oute P(x) using the binomial probability formula. Then determine whether the normal distribution can be used to estimate this probability. If so, approximate P(x) using the normal distribution and compare the result with the exact ability. =74, p= 0.73, and x= 57 here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1). here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2). =74, p=0.73, and x= 57, find P(x) using the binomial probability distribution, = (Round to four decimal places as needed.) the normal distribution be used to approximate this probability? A. Yes, the normal distribution can be used because np(1-p)s10. B. No, the normal distribution cannot be used because np(1-p)< 10. C. No, the normal distribution cannot be used because np(1 - p)2 10. D. Yes, the normal distribution can be used because np(1-p)2 10. roximate P(x) using the normal distribution. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes in your choice. A. P(x) = (Round to four decimal places as needed.) B. The normal distribution cannot be used to approximate the binomial distribution in this case.
oute P(x) using the binomial probability formula. Then determine whether the normal distribution can be used to estimate this probability. If so, approximate P(x) using the normal distribution and compare the result with the exact ability. =74, p= 0.73, and x= 57 here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1). here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2). =74, p=0.73, and x= 57, find P(x) using the binomial probability distribution, = (Round to four decimal places as needed.) the normal distribution be used to approximate this probability? A. Yes, the normal distribution can be used because np(1-p)s10. B. No, the normal distribution cannot be used because np(1-p)< 10. C. No, the normal distribution cannot be used because np(1 - p)2 10. D. Yes, the normal distribution can be used because np(1-p)2 10. roximate P(x) using the normal distribution. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes in your choice. A. P(x) = (Round to four decimal places as needed.) B. The normal distribution cannot be used to approximate the binomial distribution in this case.
College Algebra
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter9: Counting And Probability
Section9.3: Binomial Probability
Problem 2E: If a binomial experiment has probability p success, then the probability of failure is...
Related questions
Question
5: need help
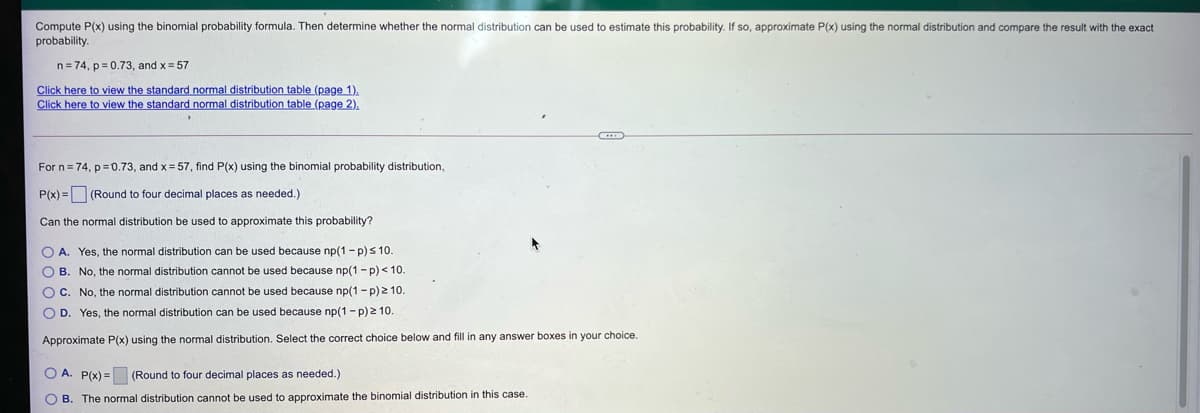
Transcribed Image Text:Compute P(x) using the binomial probability formula. Then determine whether the normal distribution can be used to estimate this probability. If so, approximate P(x) using the normal distribution and compare the result with the exact
probability.
n= 74, p= 0.73, and x = 57
Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1).
Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2).
For n= 74, p=0.73, and x= 57, find P(x) using the binomial probability distribution,
P(x) = (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
Can the normal distribution be used to approximate this probability?
O A. Yes, the normal distribution can be used because np(1 - p)s 10.
O B. No, the normal distribution cannot be used because np(1 - p) < 10.
O C. No, the normal distribution cannot be used because np(1 - p)2 10.
O D. Yes, the normal distribution can be used because np(1 - p)2 10.
Approximate P(x) using the normal distribution. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes in your choice.
O A. P(x) =
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
O B. The normal distribution cannot be used
approximate the binomial distribution in this case.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning