Jamal purchased equipment and used materials to develop a patent. The development costs were deducted on prior returns. The bases and fair market values of the assets are presented below. Assets Fair Market Value Basis Equipment $350,000 Cost $350,000 Less: depreciation (250,000) Patent 250,000 $600,000 $100,000 Sarah has made an offer to purchase the assets. Under one plan, she would pay $200,000 now and $400,000 plus interest at 5% (the Federal rate) in one year. Alternatively, Jamal would incorporate the assets and then sell the stock to Sarah. Incorporating the assets would not be a taxable event to Jamal, and his basis in the stock would equal his basis in the assets of $100,000. The corporation's basis in the assets would also be $100,000, the same as Jamal's basis for the stock. Because the corporation would have a basis in the assets of less than the fair market value (and therefore, there would be less depreciation and amortization than with an asset sale by Jamal), Sarah would pay $200,000 in the current year but only $350,000, plus interest at 5%, in one year. Assume that Jamal's combined Federal and state marginal tax rate is 35% and his combined capital gain tax rate is 20%. In your computations, round the gross profit to four decimal places before converting to the percentage. (For example: .754788 would be rounded to .7548 and used as 75.48%.) Use rounded gross profit in subsequent computations. If required, round your final answers to the nearest dollar. a. Jamal's recognized gain in the vear of sale from the installment sale of his assets is $ 450.000
Jamal purchased equipment and used materials to develop a patent. The development costs were deducted on prior returns. The bases and fair market values of the assets are presented below. Assets Fair Market Value Basis Equipment $350,000 Cost $350,000 Less: depreciation (250,000) Patent 250,000 $600,000 $100,000 Sarah has made an offer to purchase the assets. Under one plan, she would pay $200,000 now and $400,000 plus interest at 5% (the Federal rate) in one year. Alternatively, Jamal would incorporate the assets and then sell the stock to Sarah. Incorporating the assets would not be a taxable event to Jamal, and his basis in the stock would equal his basis in the assets of $100,000. The corporation's basis in the assets would also be $100,000, the same as Jamal's basis for the stock. Because the corporation would have a basis in the assets of less than the fair market value (and therefore, there would be less depreciation and amortization than with an asset sale by Jamal), Sarah would pay $200,000 in the current year but only $350,000, plus interest at 5%, in one year. Assume that Jamal's combined Federal and state marginal tax rate is 35% and his combined capital gain tax rate is 20%. In your computations, round the gross profit to four decimal places before converting to the percentage. (For example: .754788 would be rounded to .7548 and used as 75.48%.) Use rounded gross profit in subsequent computations. If required, round your final answers to the nearest dollar. a. Jamal's recognized gain in the vear of sale from the installment sale of his assets is $ 450.000
Chapter18: Accounting Periods And Methods
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 52P
Related questions
Question
100%

Transcribed Image Text:b. What are Jamal's after-tax net proceeds if he sells the assets? $
What are Jamal's after-tax net proceeds if he sells the stock? $
1,800 x
Assuming that Jamal's time value of money is 5%, he would prefer sale of the assets
v.
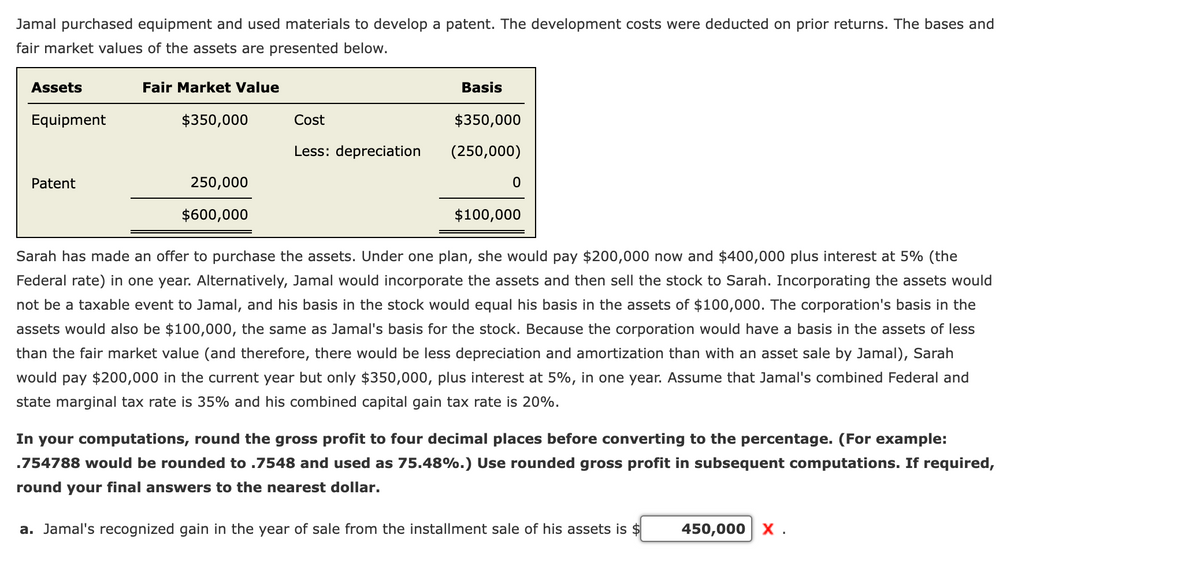
Transcribed Image Text:Jamal purchased equipment and used materials to develop a patent. The development costs were deducted on prior returns. The bases and
fair market values of the assets are presented below.
Assets
Fair Market Value
Basis
Equipment
$350,000
Cost
$350,000
Less: depreciation
(250,000)
Patent
250,000
$600,000
$100,000
Sarah has made an offer to purchase the assets. Under one plan, she would pay $200,000 now and $400,000 plus interest at 5% (the
Federal rate) in one year. Alternatively, Jamal would incorporate the assets and then sell the stock to Sarah. Incorporating the assets would
not be a taxable event to Jamal, and his basis in the stock would equal his basis in the assets of $100,000. The corporation's basis in the
assets would also be $100,000, the same as Jamal's basis for the stock. Because the corporation would have a basis in the assets of less
than the fair market value (and therefore, there would be less depreciation and amortization than with an asset sale by Jamal), Sarah
would pay $200,000 in the current year but only $350,000, plus interest at 5%, in one year. Assume that Jamal's combined Federal and
state marginal tax rate is 35% and his combined capital gain tax rate is 20%.
In your computations, round the gross profit to four decimal places before converting to the percentage. (For example:
.754788 would be rounded to .7548 and used as 75.48%.) Use rounded gross profit in subsequent computations. If required,
round your final answers to the nearest dollar.
a. Jamal's recognized gain in the year of sale from the installment sale of his assets is $
450,000 X .
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Individual Income Taxes
Accounting
ISBN:
9780357109731
Author:
Hoffman
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT



Individual Income Taxes
Accounting
ISBN:
9780357109731
Author:
Hoffman
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College