One card is selected at random from an ordinary deck of 52 playing cards. Events A, B, and C are defined below. Find the probabilities for parts (a) through (h) below and express your results in words. Compute the conditional probabilities directly; do not use the conditional probability rule. Note that the ace has the highest value. A = event a card higher than 8 is selected B = event a queen is selected C = event a heart is selected a. Find P(B). Express your result in words. The probability that a queen is selected is 13 (Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.) b. Find P(BJA). Express your result in words. Question Viewer The probability that a queen is selected, given that a card higher than 8 is not selected is 0- (Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.) c. Find P(B|C). Express your result in words. The probability that a queen is selected, given that a heart is selected is (Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.) d. Find P(B|(not A). Express your result in words. The probability that a queen is selected, given that a card higher than 8 is not selected is. (Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.)
One card is selected at random from an ordinary deck of 52 playing cards. Events A, B, and C are defined below. Find the probabilities for parts (a) through (h) below and express your results in words. Compute the conditional probabilities directly; do not use the conditional probability rule. Note that the ace has the highest value. A = event a card higher than 8 is selected B = event a queen is selected C = event a heart is selected a. Find P(B). Express your result in words. The probability that a queen is selected is 13 (Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.) b. Find P(BJA). Express your result in words. Question Viewer The probability that a queen is selected, given that a card higher than 8 is not selected is 0- (Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.) c. Find P(B|C). Express your result in words. The probability that a queen is selected, given that a heart is selected is (Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.) d. Find P(B|(not A). Express your result in words. The probability that a queen is selected, given that a card higher than 8 is not selected is. (Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.)
College Algebra
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter9: Counting And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7CC
Related questions
Question
Plzz Verify the blanks is correct fill Or not and solve a) and f) question.. Ty
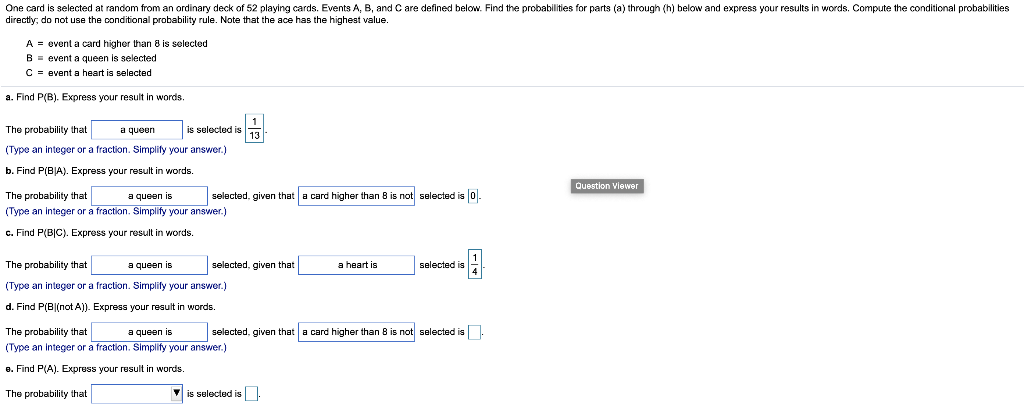
Transcribed Image Text:One card is selected at random from an ordinary deck of 52 playing cards. Events A, B, and C are defined below. Find the probabilities for parts (a) through (h) below and express your results in words. Compute the conditional probabilities
directly; do not use the conditional probability rule. Note that the ace has the highest value.
A = event a card higher than 8 is selected
B = event a queen is selected
C = event a heart is selected
a. Find P(B). Express your result in words.
The probability that
a queen
is selected is
(Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.)
b. Find P(BJA). Express your result in words.
Question Viewer
The probability that
a queen is
selected, given that a card higher than 8 is not selected is 0.
(Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.)
c. Find P(B|C). Express your result in words.
The probability that
a queen is
selected, given that
a heart is
selected is
(Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.)
d. Find P(B|(not A)). Express your result in words.
The probability that
a queen is
selected, given that a card higher than 8 is not selected is.
(Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.)
8. Find P(A). Express your result in words.
The probability that
V is selected is
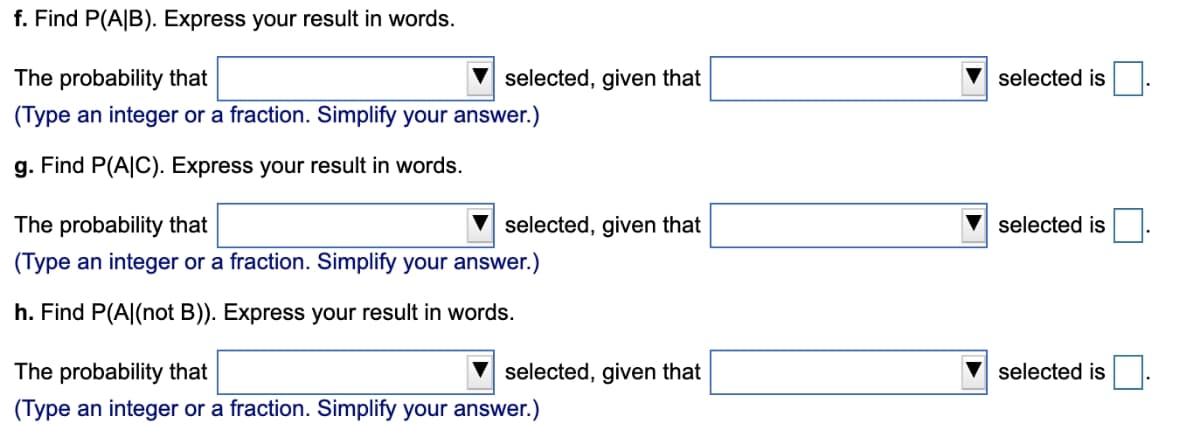
Transcribed Image Text:f. Find P(A|B). Express your result in words.
The probability that
selected, given that
selected is.
(Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.)
g. Find P(A|C). Express your result in words.
The probability that
selected, given that
selected is
(Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.)
h. Find P(A|(not B)). Express your result in words.
The probability that
selected, given that
selected is
(Type an integer or a fraction. Simplify your answer.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, probability and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning