Macmillan Learning A distillation column, as shown in the figure, is a device used to separate components with different volatilities. In a specific process, a distillation column is used to separate a feed stream containing 0.4500 mol ethanol/mol and 0.5500 mol water/mol into two product streams: an overhead stream that is ethanol-rich and a bottoms stream that is water-rich. Vapor containing 0.7910 mol ethanol/mol and 0.2090 mol water/mol leaves the top of the distillation column and enters a condenser, where the stream condenses completely into a liquid. This stream is then split; the reflux returns to the column, and the overhead product leaves the process. The ratio of the flow rates of reflux to overhead product is given by the reflux ratio R= AM flow rate of reflux flow rate of overhead product = YE/XE yw/xw YE/XE (1-YE)/(1-XE) Feed YE/(1-YE) XE/(1 − XE) Distillation column Reflux Boilup and for this particular process, R = 1.69. Liquid leaving the bottom of the distillation column enters a reboiler, where a fraction of the stream is vaporized and returns to the distillation column as boilup, while the liquid fraction leaves the process as bottoms product. The composition of the boilup and the bottoms-product streams are governed by the relative volatility, a, of ethanol and water. Condenser Overhead product Reboiler Bottoms product where yg is the mole fraction of ethanol in the vapor stream, yw is the mole fraction of water in the vapor stream, xg is the mole fraction of ethanol in the liquid stream, and xw is the mole fraction of water in the liquid stream. For this particular process a = 6.286, and the ratio of ethanol leaving the reboiler in the boilup to ethanol leaving the reboiler in the bottoms product is 1880 mol of overhead product is produced. Given this basis, answer the questions. 86°F Mostly sunny
Macmillan Learning A distillation column, as shown in the figure, is a device used to separate components with different volatilities. In a specific process, a distillation column is used to separate a feed stream containing 0.4500 mol ethanol/mol and 0.5500 mol water/mol into two product streams: an overhead stream that is ethanol-rich and a bottoms stream that is water-rich. Vapor containing 0.7910 mol ethanol/mol and 0.2090 mol water/mol leaves the top of the distillation column and enters a condenser, where the stream condenses completely into a liquid. This stream is then split; the reflux returns to the column, and the overhead product leaves the process. The ratio of the flow rates of reflux to overhead product is given by the reflux ratio R= AM flow rate of reflux flow rate of overhead product = YE/XE yw/xw YE/XE (1-YE)/(1-XE) Feed YE/(1-YE) XE/(1 − XE) Distillation column Reflux Boilup and for this particular process, R = 1.69. Liquid leaving the bottom of the distillation column enters a reboiler, where a fraction of the stream is vaporized and returns to the distillation column as boilup, while the liquid fraction leaves the process as bottoms product. The composition of the boilup and the bottoms-product streams are governed by the relative volatility, a, of ethanol and water. Condenser Overhead product Reboiler Bottoms product where yg is the mole fraction of ethanol in the vapor stream, yw is the mole fraction of water in the vapor stream, xg is the mole fraction of ethanol in the liquid stream, and xw is the mole fraction of water in the liquid stream. For this particular process a = 6.286, and the ratio of ethanol leaving the reboiler in the boilup to ethanol leaving the reboiler in the bottoms product is 1880 mol of overhead product is produced. Given this basis, answer the questions. 86°F Mostly sunny
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Macmillan Learning
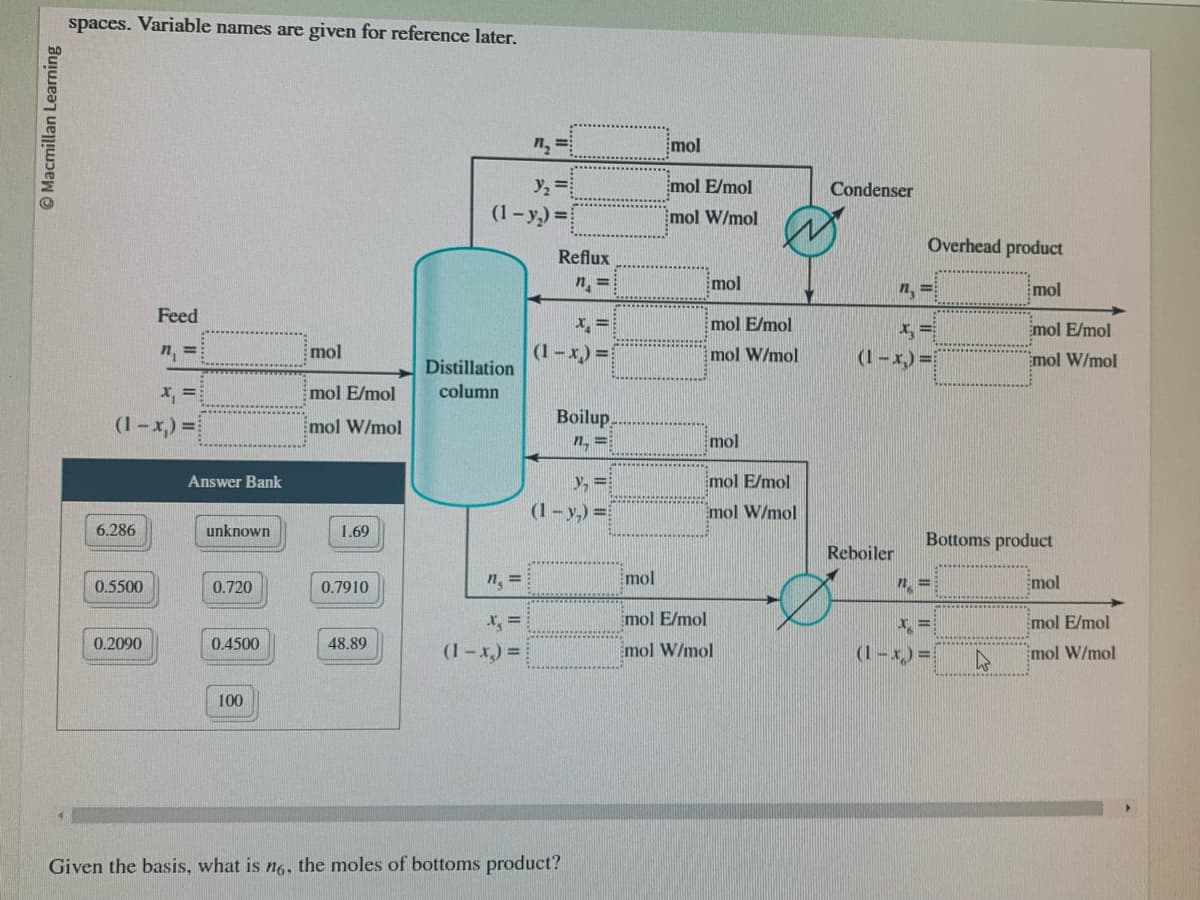
spaces. Variable names are given for reference later.
x₁ =
(1-x) =
6.286
0.5500
Feed
0.2090
Answer Bank
unknown
0.720
0.4500
100
mol
mol E/mol
mol W/mol
1.69
0.7910
48.89
n₂ =
y₂ =
(1-y₂2)=
Distillation
column
n₁ =
x₂ =
(1-x) =
Reflux
n =
x₂ =
(1-x) =
Boilup
n₂ =
y₂ =
(1-y₂)=
Given the basis, what is no, the moles of bottoms product?
mol
mol E/mol
mol W/mol
mol
mol E/mol
mol W/mol
mol
mol E/mol
mol W/mol
mol
mol E/mol
Emol W/mol
Condenser
Overhead product
mol
mol E/mol
mol W/mol
Reboiler
n =
(1-x₂)=
Bottoms product
n =
x =
(1-x) =
A
mol
mol E/mol
mol W/mol
Transcribed Image Text:ment Score:
n 1 of 3
0%
Macmillan Learning
R=
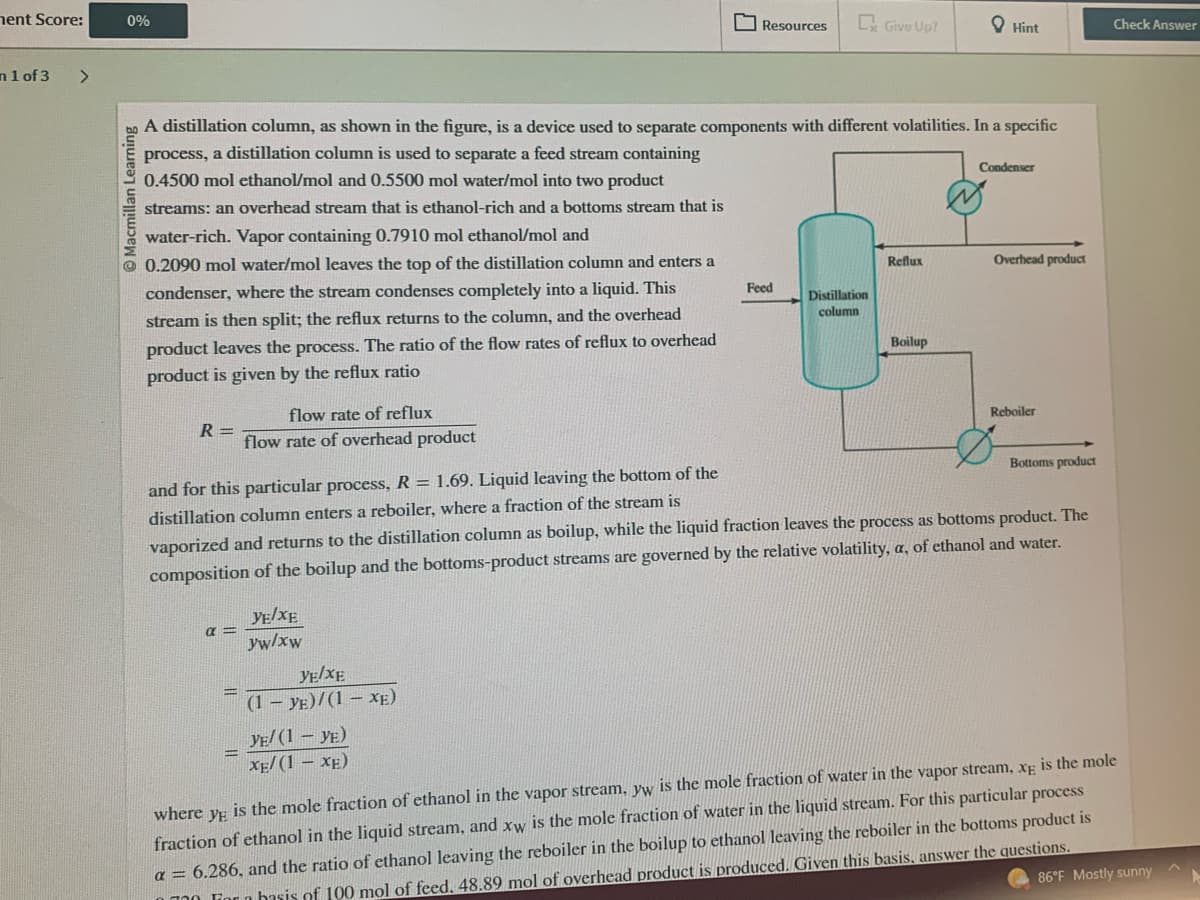
A distillation column, as shown in the figure, is a device used to separate components with different volatilities. In a specific
process, a distillation column is used to separate a feed stream containing
0.4500 mol ethanol/mol and 0.5500 mol water/mol into two product
streams: an overhead stream that is ethanol-rich and a bottoms stream that is
water-rich. Vapor containing 0.7910 mol ethanol/mol and
0.2090 mol water/mol leaves the top of the distillation column and enters a
condenser, where the stream condenses completely into a liquid. This
stream is then split; the reflux returns to the column, and the overhead
product leaves the process. The ratio of the flow rates of reflux to overhead
product is given by the reflux ratio
flow rate of reflux
flow rate of overhead product
α=
YE/XE
yw/xw
Resources Ex Give Up!
YE/XE
(1 - YE)/(1-XE)
YE/ (1 - YE)
XE/(1 − XE)
Feed
Distillation
column
Reflux
Hint
Boilup
Condenser
and for this particular process, R = 1.69. Liquid leaving the bottom of the
distillation column enters a reboiler, where a fraction of the stream is
vaporized and returns to the distillation column as boilup, while the liquid fraction leaves the process as bottoms product. The
composition of the boilup and the bottoms-product streams are governed by the relative volatility, a, of ethanol and water.
Overhead product
Reboiler
Bottoms product
Check Answer
where YE
is the mole fraction of ethanol in the vapor stream, yw is the mole fraction of water in the vapor stream, xg is the mole
fraction of ethanol in the liquid stream, and xw is the mole fraction of water in the liquid stream. For this particular process
a = 6.286, and the ratio of ethanol leaving the reboiler in the boilup to ethanol leaving the reboiler in the bottoms product is
86°F Mostly sunny
700 Fior a basis of 100 mol of feed. 48.89 mol of overhead product is produced. Given this basis, answer the questions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The