Part A In each pair, identify the solution that will have a higher boiling point. Explain. 1. 1.50 moles of LiOH (strong electrolyte) and 3.00 moles of KOH (strong electrolyte) each in 1.0 kg of water 2.0.40 mole of A1(NO3)3 (strong electrolyte) and 0.40 mole of CsCl (strong electrolyte) each in 1.0 kg of water Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. Make certain each sentence is complete before submitting your answer. 3.00 moles of KOH CsCl two decomposes dissociates less more 1.50 moles of LiOH one remains unchanged AI(NO3)3 three four in 1.0 kg of water will have a higher boiling point because it has particle(s) in solution. 2.0.40 mole of Reset Help in 1.0 kg of water has a higher boiling point because each in water to give particle(s), whereas each to give only particle(s).
Part A In each pair, identify the solution that will have a higher boiling point. Explain. 1. 1.50 moles of LiOH (strong electrolyte) and 3.00 moles of KOH (strong electrolyte) each in 1.0 kg of water 2.0.40 mole of A1(NO3)3 (strong electrolyte) and 0.40 mole of CsCl (strong electrolyte) each in 1.0 kg of water Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. Make certain each sentence is complete before submitting your answer. 3.00 moles of KOH CsCl two decomposes dissociates less more 1.50 moles of LiOH one remains unchanged AI(NO3)3 three four in 1.0 kg of water will have a higher boiling point because it has particle(s) in solution. 2.0.40 mole of Reset Help in 1.0 kg of water has a higher boiling point because each in water to give particle(s), whereas each to give only particle(s).
Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Chapter10: Properties Of Solutions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 124CP
Related questions
Question
Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right.
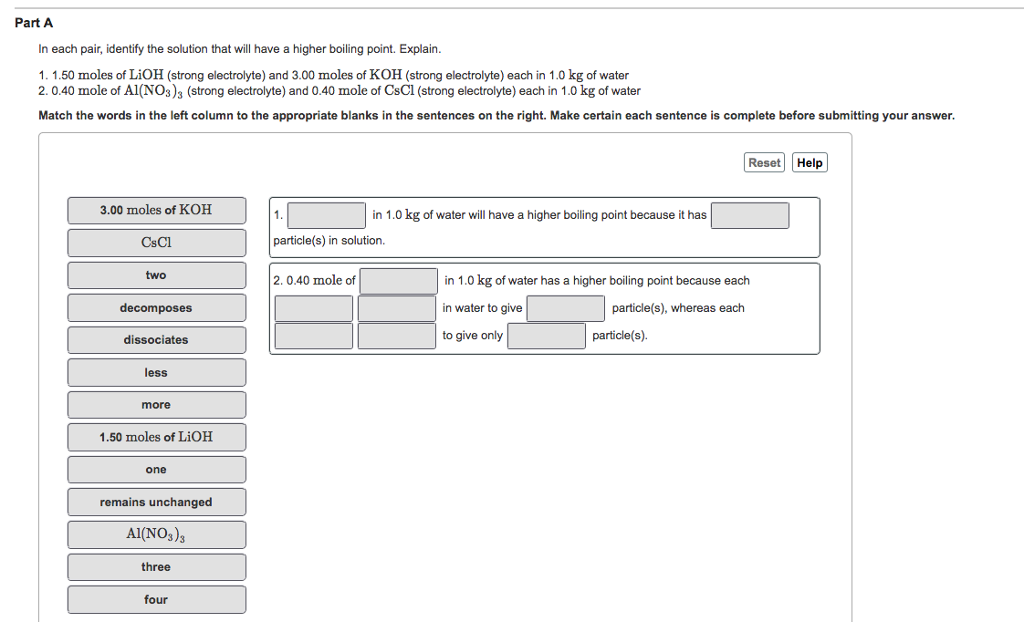
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
In each pair, identify the solution that will have a higher boiling point. Explain.
1. 1.50 moles of LiOH (strong electrolyte) and 3.00 moles of KOH (strong electrolyte) each in 1.0 kg of water
2.0.40 mole of A1(NO3)3 (strong electrolyte) and 0.40 mole of CsCl (strong electrolyte) each in 1.0 kg of water
Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. Make certain each sentence is complete before submitting your answer.
3.00 moles of KOH
CsCl
two
decomposes
dissociates
less
more
1.50 moles of LiOH
one
remains unchanged
Al(NO3)3
three
four
1.
in 1.0 kg of water will have a higher boiling point because it has
particle(s) in solution.
2.0.40 mole of
Reset Help
in 1.0 kg of water has a higher boiling point because each
in water to give
particle(s), whereas each
to give only
particle(s).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning