Inside coil 2, what is the direction of -dB/dt during this interval? ---Select-- What is the direction of the electric field inside the wire of coil 2, at a location on the top of coil 2? ---Select-- v At time t=0, what is the magnetic flux through one turn of coil 2? Remember that all turns of coil 1 contribute to the magnetic field. Note also that the coils are not very far apart (compared to their radii), so you can't use an approximate formula here. T m2 At t=0.4 s, what is the magnetic flux through one turn of coil 2? T m2 At t=0 1 turn = At t=0.4 s i turn = What is the emf in one turn of coil 2 during this time interval? |emf, turnl = The voltmeter is connected across all turns of coil 2. What is the reading on the voltmeter during this time interval? voltmeter reading is During this interval, what is the magnitude of the non-Coulomb electric field inside the wire of coil 2? Remember that the emf measured by the voltmeter involves the entire length of the wire making up coil 2. ENC = V/m
Inside coil 2, what is the direction of -dB/dt during this interval? ---Select-- What is the direction of the electric field inside the wire of coil 2, at a location on the top of coil 2? ---Select-- v At time t=0, what is the magnetic flux through one turn of coil 2? Remember that all turns of coil 1 contribute to the magnetic field. Note also that the coils are not very far apart (compared to their radii), so you can't use an approximate formula here. T m2 At t=0.4 s, what is the magnetic flux through one turn of coil 2? T m2 At t=0 1 turn = At t=0.4 s i turn = What is the emf in one turn of coil 2 during this time interval? |emf, turnl = The voltmeter is connected across all turns of coil 2. What is the reading on the voltmeter during this time interval? voltmeter reading is During this interval, what is the magnitude of the non-Coulomb electric field inside the wire of coil 2? Remember that the emf measured by the voltmeter involves the entire length of the wire making up coil 2. ENC = V/m
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Stephen L. Herman
Chapter29: Dc Generators
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1PA: You are working as an electrician in a large steel manufacturing plant, and you are in the process...
Related questions
Question
Answer all 5 parts of the question
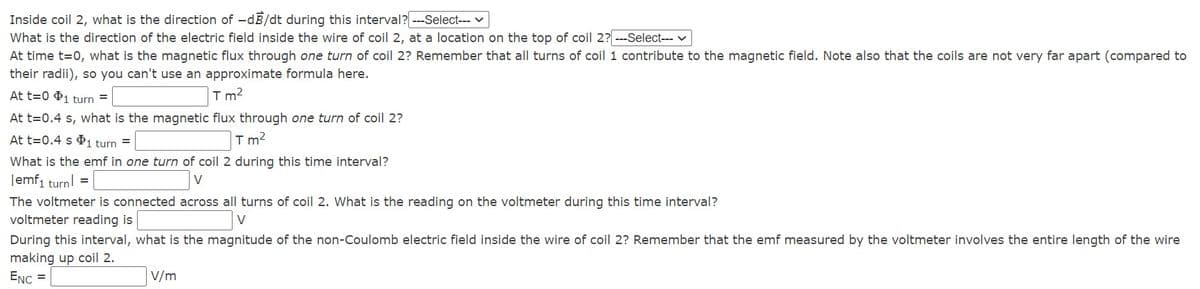
Transcribed Image Text:Inside coil 2, what is the direction of -dB/dt during this interval? ---Select--- v
What is the direction of the electric field inside the wire of coil 2, at a location on the top of coil 2? ---Select-- v
At time t=0, what is the magnetic flux through one turn of coil 2? Remember that all turns of coil 1 contribute to the magnetic field. Note also that the coils are not very far apart (compared to
their radii), so you can't use an approximate formula here.
At t=0 $1 turn =
T m?
At t=0.4 s, what is the magnetic flux through one turn of coil 2?
At t=0.4 s P1 turn =
Tm?
What is the emf in one turn of coil 2 during this time interval?
Jemf1 turnl =
V
The voltmeter is connected across all turns of coil 2. What is the reading on the voltmeter during this time interval?
voltmeter reading is
V
During this interval, what is the magnitude of the non-Coulomb electric field inside the wire of coil 2? Remember that the emf measured by the voltmeter involves the entire length of the wire
making up coil 2.
ENC =
V/m
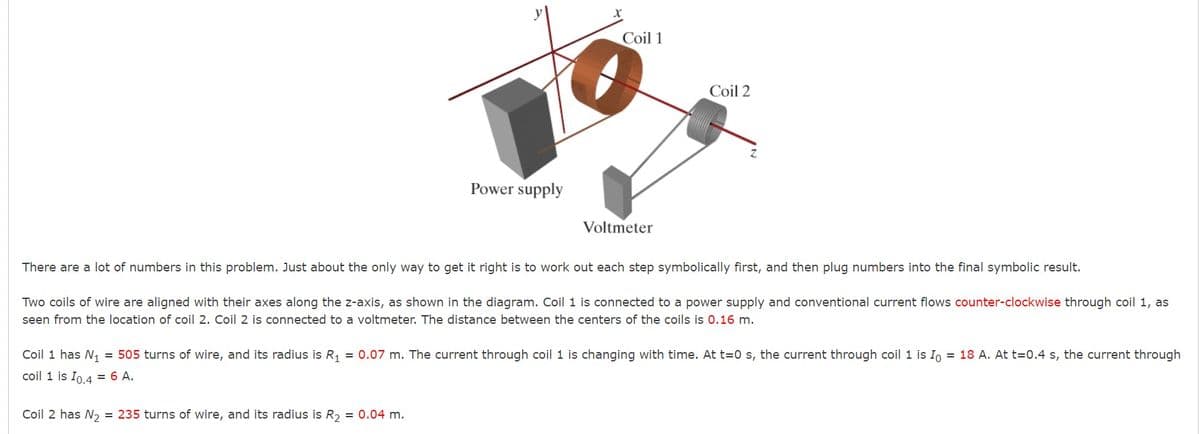
Transcribed Image Text:Coil 1
Coil 2
Power supply
Voltmeter
There are a lot of numbers in this problem. Just about the only way to get it right is to work out each step symbolically first, and then plug numbers into the final symbolic result.
Two coils of wire are aligned with their axes along the z-axis, as shown in the diagram. Coil 1 is connected to a power supply and conventional current flows counter-clockwise through coil 1, as
seen from the location of coil 2. Coil 2 is connected to a voltmeter. The distance between the centers of the coils is 0.16 m.
Coil 1 has N, = 505 turns of wire, and its radius is R, = 0.07 m. The current through coil 1 is changing with time. At t=0 s, the current through coil 1 is Io = 18 A. At t=0.4 s, the current through
coil 1 is Io.4 = 6 A.
Coil 2 has N2 = 235 turns of wire, and its radius is R, = 0.04 m.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning