Matching Type. Match each item to a choice: Two vectors having the same magnitude and direction. A rule associating each point (xy) or (xy.z) in a region of vector F(xy) or F(xy.z), respectively, Basically a vector-valued function. A vector drawn at the heads of two other vectors. If A and B are any wo vectors, the initial point of B is placed on the initial point of A, resultant vector is the diagonal formed by A and B drawn from the common initial point. Specifies a point uniquely by a pair (or triple)of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distance from fixed reference lines. If A and B are any two vectors, the initial point of B is placed on the terminal point of A, resultant vector is drawn from the initial point of A to the terminal point of B. Choices: # Equal vectors # Unit Vector # Fields 1 Coc E Triangle law E Distance Vector E Radius Vector
Matching Type. Match each item to a choice: Two vectors having the same magnitude and direction. A rule associating each point (xy) or (xy.z) in a region of vector F(xy) or F(xy.z), respectively, Basically a vector-valued function. A vector drawn at the heads of two other vectors. If A and B are any wo vectors, the initial point of B is placed on the initial point of A, resultant vector is the diagonal formed by A and B drawn from the common initial point. Specifies a point uniquely by a pair (or triple)of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distance from fixed reference lines. If A and B are any two vectors, the initial point of B is placed on the terminal point of A, resultant vector is drawn from the initial point of A to the terminal point of B. Choices: # Equal vectors # Unit Vector # Fields 1 Coc E Triangle law E Distance Vector E Radius Vector
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305632134
Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Chapter6: Power Flows
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6.59P
Related questions
Question
100%
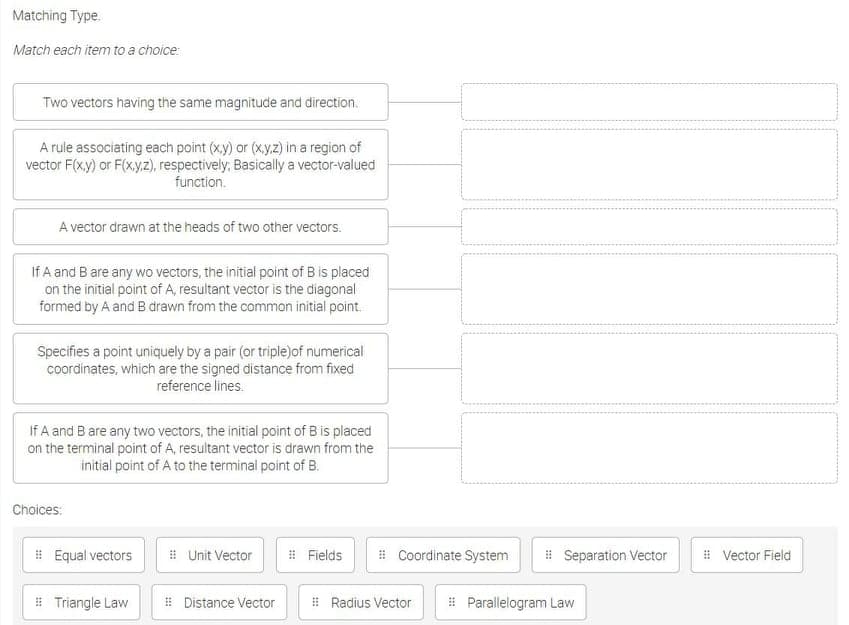
Transcribed Image Text:Matching Type.
Match each item to a choice:
Two vectors having the same magnitude and direction.
A rule associating each point (x.y) or (xy.z) in a region of
vector F(x.y) or F(x.y.z), respectively, Basically a vector-valued
function.
A vector drawn at the heads of two other vectors.
If A and B are any wo vectors, the initial point of B is placed
on the initial point of A, resultant vector is the diagonal
formed by A and B drawn from the common initial point.
Specifies a point uniquely by a pair (or triple)of numerical
coordinates, which are the signed distance from fixed
reference lines.
If A and Bare any two vectors, the initial point of B is placed
on the terminal point of A, resultant vector is drawn from the
initial point of A to the terminal point of B.
Choices:
I Equal vectors
# Unit Vector
E Fields
I Coordinate System
# Separation Vector
# Vector Field
# Triangle Law
E Distance Vector
E Radius Vector
# Parallelogram Law
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course …
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305632134
Author:
J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course …
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305632134
Author:
J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:
Cengage Learning