1. Using this information and the information in the following trial balances on December 31, 2016, prepare a value analysis and a determination and distribution of excess schedule: Inventory, December 31 Other Current Assets Paro Company Solar Company 100,000 50,000 136,000 180,000 Investment in Solar Company 400,000 Land 50,000 50,000 Buildingsand Equipment 350,000 320,000 Accumulated Depreciation (100,000) (60,000) Goodwill Other Intangibles Current Liabilities Bonds Payable Other Long-Term Liabilities 20,000 (120,000) (40,000) (200,000) Common Stock-Paro Company (200,000) Other Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par-Paro Company (100,000) Retained Earnings-Paro Company (214,000) Common Stock-Solar Company Other Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par-Solar Company Retained Earnings-Solar Company Net Sales Cost of Goods Sold Operating Expenses (100,000) (50,000) (100,000) (190,000) (520,000) (450,000) 300,000 260,000 120,000 100,000 Subsidiary Income (72,000) Dividends Declared-Paro Company 50,000 Dividends Declared-Solar Company Totals 30,000 2. Complete a worksheet for consolidated financial statements for 2016. Include columns for eliminations and adjustments, consolidated income, NCI, controlling retained earnings, and consolidated balance sheet. On January 1, 2015, Paro Company purchases 80% of the common stock of Solar Company for $320,000. Solar has common stock, other paid-in capital in excess of par, and retained earnings of $50,000, $100,000, and $150,000, respectively. Net income and dividends for two years for Solar are as follows: Net income Dividends 2015 2016 $60,000 $90,000 20,000 30,000 On January 1, 2015, the only undervalued tangible assets of Solar are inventory and the building. Inventory, for which FIFO is used, is worth $10,000 more than cost. The inventory is sold in 2015. The building, which is worth $30,000 more than book value, has a remaining life of 10 years, and straight-line depreciation is used. The remaining excess of cost over book value is attributed to goodwill.
1. Using this information and the information in the following trial balances on December 31, 2016, prepare a value analysis and a determination and distribution of excess schedule: Inventory, December 31 Other Current Assets Paro Company Solar Company 100,000 50,000 136,000 180,000 Investment in Solar Company 400,000 Land 50,000 50,000 Buildingsand Equipment 350,000 320,000 Accumulated Depreciation (100,000) (60,000) Goodwill Other Intangibles Current Liabilities Bonds Payable Other Long-Term Liabilities 20,000 (120,000) (40,000) (200,000) Common Stock-Paro Company (200,000) Other Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par-Paro Company (100,000) Retained Earnings-Paro Company (214,000) Common Stock-Solar Company Other Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par-Solar Company Retained Earnings-Solar Company Net Sales Cost of Goods Sold Operating Expenses (100,000) (50,000) (100,000) (190,000) (520,000) (450,000) 300,000 260,000 120,000 100,000 Subsidiary Income (72,000) Dividends Declared-Paro Company 50,000 Dividends Declared-Solar Company Totals 30,000 2. Complete a worksheet for consolidated financial statements for 2016. Include columns for eliminations and adjustments, consolidated income, NCI, controlling retained earnings, and consolidated balance sheet. On January 1, 2015, Paro Company purchases 80% of the common stock of Solar Company for $320,000. Solar has common stock, other paid-in capital in excess of par, and retained earnings of $50,000, $100,000, and $150,000, respectively. Net income and dividends for two years for Solar are as follows: Net income Dividends 2015 2016 $60,000 $90,000 20,000 30,000 On January 1, 2015, the only undervalued tangible assets of Solar are inventory and the building. Inventory, for which FIFO is used, is worth $10,000 more than cost. The inventory is sold in 2015. The building, which is worth $30,000 more than book value, has a remaining life of 10 years, and straight-line depreciation is used. The remaining excess of cost over book value is attributed to goodwill.
