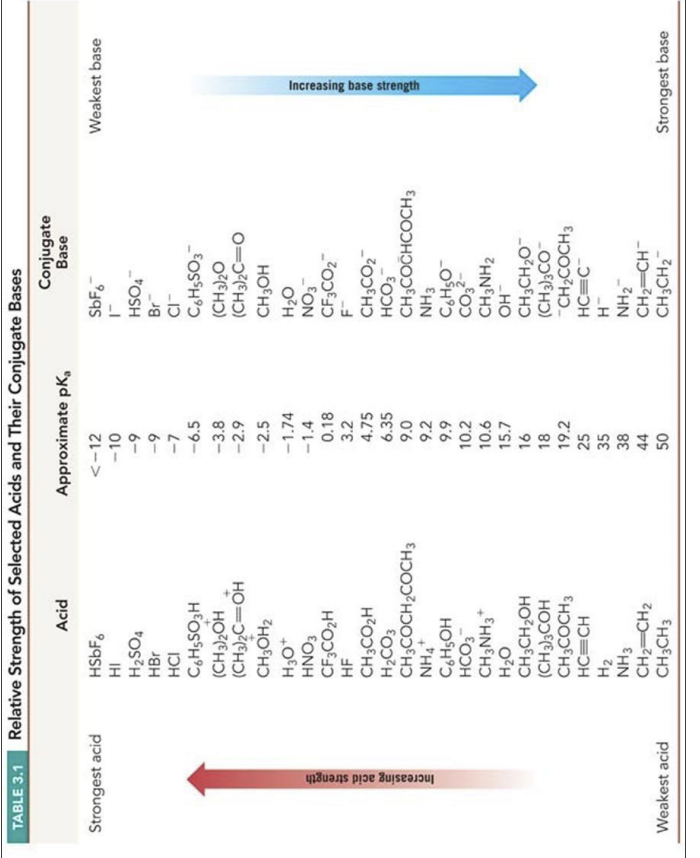
In each of the following reactions, one of the reagents contains two reactive groups (either acidic or basic). You have to decide which group will be affected under mentioned conditions. To answer this problem correctly I suggest that you use the following strategy: (i) Write the products of the reaction: conjugate acid and conjugate base. Use curved arrows to track the flow of electrons; (ii) Using Table 3.1 of the textbook estimate and write pKa values for all acidic groups you have in the reaction equation including conjugate acid; (iii) If you wrote the correct reaction the estimated pKa values should confirm that the reaction transformation changes stronger acid to weaker acid and stronger base to weaker.
In each of the following reactions, one of the reagents contains two reactive groups (either acidic or basic). You have to decide which group will be affected under mentioned conditions. To answer this problem correctly I suggest that you use the following strategy: (i) Write the products of the reaction: conjugate acid and conjugate base. Use curved arrows to track the flow of electrons; (ii) Using Table 3.1 of the textbook estimate and write pKa values for all acidic groups you have in the reaction equation including conjugate acid; (iii) If you wrote the correct reaction the estimated pKa values should confirm that the reaction transformation changes stronger acid to weaker acid and stronger base to weaker.
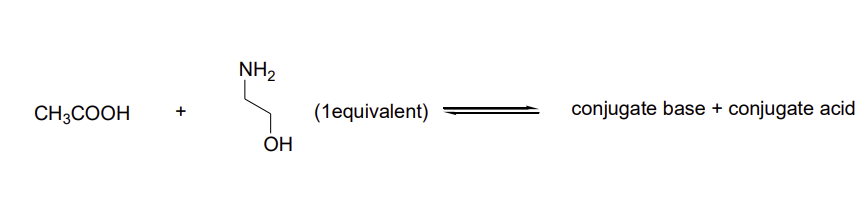
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images


