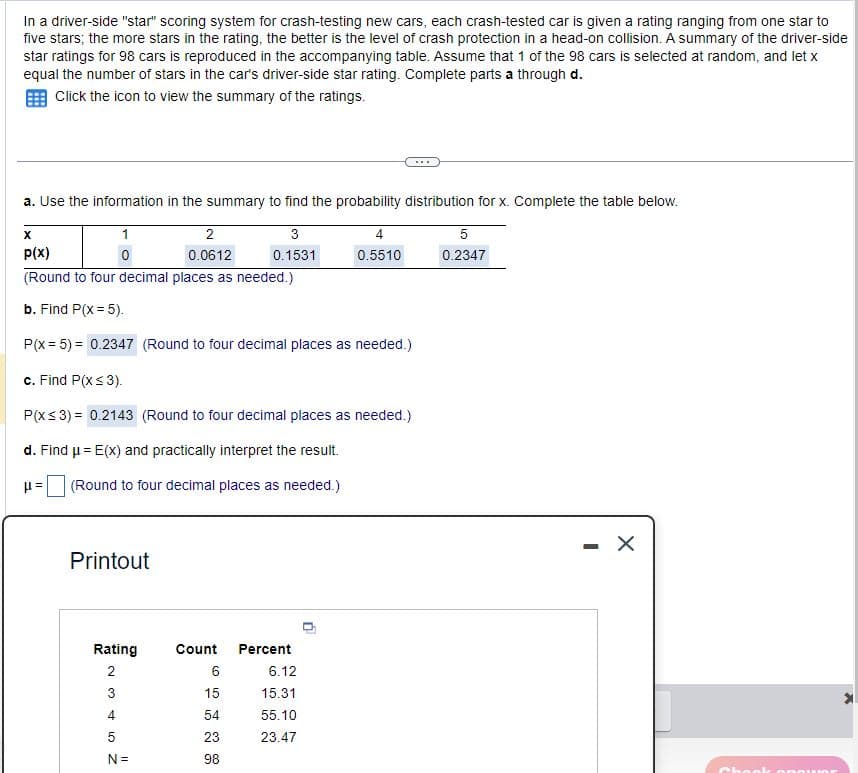
In a driver-side "star" scoring system for crash-testing new cars, each crash-tested car is given a rating ranging from one star to five stars; the more stars in the rating, the better is the level of crash protection in a head-on collision. A summary of the driver-side star ratings for 98 cars is reproduced in the accompanying table. Assume that 1 of the 98 cars is selected at random, and let x equal the number of stars in the car's driver-side star rating. Complete parts a through d. Click the icon to view the summary of the ratings. a. Use the information in the summary to find the probability distribution for x. Complete the table below. p(x) 1 0 2 0.0612 3 4 5 0.1531 0.5510 0.2347 (Round to four decimal places as needed.) b. Find P(x = 5). P(x-5)=0.2347 (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. Find P(X ≤3). P(X ≤3)=0.2143 (Round to four decimal places as needed.) d. Find μ= E(x) and practically interpret the result. μ= (Round to four decimal places as needed.) Printout Rating Count Percent 234 10 6 6.12 15 15.31 54 55.10 5 23 23.47 N = 98 - Chook onow
In a driver-side "star" scoring system for crash-testing new cars, each crash-tested car is given a rating ranging from one star to five stars; the more stars in the rating, the better is the level of crash protection in a head-on collision. A summary of the driver-side star ratings for 98 cars is reproduced in the accompanying table. Assume that 1 of the 98 cars is selected at random, and let x equal the number of stars in the car's driver-side star rating. Complete parts a through d. Click the icon to view the summary of the ratings. a. Use the information in the summary to find the probability distribution for x. Complete the table below. p(x) 1 0 2 0.0612 3 4 5 0.1531 0.5510 0.2347 (Round to four decimal places as needed.) b. Find P(x = 5). P(x-5)=0.2347 (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. Find P(X ≤3). P(X ≤3)=0.2143 (Round to four decimal places as needed.) d. Find μ= E(x) and practically interpret the result. μ= (Round to four decimal places as needed.) Printout Rating Count Percent 234 10 6 6.12 15 15.31 54 55.10 5 23 23.47 N = 98 - Chook onow
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.6: Summarizing Categorical Data
Problem 10CYU
Related questions
Question
5
Transcribed Image Text:In a driver-side "star" scoring system for crash-testing new cars, each crash-tested car is given a rating ranging from one star to
five stars; the more stars in the rating, the better is the level of crash protection in a head-on collision. A summary of the driver-side
star ratings for 98 cars is reproduced in the accompanying table. Assume that 1 of the 98 cars is selected at random, and let x
equal the number of stars in the car's driver-side star rating. Complete parts a through d.
Click the icon to view the summary of the ratings.
a. Use the information in the summary to find the probability distribution for x. Complete the table below.
p(x)
1
0
2
0.0612
3
4
5
0.1531
0.5510
0.2347
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
b. Find P(x = 5).
P(x-5)=0.2347 (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
c. Find P(X ≤3).
P(X ≤3)=0.2143 (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
d. Find μ= E(x) and practically interpret the result.
μ=
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
Printout
Rating
Count
Percent
234 10
6
6.12
15
15.31
54
55.10
5
23
23.47
N =
98
-
Chook onow
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL