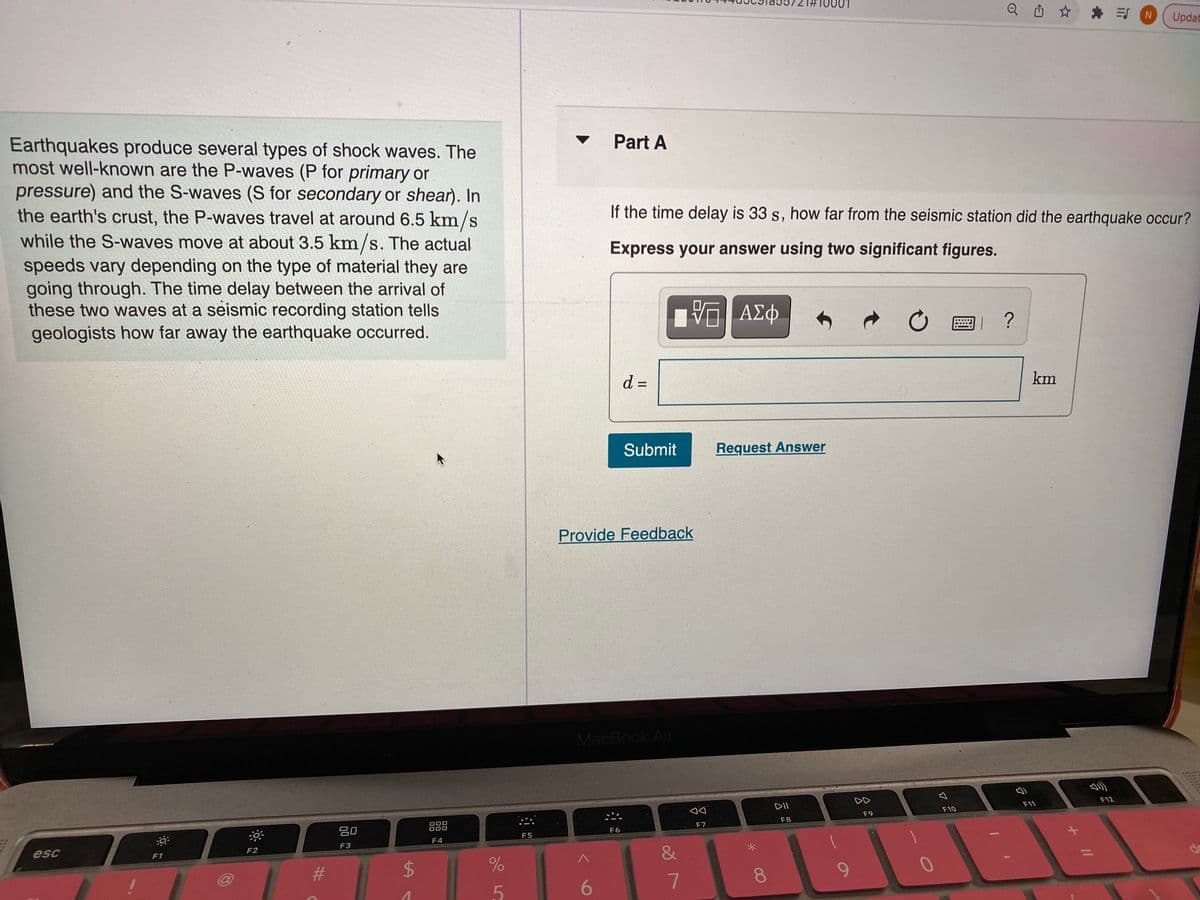
Part A Earthquakes produce several types of shock waves. The most well-known are the P-waves (P for primary or pressure) and the S-waves (S for secondary or shear). In the earth's crust, the P-waves travel at around 6.5 km/s while the S-waves move at about 3.5 km/s. The actual speeds vary depending on the type of material they are going through. The time delay between the arrival of these two waves at a seismic recording station tells geologists how far away the earthquake occurred. If the time delay is 33 s, how far from the seismic station did the earthquake occur? Express your answer using two significant figures. ? d = km Submit Request Answer
Part A Earthquakes produce several types of shock waves. The most well-known are the P-waves (P for primary or pressure) and the S-waves (S for secondary or shear). In the earth's crust, the P-waves travel at around 6.5 km/s while the S-waves move at about 3.5 km/s. The actual speeds vary depending on the type of material they are going through. The time delay between the arrival of these two waves at a seismic recording station tells geologists how far away the earthquake occurred. If the time delay is 33 s, how far from the seismic station did the earthquake occur? Express your answer using two significant figures. ? d = km Submit Request Answer
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter16: Waves
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 43P: (a) Seismographs measure the arrival times of earthquakes with a precision of 0.100 s. To get the...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:ET N
Updat
Earthquakes produce several types of shock waves. The
most well-known are the P-waves (P for primary or
pressure) and the S-waves (S for secondary or shear). In
the earth's crust, the P-waves travel at around 6.5 km/s
while the S-waves move at about 3.5 km/s. The actual
Part A
If the time delay is 33 s, how far from the seismic station did the earthquake occur?
Express your answer using two significant figures.
speeds vary depending on the type of material they are
going through. The time delay between the arrival of
these two waves at a seismic recording station tells
geologists how far away the earthquake occurred.
ΑΣφ
0圖 ?
km
%3D
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
MacBook Air
DD
DII
F12
F11
F10
吕0
000
000
F9
F8
F7
F6
F5
F4
esc
F2
F3
F1
&
%23
8
5.
%24
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College