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Chapter13: Investments And Long-term Receivables
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14RE
Related questions
Question
Complete the following
Acquired Company's Balance Sheet Before Purchase
Amortization Schedule
Income Distribution Schedules
Consolidated worksheet
eliminations
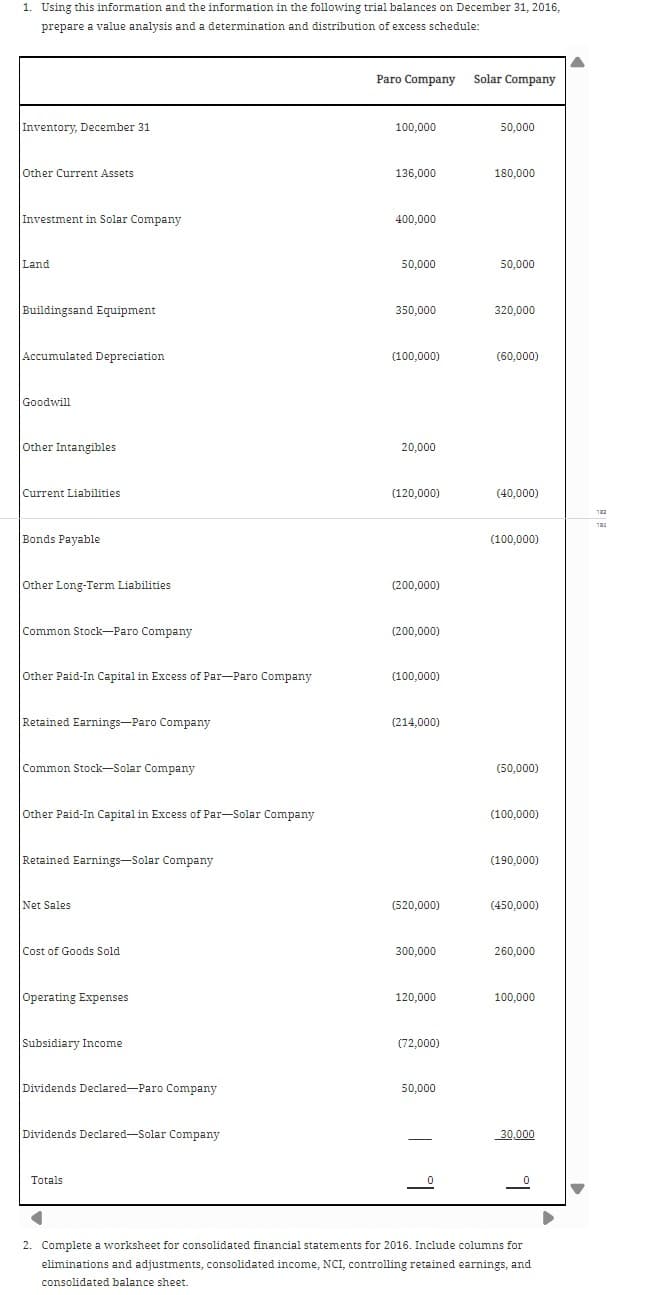
Transcribed Image Text:1. Using this information and the information in the following trial balances on December 31, 2016,
prepare a value analysis and a determination and distribution of excess schedule:
Inventory, December 31
Other Current Assets
Paro Company Solar Company
100,000
50,000
136,000
180,000
Investment in Solar Company
400,000
Land
50,000
50,000
Buildingsand Equipment
350,000
320,000
Accumulated Depreciation
(100,000)
(60,000)
Goodwill
Other Intangibles
Current Liabilities
Bonds Payable
Other Long-Term Liabilities
20,000
(120,000)
(40,000)
(200,000)
Common Stock-Paro Company
(200,000)
Other Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par-Paro Company
(100,000)
Retained Earnings-Paro Company
(214,000)
Common Stock-Solar Company
Other Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par-Solar Company
Retained Earnings-Solar Company
Net Sales
Cost of Goods Sold
Operating Expenses
(100,000)
(50,000)
(100,000)
(190,000)
(520,000)
(450,000)
300,000
260,000
120,000
100,000
Subsidiary Income
(72,000)
Dividends Declared-Paro Company
50,000
Dividends Declared-Solar Company
Totals
30,000
2. Complete a worksheet for consolidated financial statements for 2016. Include columns for
eliminations and adjustments, consolidated income, NCI, controlling retained earnings, and
consolidated balance sheet.
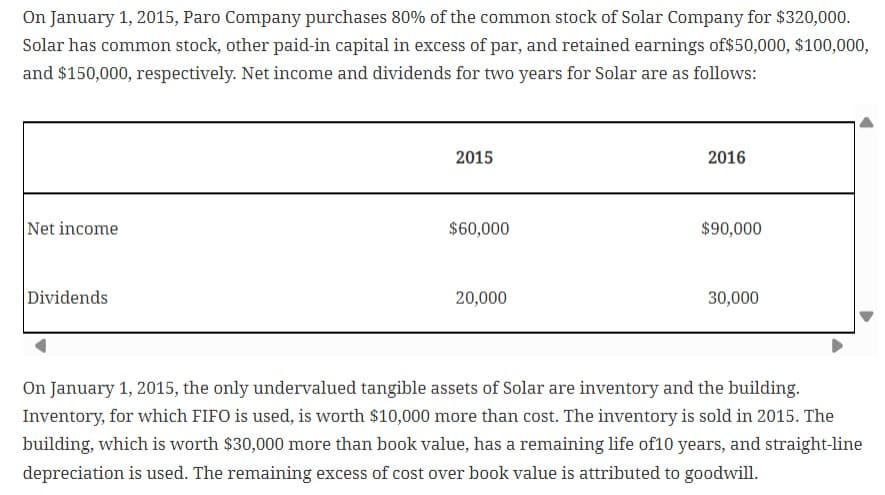
Transcribed Image Text:On January 1, 2015, Paro Company purchases 80% of the common stock of Solar Company for $320,000.
Solar has common stock, other paid-in capital in excess of par, and retained earnings of $50,000, $100,000,
and $150,000, respectively. Net income and dividends for two years for Solar are as follows:
Net income
Dividends
2015
2016
$60,000
$90,000
20,000
30,000
On January 1, 2015, the only undervalued tangible assets of Solar are inventory and the building.
Inventory, for which FIFO is used, is worth $10,000 more than cost. The inventory is sold in 2015. The
building, which is worth $30,000 more than book value, has a remaining life of 10 years, and straight-line
depreciation is used. The remaining excess of cost over book value is attributed to goodwill.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Excel Applications for Accounting Principles
Accounting
ISBN:
9781111581565
Author:
Gaylord N. Smith
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Excel Applications for Accounting Principles
Accounting
ISBN:
9781111581565
Author:
Gaylord N. Smith
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305088436
Author:
Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

