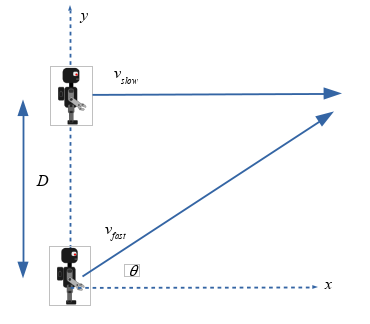
In this challenge we will find the angle needed to aim one robot at another as in the diagram below. The lower robot travels at constant speed vfast and the upper robot travels at constant speed vslow. So both have zero acceleration. The initial vertical distance between them is D. Your challenge is to find the angle needed to cause a collision, the time of the collision, and the location of the collision.
In this challenge we will find the angle needed to aim one robot at another as in
the diagram below.
The lower robot travels at constant speed vfast and the upper robot travels at
constant speed vslow. So both have zero acceleration. The initial vertical distance
between them is D. Your challenge is to find the angle needed to cause a
collision, the time of the collision, and the location of the collision.
Some notes that may help:
1. We can treat motion along the horizontal and vertical in the picture
separately and write separate equations for them. Let’s call horizontal x and
vertical y.
1. We then need to find
other words you need equations for xslow, yslow, xfast, yfast.
1. The fast robot has velocity in the x and y directions. The x-component of the
robot’s velocity is while the y component is
. The initial position of the fast robot is (0,0). So we can write the kinematic
equations (eq 1) as
and
1. The slow robot has velocity only in the x direction. In the y direction the
velocity is zero. The initial position of the slow robot is (0,D).
The data will be provided or measured in lab. It is strongly suggested you work
with the equations in variable form as above, and plug in the numbers only at the
last step.
vslow = _____
vfast = _____
D = _____
*********************************************************
here is the data but don't plug in until the end. Vs=1 m/s, vf = 2 m/s, D = 3 m
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps









