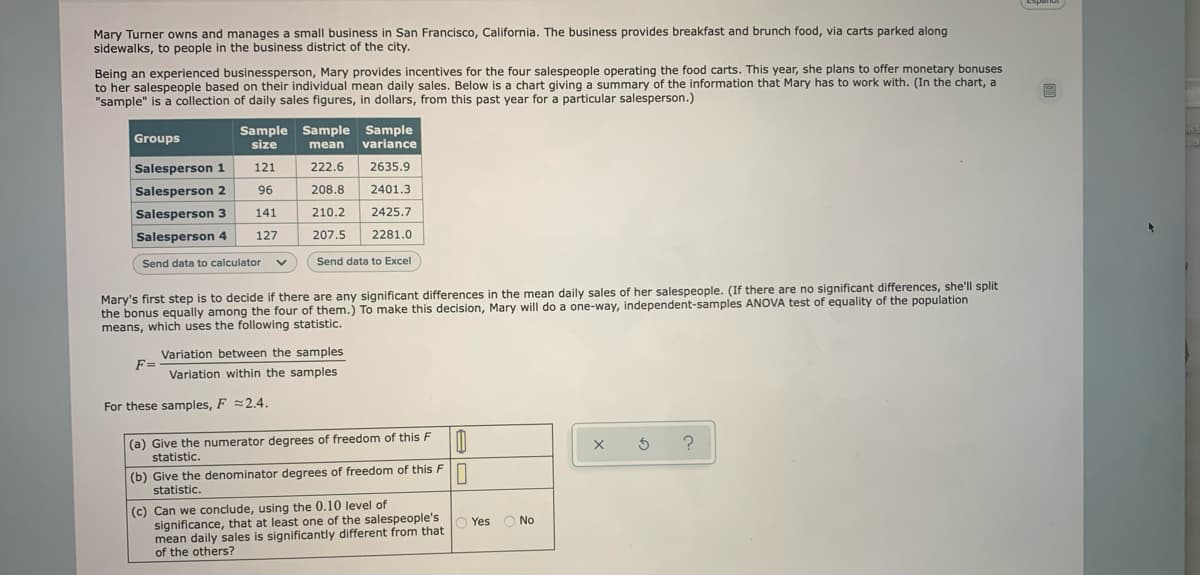
Mary Turner owns and manages a small business in San Francisco, California. The business provides breakfast and brunch food, via carts parked along sidewalks, to people in the business district of the city. Being an experienced businessperson, Mary provides incentives for the four salespeople operating the food carts. This year, she plans to offer monetary bonuses to her salespeople based on their individual mean daily sales. Below is a chart giving a summary of the information that Mary has to work with. (In the chart, a "sample" is a collection of daily sales figures, in dollars, from this past year for a particular salesperson.) Sample Sample Sample size Groups variance mean Salesperson 1 121 222.6 2635.9 Salesperson 2 96 208.8 2401.3 Salesperson 3 141 210.2 2425.7 Salesperson 4 127 207.5 2281.0 Send data to calculator Send data to Excel Mary's first step is to decide if there are any significant differences in the mean daily sales of her salespeople. (If there are no significant differences, she'll split the bonus equally among the four of them.) To make this decision, Mary will do a one-way, independent-samples ANOVA test of equality of the population means, which uses the following statistic. Variation between the samples F= Variation within the samples For these samples, F =2.4. (a) Give the numerator degrees of freedom of this F statistic. (b) Give the denominator degrees of freedom of this F statistic. (c) Can we conclude, using the 0.10 level of significance, that at least one of the salespeople's mean daily sales is significantly different from that of the others? Yes No
Mary Turner owns and manages a small business in San Francisco, California. The business provides breakfast and brunch food, via carts parked along sidewalks, to people in the business district of the city. Being an experienced businessperson, Mary provides incentives for the four salespeople operating the food carts. This year, she plans to offer monetary bonuses to her salespeople based on their individual mean daily sales. Below is a chart giving a summary of the information that Mary has to work with. (In the chart, a "sample" is a collection of daily sales figures, in dollars, from this past year for a particular salesperson.) Sample Sample Sample size Groups variance mean Salesperson 1 121 222.6 2635.9 Salesperson 2 96 208.8 2401.3 Salesperson 3 141 210.2 2425.7 Salesperson 4 127 207.5 2281.0 Send data to calculator Send data to Excel Mary's first step is to decide if there are any significant differences in the mean daily sales of her salespeople. (If there are no significant differences, she'll split the bonus equally among the four of them.) To make this decision, Mary will do a one-way, independent-samples ANOVA test of equality of the population means, which uses the following statistic. Variation between the samples F= Variation within the samples For these samples, F =2.4. (a) Give the numerator degrees of freedom of this F statistic. (b) Give the denominator degrees of freedom of this F statistic. (c) Can we conclude, using the 0.10 level of significance, that at least one of the salespeople's mean daily sales is significantly different from that of the others? Yes No
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.4: Distributions Of Data
Problem 19PFA
Related questions
Question
Question #15
Transcribed Image Text:(Espanol
Mary Turner owns and manages a small business in San Francisco, California. The business provides breakfast and brunch food, via carts parked along
sidewalks, to people in the business district of the city.
Being an experienced businessperson, Mary provides incentives for the four salespeople operating the food carts. This year, she plans to offer monetary bonuses
to her salespeople based on their individual mean daily sales. Below is a chart giving a summary of the information that Mary has to work with. (In the chart, a
"sample" is a collection of daily sales figures, in dollars, from this past year for a particular salesperson.)
Sample Sample Sample
size
Groups
variance
mean
Salesperson 1
121
222.6
2635.9
Salesperson 2
96
208.8
2401.3
Salesperson 3
141
210.2
2425.7
Salesperson 4
127
207.5
2281.0
Send data to calculator
Send data to Excel
Mary's first step is to decide if there are any significant differences in the mean daily sales of her salespeople. (If there are no significant differences, she'll split
the bonus equally among the four of them.) To make this decision, Mary will do a one-way, independent-samples ANOVA test of equality of the population
means, which uses the following statistic.
Variation between the samples
F=
Variation within the samples
For these samples, F =2.4.
(a) Give the numerator degrees of freedom of this F
statistic.
(b) Give the denominator degrees of freedom of this Fn
statistic.
(c) Can we conclude, using the 0.10 level of
significance, that at least one of the salespeople's
mean daily sales is significantly different from that
of the others?
O Yes
No
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill


Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill
