Part 2: Component Method Do this only! Using the component method, determine the magnitude and direction of the forces described in Part 2 and analytically determine the magnitude and direction of their resultant. Record your results in the table below. Component Determination Magnitude Vector X-Component Y- Component 1 R Resultant R OR=
Part 2: Component Method Do this only! Using the component method, determine the magnitude and direction of the forces described in Part 2 and analytically determine the magnitude and direction of their resultant. Record your results in the table below. Component Determination Magnitude Vector X-Component Y- Component 1 R Resultant R OR=
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Chapter1: A Physics Toolkit
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 60A
Related questions
Question
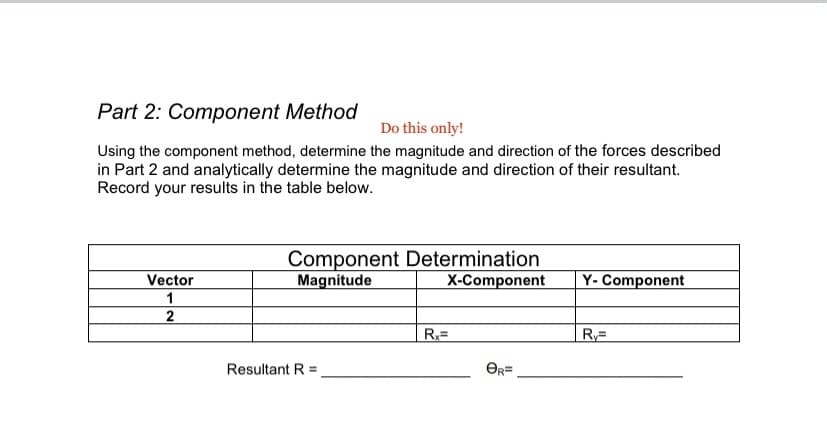
Transcribed Image Text:Part 2: Component Method
Do this only!
Using the component method, determine the magnitude and direction of the forces described
in Part 2 and analytically determine the magnitude and direction of their resultant.
Record your results in the table below.
Component Determination
Magnitude
Vector
X-Component
Y- Component
1
Resultant R =
OR=

Transcribed Image Text:Do! Graphical Error = graphical value – calculated value
calculated value
+100%
Parts 2, 3, and 4
Repeat the steps in Part 1 to determine the resultant of the three additional force
combinations (2, 3, and 4) shown below using the (1) experimental, (2) graphical, and
(3) component methods for each combination of force vectors (Don't forget to include
the percent error for each).
In this section, skip any mention of Graphical or Experimental.
Use only Component method.
Force Combinations
Vector Magnitude Direction Vector Magnitude Direction
B 130 gm
140 gm
2
A
175 gm
60°
160°
3
A
110 gm
1450
B
230°
4
A
150 gm
45°
B
180 gm
290°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill