Lab Data Verify your calculation. In your set-up, do your units cancel? Did you report your data to the correct number of significant figures? Mass of magnesium (g) Moles of magnesium (mol) Temperature of water (°C) Temperature of water (K) Vapor pressure of water (mmHg) Barometric pressure (mmHg) Observations eudiometer started to bubble up Volume of hydrogen gas collected (mL) Volume of hydrogen gas collected (L) Pressure of hydrogen gas (mmHg) Pressure of hydrogen gas (atm) Moles of hydrogen gas produced (mol) Ideal gas constant (L-atm-mol-¹-K-¹) 0.013 0.00053 22.0 295.15 19.8 776.0 - X 13.00 0.01300 756.2 I 0.00053 0.082 NOT
Lab Data Verify your calculation. In your set-up, do your units cancel? Did you report your data to the correct number of significant figures? Mass of magnesium (g) Moles of magnesium (mol) Temperature of water (°C) Temperature of water (K) Vapor pressure of water (mmHg) Barometric pressure (mmHg) Observations eudiometer started to bubble up Volume of hydrogen gas collected (mL) Volume of hydrogen gas collected (L) Pressure of hydrogen gas (mmHg) Pressure of hydrogen gas (atm) Moles of hydrogen gas produced (mol) Ideal gas constant (L-atm-mol-¹-K-¹) 0.013 0.00053 22.0 295.15 19.8 776.0 - X 13.00 0.01300 756.2 I 0.00053 0.082 NOT
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter1: Basic Concepts Of Chemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 22RPS: The accepted value of the melting point of pureaspirin is 135 C. Trying to verify that value, you...
Related questions
Question
please find the answer of red square.Convert pressure of hydrogen gas produced to atm. Record in Lab Data
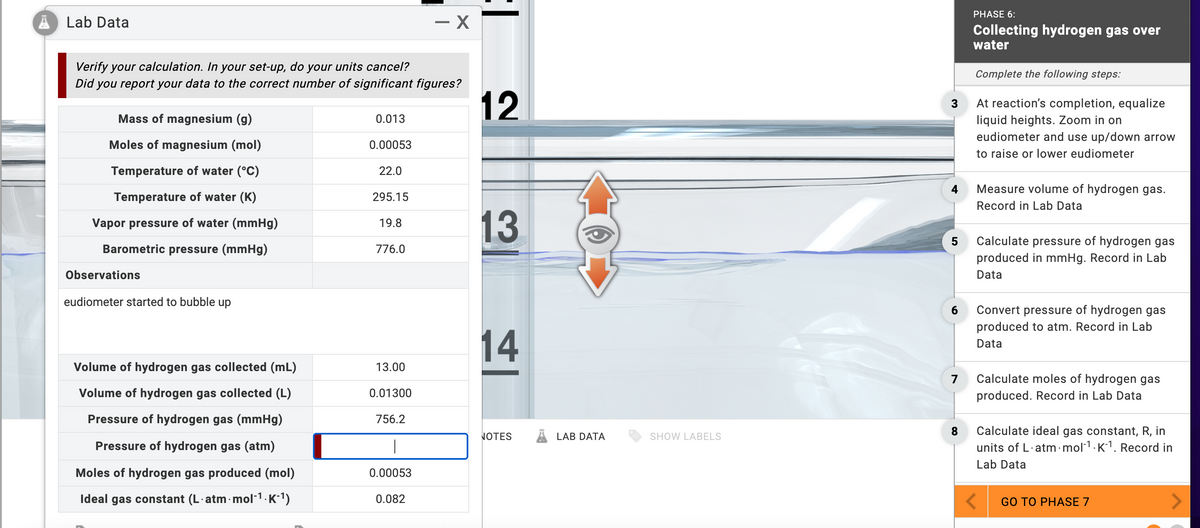
Transcribed Image Text:Lab Data
Verify your calculation. In your set-up, do your units cancel?
Did you report your data to the correct number of significant figures?
Mass of magnesium (g)
Moles of magnesium (mol)
Temperature of water (°C)
Temperature of water (K)
Vapor pressure of water (mmHg)
Barometric pressure (mmHg)
Observations
eudiometer started to bubble up
Volume of hydrogen gas collected (mL)
Volume of hydrogen gas collected (L)
Pressure of hydrogen gas (mmHg)
Pressure of hydrogen gas (atm)
Moles of hydrogen gas produced (mol)
Ideal gas constant (L.atm.mol-¹·K-¹)
0.013
0.00053
22.0
295.15
19.8
776.0
13.00
0.01300
756.2
1
0.00053
- X
0.082
12
13
14
NOTES ALAB DATA
SHOW LABELS
3
4
5
6
7
8
PHASE 6:
Collecting hydrogen gas over
water
Complete the following steps:
At reaction's completion, equalize
liquid heights. Zoom in on
eudiometer and use up/down arrow
to raise or lower eudiometer
Measure volume of hydrogen gas.
Record in Lab Data
Calculate pressure of hydrogen gas
produced in mmHg. Record in Lab
Data
Convert pressure of hydrogen gas
produced to atm. Record in Lab
Data
Calculate moles of hydrogen gas
produced. Record in Lab Data
Calculate ideal gas constant, R, in
units of L.atm.mol-1 K-1. Record in
Lab Data
GO TO PHASE 7
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning