One side of a right triangle is known to be 26 cm exactly. The angle opposite to this side is measured to be 60", with a possible error of +0.3". Round your answers to three decimal places. (a) Use differentials to estimate the errors in the adjacent side and the hypotenuse. Propagated error in the adjacent side: + cm Propagated error in the hypotenuse: + cm (b) Estimate the percentage errors in the adjacent side and hypotenuse. Percentage error in the adjacent side: + i % Percentage error in the hypotenuse: + i
One side of a right triangle is known to be 26 cm exactly. The angle opposite to this side is measured to be 60", with a possible error of +0.3". Round your answers to three decimal places. (a) Use differentials to estimate the errors in the adjacent side and the hypotenuse. Propagated error in the adjacent side: + cm Propagated error in the hypotenuse: + cm (b) Estimate the percentage errors in the adjacent side and hypotenuse. Percentage error in the adjacent side: + i % Percentage error in the hypotenuse: + i
Mathematics For Machine Technology
8th Edition
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Peterson, John.
Chapter59: Areas Of Rectangles, Parallelograms, And Trapezoids
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 79A
Related questions
Question
One side of a right triangle is known to be 26 cm exactly. The angle opposite to this side is measured to be 60∘, with a possible error of ±0.3∘.
Round your answers to three decimal places.
(a) Use differentials to estimate the errors in the adjacent side and the hypotenuse.
Propagated error in the adjacent side: ± ? cm
Propagated error in the hypotenuse: ± ?; cm
(b) Estimate the percentage errors in the adjacent side and hypotenuse.
Percentage error in the adjacent side: ± ? %
Percentage error in the hypotenuse: ± ? %
(a) Use differentials to estimate the errors in the adjacent side and the hypotenuse.
Propagated error in the adjacent side: ± ? cm
Propagated error in the hypotenuse: ± ?; cm
(b) Estimate the percentage errors in the adjacent side and hypotenuse.
Percentage error in the adjacent side: ± ? %
Percentage error in the hypotenuse: ± ? %
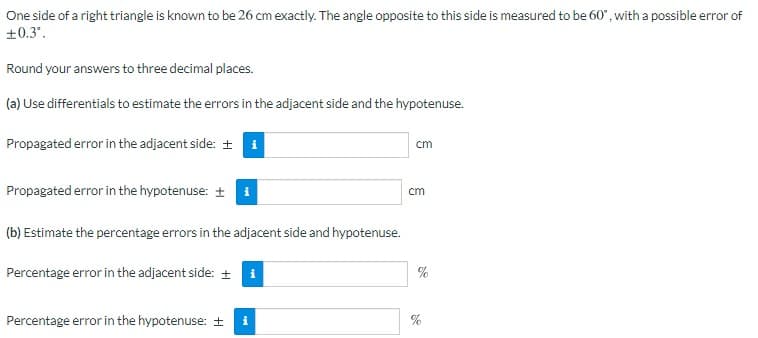
Transcribed Image Text:One side of a right triangle is known to be 26 cm exactly. The angle opposite to this side is measured to be 60", with a possible error of
+0.3'.
Round your answers to three decimal places.
(a) Use differentials to estimate the errors in the adjacent side and the hypotenuse.
Propagated error in the adjacent side: + i
cm
Propagated error in the hypotenuse: + i
cm
(b) Estimate the percentage errors in the adjacent side and hypotenuse.
Percentage error in the adjacent side: +
%
Percentage error in the hypotenuse: +
%
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning