Oil is cooled from an initial temperature of 96°C to 60°C by water in an adiabatic concentric heat exchanger. The flow rates for the oil and water are 0.7 kg s-1 and 0.4 kg s-1 respectively. If water enters the heat exchanger with a temperature of 20°C, what is the temperature of the water when it leaves the heat exchanger? State any assumptions made in the calculation. Assume the following heat capacities are constant as a function of temperature, CP(Oil) = 2131 J kg-1 K-1 and Cp(Water) = 4178 J kg-1 K-1.
Oil is cooled from an initial temperature of 96°C to 60°C by water in an adiabatic concentric heat exchanger. The flow rates for the oil and water are 0.7 kg s-1 and 0.4 kg s-1 respectively. If water enters the heat exchanger with a temperature of 20°C, what is the temperature of the water when it leaves the heat exchanger? State any assumptions made in the calculation. Assume the following heat capacities are constant as a function of temperature, CP(Oil) = 2131 J kg-1 K-1 and Cp(Water) = 4178 J kg-1 K-1.
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
Oil is cooled from an initial temperature of 96°C to 60°C by water in an adiabatic concentric
heat exchanger. The flow rates for the oil and water are 0.7 kg s-1 and 0.4 kg s-1 respectively.
If water enters the heat exchanger with a temperature of 20°C, what is the temperature of
the water when it leaves the heat exchanger? State any assumptions made in the
calculation.
Assume the following heat capacities are constant as a function of temperature, CP(Oil) =
2131 J kg-1 K-1 and Cp(Water) = 4178 J kg-1 K-1.
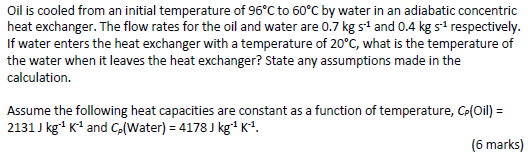
Transcribed Image Text:Oil is cooled from an initial temperature of 96°C to 60°C by water in an adiabatic concentric
heat exchanger. The flow rates for the oil and water are 0.7 kg s' and 0.4 kg s respectively.
If water enters the heat exchanger with a temperature of 20°C, what is the temperature of
the water when it leaves the heat exchanger? State any assumptions made in the
calculation.
Assume the following heat capacities are constant as a function of temperature, Ce(Oil) =
2131 J kg K' and Co(Water) = 4178 J kg'K*.
(6 marks)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The