numMembers is read from input as the size of the vector. Then, numMembers elements are read from input into the vector bikingRoster. Use a loop to access each element in the vector and if the element is less than averageMembers, output the element followed by a space.
numMembers is read from input as the size of the vector. Then, numMembers elements are read from input into the vector bikingRoster. Use a loop to access each element in the vector and if the element is less than averageMembers, output the element followed by a space.
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Chapter1: Computer Networks And The Internet
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem R1RQ: What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end...
Related questions
Question
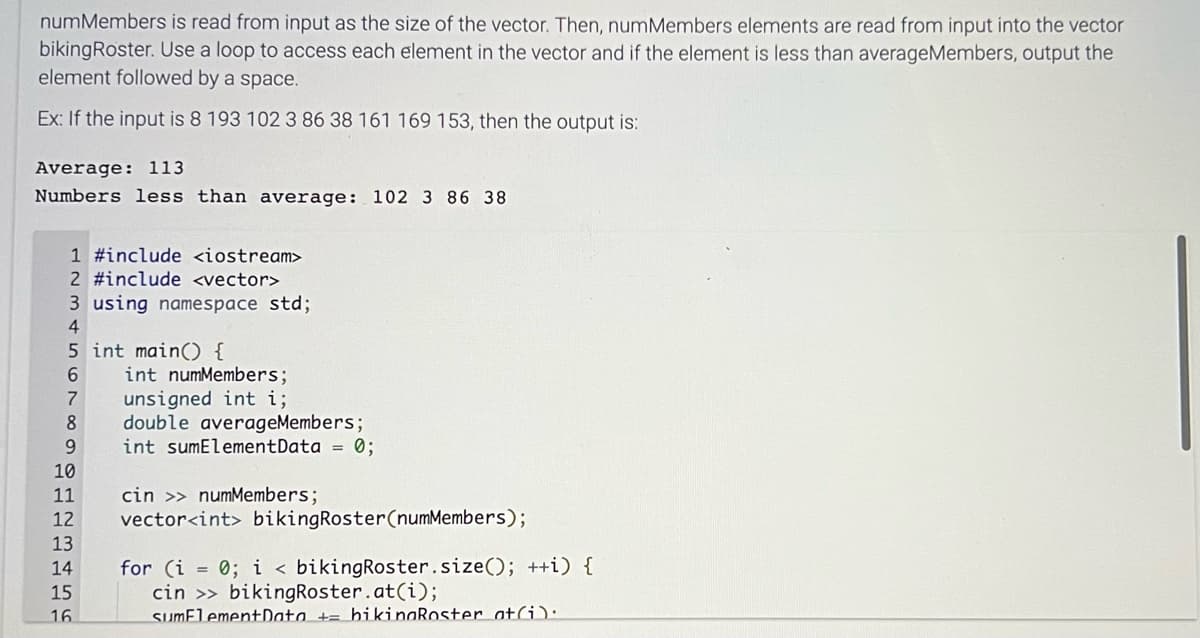
Transcribed Image Text:numMembers is read from input as the size of the vector. Then, numMembers elements are read from input into the vector
bikingRoster. Use a loop to access each element in the vector and if the element is less than averageMembers, output the
element followed by a space.
Ex: If the input is 8 193 102 3 86 38 161 169 153, then the output is:
Average: 113
Numbers less than average: 102 3 86 38
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <vector>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 int main() {
6
7
unsigned int i;
8 double averageMembers;
9
int sumElementData = 0;
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
int numMembers;
cin >> numMembers;
vector<int> bikingRoster (numMembers);
for (i = 0; i < bikingRoster.size(); ++i) {
cin >> bikingRoster.at(i);
sumElement Data + bikingRoster at(i):
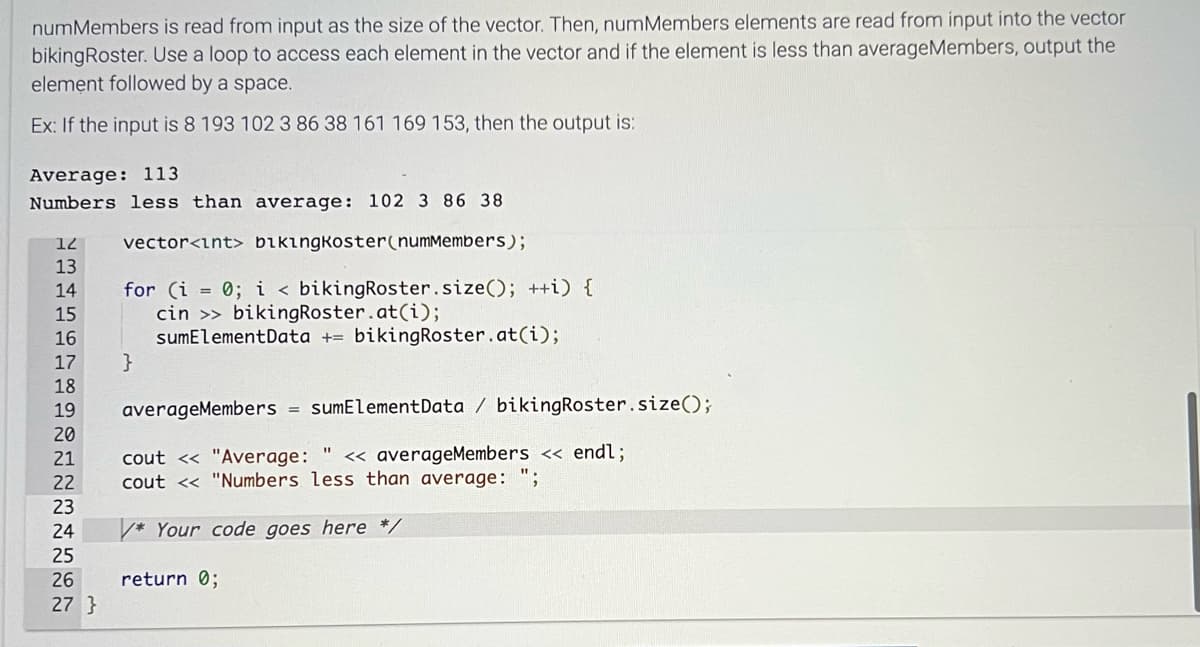
Transcribed Image Text:numMembers is read from input as the size of the vector. Then, numMembers elements are read from input into the vector
bikingRoster. Use a loop to access each element in the vector and if the element is less than averageMembers, output the
element followed by a space.
Ex: If the input is 8 193 102 3 86 38 161 169 153, then the output is:
Average: 113
Numbers less than average: 102 3 86 38
vector<int> bikingkoster(numMembers);
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
~22222
23
24
25
26
27 }
for (i = 0; i < bikingRoster.size(); ++i) {
cin >> bikingRoster.at(i);
sumElementData + bikingRoster.at(i);
}
averageMembers = sumElement Data / bikingRoster.size();
cout << "Average: " << averageMembers << endl;
cout << "Numbers less than average: ";
* Your code goes here */
return 0;
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093422
Author:
Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133750423
Author:
VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:
Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781119368830
Author:
FITZGERALD
Publisher:
WILEY