Isthenia gravis, you have to understand the chain of events from the conscious decision to move a limb to the eventual stimulation of a muscle cell. Describe how nerve impulse conducted down the axon of a motor neuron induce contraction of the Mr. Aletha's muscle cells (Figure 31.1). 2. If you want to lift a whole bag of groceries versus a single apple, how do you increase the force with which you contract a muscle such as your biceps? What is a motor unit? What is the difference between temporal and spatial summation? 3. What is the neurotransmitter that acts at the motor endplate to initiate muscle contraction?
Isthenia gravis, you have to understand the chain of events from the conscious decision to move a limb to the eventual stimulation of a muscle cell. Describe how nerve impulse conducted down the axon of a motor neuron induce contraction of the Mr. Aletha's muscle cells (Figure 31.1). 2. If you want to lift a whole bag of groceries versus a single apple, how do you increase the force with which you contract a muscle such as your biceps? What is a motor unit? What is the difference between temporal and spatial summation? 3. What is the neurotransmitter that acts at the motor endplate to initiate muscle contraction?
Anatomy & Physiology
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Chapter16: The Neurological Exam
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5ILQ: Watch this short video (http://openstaxcollege.org/l/facialnerve) to see an examination of the...
Related questions
Question
How can we answer these questions?
Transcribed Image Text:rences Mailings
5
Review View Help
ALT
1- v i- v a- v
Paragraph
DIU 201 1011 ZVEJ
→=
a
Normal
No Spacing
Heading 1
Styles
Q Search
Heading 2
TIVIZOLaFRuva
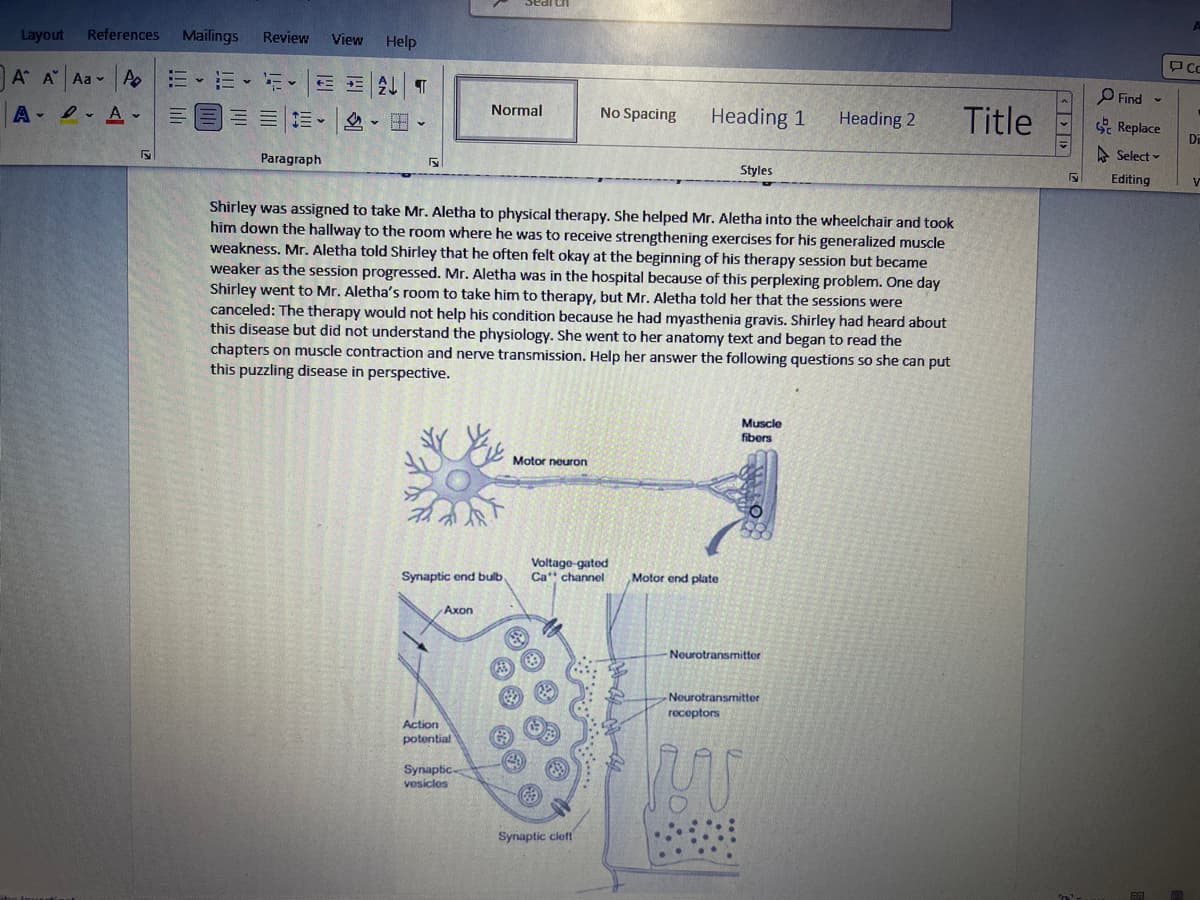
1.To understand myasthenia gravis, you have to understand the chain of events from the conscious decision to
move a limb to the eventual stimulation of a muscle cell. Describe how nerve impulse conducted down the axon
of a motor neuron induce contraction of the Mr. Aletha's muscle cells (Figure 31.1).
2. If you want to lift a whole bag of groceries versus a single apple, how do you increase the force with which
you contract a muscle such as your biceps? What is a motor unit? What is the difference between temporal and
spatial summation?
3. What is the neurotransmitter that acts at the motor endplate to initiate muscle contraction?
4. Muscle cells are full of the actin and myosin proteins.
a. Briefly describe the arrangement of the actin and myosin molecules within the cell. How does the interaction
between actin and myosin result in shortening of the muscle cell?
b. Which molecule provides the energy to break the actin-myosin bond?
c. Would the muscle be able to contract if they run out of energy? Explain why.
d. What happens to muscles in the case of death? Why do the muscles stay in contracted state and relax only
after a certain period of time?
5.Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune cells attack and destroy the
acetylcholine (Ach) receptors in the motor end plates of muscles in the shoulder, neck, and face. When muscle
do not contracts. Muscle atrophy (loss of muscle mass) is caused by not using the muscles enough. Why would
Mr. Aletha experience a progressive weakening even if he tries to do more exercise?
6. Do aerobic (endurance) and resistance exercises produce the same effect on muscles? How do endurance
and anaerobic exercises normally enhance your ability to contract muscles?
T
Transcribed Image Text:Layout References Mailings Review View Help
A A Aa AE-E
A
A.
F
EL T
Paragraph
Synaptic end bulb,
Axon
Normal
Action
potential
Synaptic
vesicles
Shirley was assigned to take Mr. Aletha to physical therapy. She helped Mr. Aletha into the wheelchair and took
him down the hallway to the room where he was to receive strengthening exercises for his generalized muscle
weakness. Mr. Aletha told Shirley that he often felt okay at the beginning of his therapy session but became
weaker as the session progressed. Mr. Aletha was in the hospital because of this perplexing problem. One day
Shirley went to Mr. Aletha's room to take him to therapy, but Mr. Aletha told her that the sessions were
canceled: The therapy would not help his condition because he had myasthenia gravis. Shirley had heard about
this disease but did not understand the physiology. She went to her anatomy text and began to read the
chapters on muscle contraction and nerve transmission. Help her answer the following questions so she can put
this puzzling disease in perspective.
(*)
8
Motor neuron
G
No Spacing
Voltage-gated
Ca channel
Synaptic cleft
Heading 1
Motor end plate
Styles
Muscle
fibers
- Neurotransmitter
W
Neurotransmitter
receptors
Heading 2
Title
Find
Replace
Select
FE Editing
PCC
Di
V
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira…
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:
9781305634350
Author:
Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. Schroeder
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira…
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:
9781305634350
Author:
Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. Schroeder
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning