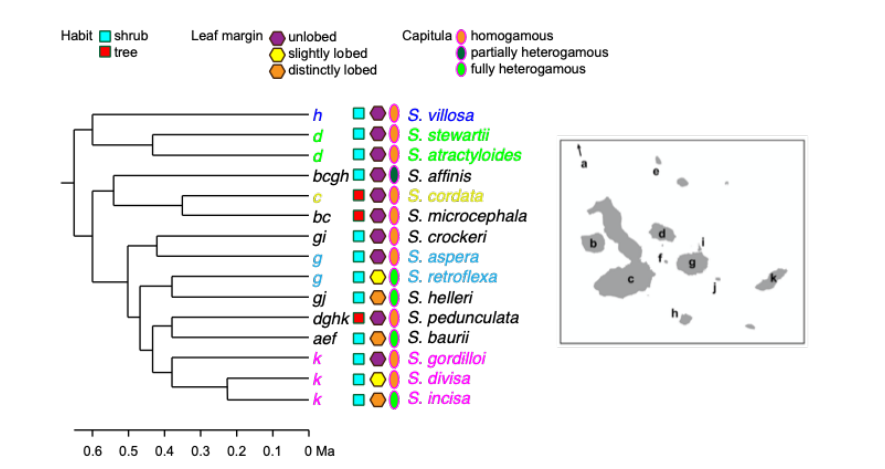
In island radiations we often see the following pattern: similar forms found in different species living in similar habitats on different islands. This pattern raises the question: did the form evolve once on a single island in a single species and then spread to multiple islands by dispersal (let’s call this the “dispersal model”)? Or did a single species first disperse to different islands, then ecologically adapt to the many different environments on each (let’s call this the “convergence model”)? A phylogeny can help us identify which of these processes is at play. Considering the three traits shown on this tree, which model appears to have more support: the dispersal model or the convergence model? Explain how you arrived at this conclusion.
In island radiations we often see the following pattern: similar forms found in different species living in similar habitats on different islands. This pattern raises the question: did the form evolve once on a single island in a single species and then spread to multiple islands by dispersal (let’s call this the “dispersal model”)? Or did a single species first disperse to different islands, then ecologically adapt to the many different environments on each (let’s call this the “convergence model”)? A phylogeny can help us identify which of these processes is at play. Considering the three traits shown on this tree, which model appears to have more support: the dispersal model or the convergence model? Explain how you arrived at this conclusion.
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
15th Edition
ISBN:9781337408332
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Chapter29: Life Cycles Of Flowering Plants
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4SQ: In flowrers, the structures that produce male gametophytes are called ______; the structures that...
Related questions
Question
1. In island radiations we often see the following pattern: similar forms found in different species living in similar habitats on different islands. This pattern raises the question: did the form evolve once on a single island in a single species and then spread to multiple islands by dispersal (let’s call this the “dispersal model”)? Or did a single species first disperse to different islands, then ecologically adapt to the many different environments on each (let’s call this the “convergence model”)? A phylogeny can help us identify which of these processes is at play. Considering the three traits shown on this tree, which model appears to have more support: the dispersal model or the convergence model? Explain how you arrived at this conclusion.
Transcribed Image Text:Habit O shrub
| tree
Leaf margin O unlobed
slightly lobed
distinctly lobed
Capitula O homogamous
partially heterogamous
fully heterogamous
S. villosa
S. stewarti
0 S. atractyloides
S. affinis
S. cordata
100 S. microcephala
S. crockeri
S. aspera
S. retroflexa
S. helleri
S. pedunculata
S. baurii
S. gordilloi
S. divisa
S. incisa
- bcghl
- bc
- gi
- gj
- dghk|
- aef
k
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3 0.2 0.1
O Ma
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781337408332
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781337408332
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning