Ming Chen began a professional practice on June 1 and plans to prepare financial statements at the end of each month. During June, Ming Chen (the owner) completed these transactions. a. Owner invested $60,000 cash in the company along with equipment that had a $15,000 market value in exchange for its common stock. b. The company paid $1,500 cash for rent of office space for the month.
Ming Chen began a professional practice on June 1 and plans to prepare financial statements at the end of each month. During June, Ming Chen (the owner) completed these transactions. a. Owner invested $60,000 cash in the company along with equipment that had a $15,000 market value in exchange for its common stock. b. The company paid $1,500 cash for rent of office space for the month.
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career Approach
13th Edition
ISBN:9781337280570
Author:Scott, Cathy J.
Publisher:Scott, Cathy J.
Chapter2: T Accounts, Debits And Credits, Trial Balance, And Financial Statements
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1PA: During December of this year, G. Elden established Ginnys Gym. The following asset, liability, and...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
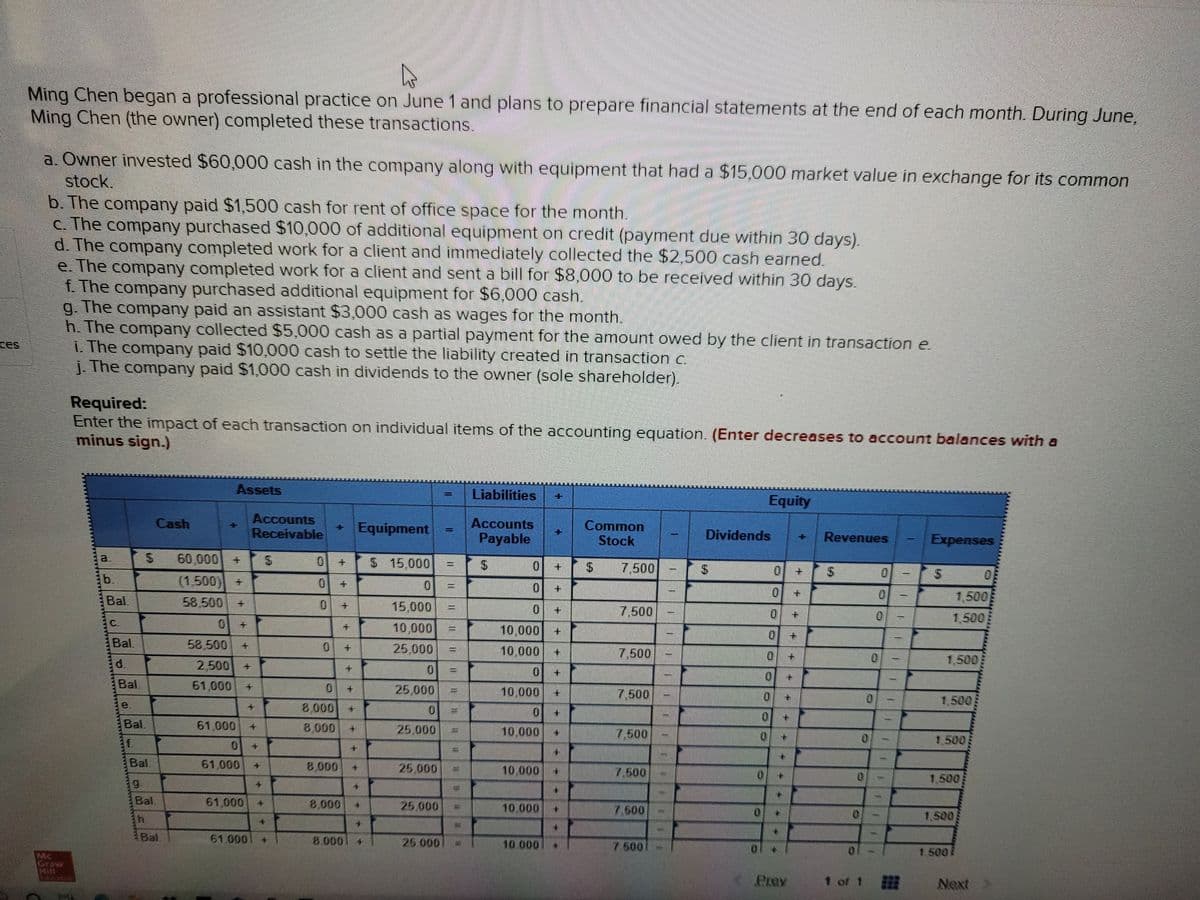
Transcribed Image Text:Ming Chen began a professional practice on June 1 and plans to prepare financial statements at the end of each month. During June,
Ming Chen (the owner) completed these transactions.
a. Owner invested $60,000 cash in the company along with equipment that had a $15,000 market value in exchange for its common
stock.
b. The company paid $1,500 cash for rent of office space for the month.
C. The company purchased $10,000 of additional equipment on credit (payment due within 30 days).
d. The company completed work for a client and immediately collected the $2,500 cash earned.
e. The company completed work for a client and sent a bill for $8,000 to be received within 30 days.
f. The company purchased additional equipment for $6,000 cash.
g. The company paid an assistant $3,000 cash as wages for the month.
h. The company collected $5,000 cash as a partial payment for the amount owed by the client in transaction e
i. The company paid $10,000 cash to settle the liability created in transaction c.
J. The company paid $1,000 cash in dividends to the owner (sole shareholder).
ces
Required:
Enter the impact of each transaction on individual items of the accounting equation. (Enter decreases to account balances with a
minus sign.)
Assets
Liabilities
Equity
Accounts
Receivable
Cash
Equipment
Accounts
Payable
Common
Stock
Dividends
Revenues
Expenses
a.
60,000
$ 15,000
0.
%3D
7,500
24
%24
b.
(1,500) +
Bal
0.
1,500
58,500
15,000
于
7,500
1,500
C.
10,000
10,000
Bal.
58,500
25,000
10,000
7,500
d.
2,500
1,500
Bal.
61,000
25,000
10,000
7,500
0.
1,500
e.
8,000
0.
0.
Bal.
61,000
8,000
25.000
10,000
f.
7,500
0.
1.500
Bal.
61,000
8,000
25.000
10 000
7.500
1,500
9.
Bal.
61,000
8.000
25.000
10,000
7.500
0.
1.500
h.
Bal
61. 000
8.000
25.000
10.000
7.500
1.500
Mc.
Graw
Hill
Prav
1 of 1
Next
キ
4.
卡
%24
1.
%24
%24
+.
4,
%24
4.
4.
%24
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Accounting (Book Only): A Career Approach
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337280570
Author:
Scott, Cathy J.
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

College Accounting (Book Only): A Career Approach
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305084087
Author:
Cathy J. Scott
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

College Accounting (Book Only): A Career Approach
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337280570
Author:
Scott, Cathy J.
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

College Accounting (Book Only): A Career Approach
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305084087
Author:
Cathy J. Scott
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272124
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning