Note: The diagram shown below is a top-down view. Imagine that that process is occurring on a table and that you are looking down at it.* Two projectiles of mass 4-kg and 12-kg traveling at 10-m/s and 20-m/s, respectively, undergo a completely inelastic collision at the intersection of their lines of travel, as shown below. Prior to the collision the projectiles travel along a frictionless surface; however, after the collision the surface is rough and is characterized by a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.15. At what angle should a spring of constant 80-N/m be placed in order to “catch” the projectiles after the collision? If the spring is located 4-m away from the collision point, what will be the maximum compression of said spring?
Note: The diagram shown below is a top-down view. Imagine that that process is occurring on a table and that you are looking down at it.* Two projectiles of mass 4-kg and 12-kg traveling at 10-m/s and 20-m/s, respectively, undergo a completely inelastic collision at the intersection of their lines of travel, as shown below. Prior to the collision the projectiles travel along a frictionless surface; however, after the collision the surface is rough and is characterized by a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.15. At what angle should a spring of constant 80-N/m be placed in order to “catch” the projectiles after the collision? If the spring is located 4-m away from the collision point, what will be the maximum compression of said spring?
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Chapter16: Oscillatory Motion And Waves
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5PE: When an 80.0kg man stands on a pogo stick, the spring is compressed 0.120 m. (a) What is the force...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
*Note: The diagram shown below is a top-down view. Imagine that that process is occurring on a table and that you are looking down at it.* Two projectiles of mass 4-kg and 12-kg traveling at 10-m/s and 20-m/s, respectively, undergo a completely inelastic collision at the intersection of their lines of travel, as shown below. Prior to the collision the projectiles travel along a frictionless surface; however, after the collision the surface is rough and is characterized by a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.15.
- At what angle should a spring of constant 80-N/m be placed in order to “catch” the projectiles after the collision?
- If the spring is located 4-m away from the collision point, what will be the maximum compression of said spring?
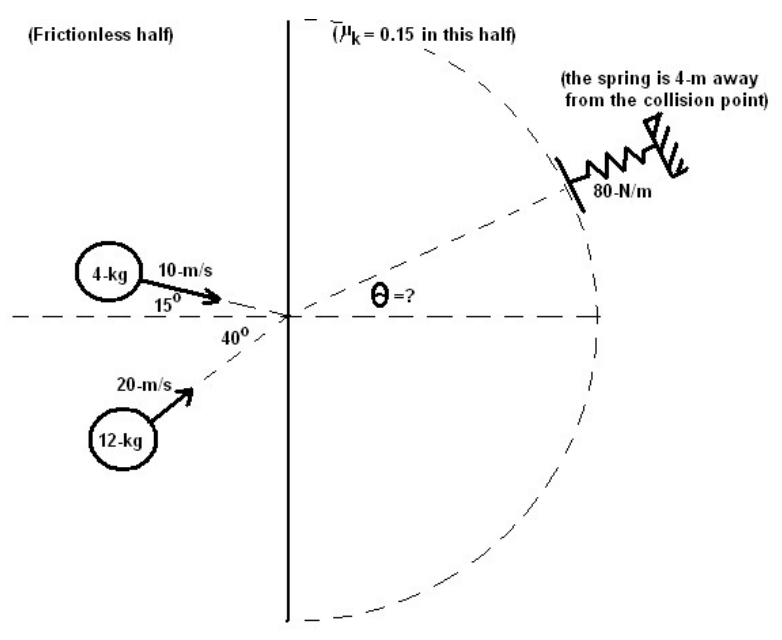
Transcribed Image Text:(Frictionless half)
(Pk= 0.15 in this half)
(the spring is 4-m away
from the collision point)
80-N/m
4-kg
10-m/s
150
=?
40°.
20-m/s,
12-kg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning