P17B.7 Pharmacokinetics is the study of the rates of absorption and elimination of drugs by organisms. In most cases, elimination is slower than absorption and is a more important determinant of availability of a drug for binding to its target. A drug can be eliminated by many mechanisms, such as metabolism in the liver, intestine, or kidney followed by excretion of breakdown products through urine or faeces. As an example of pharmacokinetic analysis, consider the elimination of beta adrenergic blocking agents (beta blockers), which are used in the treatment of hypertension. After intravenous administration of a beta blocker, the blood plasma of a patient was analysed for remaining drug and the data are shown below, where c is the drug concentration measured at a time t after the injection. t/min 30 60 120 150 240 360 480 c/(ng cm) 152 699 622 413 292 60 24 (a) Is the decay of the concentration of the drug first- or second-order in the drug? (b) Calculate the rate constant and half-life of the process. Comment: An essential aspect of drug development is the optimization of the half-life of elimination, which needs to be long enough to allow the drug to find and act on its target organ but not so long that harmful side effects become important.
P17B.7 Pharmacokinetics is the study of the rates of absorption and elimination of drugs by organisms. In most cases, elimination is slower than absorption and is a more important determinant of availability of a drug for binding to its target. A drug can be eliminated by many mechanisms, such as metabolism in the liver, intestine, or kidney followed by excretion of breakdown products through urine or faeces. As an example of pharmacokinetic analysis, consider the elimination of beta adrenergic blocking agents (beta blockers), which are used in the treatment of hypertension. After intravenous administration of a beta blocker, the blood plasma of a patient was analysed for remaining drug and the data are shown below, where c is the drug concentration measured at a time t after the injection. t/min 30 60 120 150 240 360 480 c/(ng cm) 152 699 622 413 292 60 24 (a) Is the decay of the concentration of the drug first- or second-order in the drug? (b) Calculate the rate constant and half-life of the process. Comment: An essential aspect of drug development is the optimization of the half-life of elimination, which needs to be long enough to allow the drug to find and act on its target organ but not so long that harmful side effects become important.
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Chapter23: Organic Polymers, Natural And Synthetic
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 46QAP: Glycolysis is the process by which glucose is metabolized to lactic acid according to the equation...
Related questions
Question
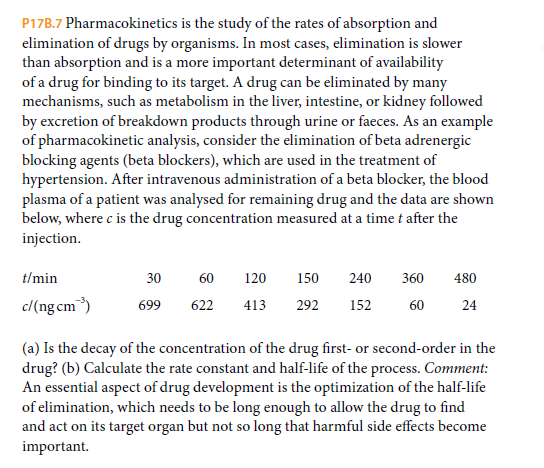
Transcribed Image Text:P17B.7 Pharmacokinetics is the study of the rates of absorption and
elimination of drugs by organisms. In most cases, elimination is slower
than absorption and is a more important determinant of availability
of a drug for binding to its target. A drug can be eliminated by many
mechanisms, such as metabolism in the liver, intestine, or kidney followed
by excretion of breakdown products through urine or faeces. As an example
of pharmacokinetic analysis, consider the elimination of beta adrenergic
blocking agents (beta blockers), which are used in the treatment of
hypertension. After intravenous administration of a beta blocker, the blood
plasma of a patient was analysed for remaining drug and the data are shown
below, where c is the drug concentration measured at a time t after the
injection.
t/min
30
60
120
150
240
360
480
c/(ng cm)
152
699
622
413
292
60
24
(a) Is the decay of the concentration of the drug first- or second-order in the
drug? (b) Calculate the rate constant and half-life of the process. Comment:
An essential aspect of drug development is the optimization of the half-life
of elimination, which needs to be long enough to allow the drug to find
and act on its target organ but not so long that harmful side effects become
important.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning