In Figure 2, two skaters, each of mass 52 kg, approach each other along parallel paths separated by 2.6 m. They have opposite velocities of 1.5 m/s each. One skater carries one end of a long pole of negligible mass, and the other skater grabs the other end as she passes. The skaters then rotate around the center of the pole. Assume that the friction between skates and ice is negligible and the skaters can be treated as mass points. Calculate (a) the angular speed of the skaters (b) the kinetic energy of the two-skater system Next, the skaters pull along the pole until they separated by 1.0 m. Calculate (c) the new angular speed of the skaters (d) the new kinetic energy of the two-skater system 1.5 m/s 2.6 m 1.5 m/s Figure 2
In Figure 2, two skaters, each of mass 52 kg, approach each other along parallel paths separated by 2.6 m. They have opposite velocities of 1.5 m/s each. One skater carries one end of a long pole of negligible mass, and the other skater grabs the other end as she passes. The skaters then rotate around the center of the pole. Assume that the friction between skates and ice is negligible and the skaters can be treated as mass points. Calculate (a) the angular speed of the skaters (b) the kinetic energy of the two-skater system Next, the skaters pull along the pole until they separated by 1.0 m. Calculate (c) the new angular speed of the skaters (d) the new kinetic energy of the two-skater system 1.5 m/s 2.6 m 1.5 m/s Figure 2
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter11: Collisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 49PQ: Two skateboarders, with masses m1 = 75.0 kg and m2 = 65.0 kg, simultaneously leave the opposite...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
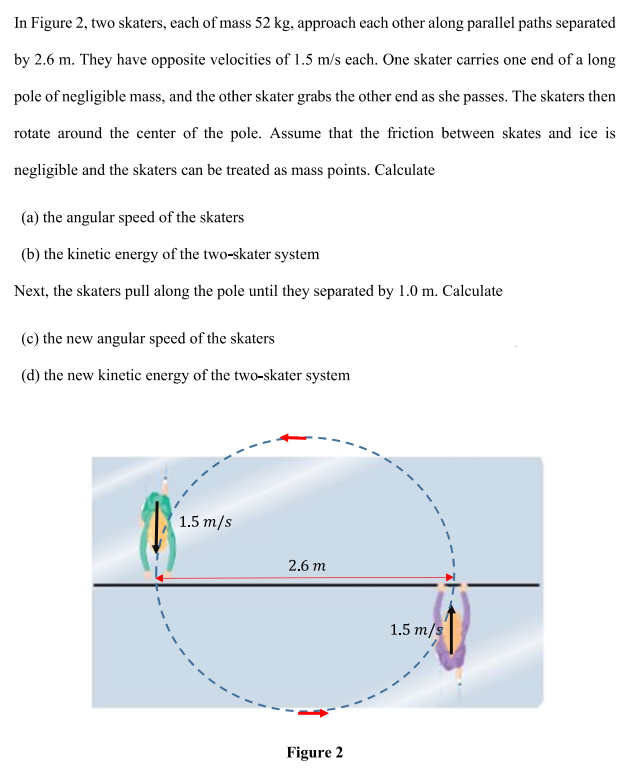
Transcribed Image Text:In Figure 2, two skaters, each of mass 52 kg, approach each other along parallel paths separated
by 2.6 m. They have opposite velocities of 1.5 m/s each. One skater carries one end of a long
pole of negligible mass, and the other skater grabs the other end as she passes. The skaters then
rotate around the center of the pole. Assume that the friction between skates and ice is
negligible and the skaters can be treated as mass points. Calculate
(a) the angular speed of the skaters
(b) the kinetic energy of the two-skater system
Next, the skaters pull along the pole until they separated by 1.0 m. Calculate
(c) the new angular speed of the skaters
(d) the new kinetic energy of the two-skater system
1.5 m/s
2.6 m
1.5 m/s
Figure 2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill