n=-2 n=1 1 1 n=-1 n=2 n=0 0 n=3
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305071742
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter9: Vectors In Two And Three Dimensions
Section9.FOM: Focus On Modeling: Vectors Fields
Problem 11P
Related questions
Question
Could someone answer last part (detailed solutions) thanks
Transcribed Image Text:-1
-1
n=-2
0
n=1
1
1
-1
-1
n=-1
0
n = 2
-1
n=0
0
n=3
0
1
1

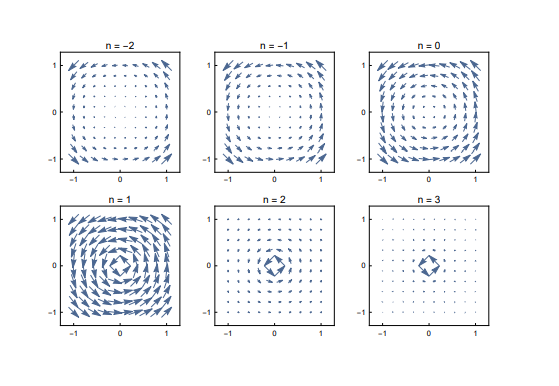
Transcribed Image Text:6. Consider the family of rotating vector fields
V(x, y, z)
=
(x² + y²)n/2
- (²-OV ₂
VxX=
i +
as shown over the page.
(i) Compute the curl of V; i.e. Vx X. Simplify your answer as much as possible.
(ii) Convert the Cartesian forms of V and V x V into cylindrical forms. Simplify your answers as
much as possible.
(iii) State the domains for V and Vx V- it will change with n.
(iv) Using the cylindrical form of V confirm your curl answer in (ii) with the cylindrical form of curl,
I
(x² + y²)n/2³ + Ok,
8V/₂2
(Ə(pV₂)
+7
-V) e
ép-
es +
др
(v) For a cylindrical vector field Green's Theorem in the (zy) plane can be written
= // vxv.è, ds.
nĘ Z
ᎯᏙ .
Әр
ᎯᏙᎥ "
ap
(This is really Stokes's Theorem with n = è.).
Evaluate the line integral and the surface integral above on the unit circle centred at the origin.
Explain the discrepancy in the two values and suggest a way to correct it. Hint: consider the
domain.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning