Let F(x, y, z) = zi + xj – yk and the curve Cbe the boundary of that portion of the surface S above the rectangular region D: 0 < x< 1,0< y< 2. Use Stokes' Theorem to convert |curl F• dS to a line integral and then rewrite the line integral as a double integral. 2 а) (2u + 1)dv du x. b) (1 2u)dv du c) (2и + 1) dv du d) SL (1 – 24). dv du
Let F(x, y, z) = zi + xj – yk and the curve Cbe the boundary of that portion of the surface S above the rectangular region D: 0 < x< 1,0< y< 2. Use Stokes' Theorem to convert |curl F• dS to a line integral and then rewrite the line integral as a double integral. 2 а) (2u + 1)dv du x. b) (1 2u)dv du c) (2и + 1) dv du d) SL (1 – 24). dv du
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter9: Systems Of Equations And Inequalities
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12T
Related questions
Question
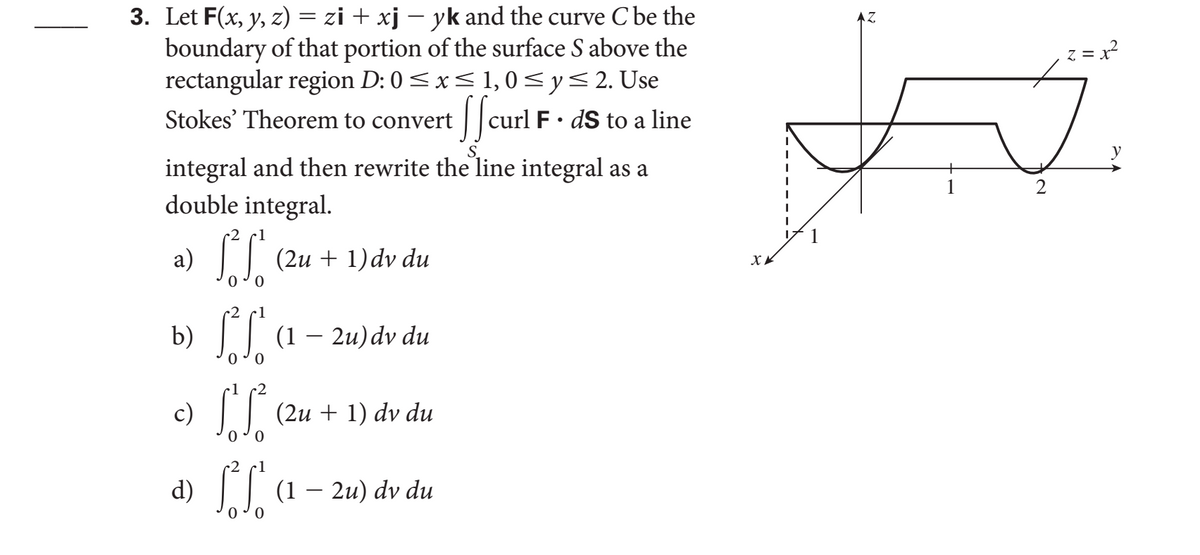
Transcribed Image Text:3. Let F(x, y, z) = zi + xj – yk and the curve C be the
boundary of that portion of the surface S above the
rectangular region D: 0<x< 1,0 <y<2. Use
/ |curl F ·
z = x?
Stokes' Theorem to convert
dS to a
line
y
integral and then rewrite the line integral as a
double integral.
a) || (2u + 1) dv du
x.
0 0
b) || (1 – 2u)dv du
c)
I| (2u + 1)
dv du
0 o
1
d)
(1 – 2u) dv du
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage