Part A What is the pH of a buffer prepared by adding 0.708 mol of the weak acid HA to 0.507 mol of NaA in 2.00 L of solution? The dissociation constant K, of HA is 5.66 x 10 7. Express the pH numerically to three decimal places. > View Available Hint(o) pH = Submit Part B What is the pHafter 0.150 mol of HCl is added to the buffer from Part A? Assume no volume change on the addition of the acid. Express the pH numerically to three decimal places. • View Available Hintțo) ? Pav DA pH = Submit
Part A What is the pH of a buffer prepared by adding 0.708 mol of the weak acid HA to 0.507 mol of NaA in 2.00 L of solution? The dissociation constant K, of HA is 5.66 x 10 7. Express the pH numerically to three decimal places. > View Available Hint(o) pH = Submit Part B What is the pHafter 0.150 mol of HCl is added to the buffer from Part A? Assume no volume change on the addition of the acid. Express the pH numerically to three decimal places. • View Available Hintțo) ? Pav DA pH = Submit
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Chapter16: Acid-base Equilibria
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 16.149QP: A solution of weak base is titrated to the equivalence point with a strong acid. Which one of the...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Part C
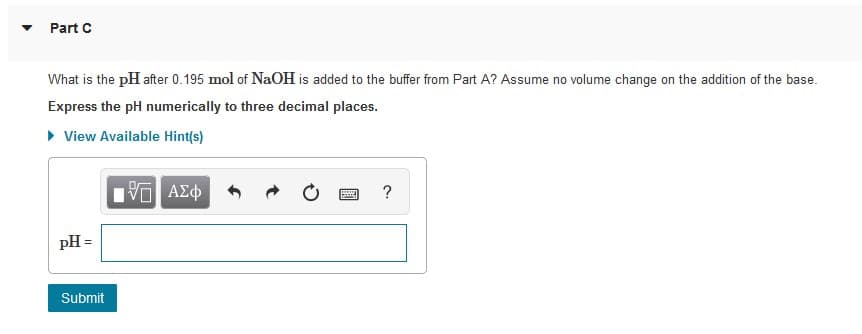
What is the pH after 0.195 mol of NaOH is added to the buffer from Part A? Assume no volume change on the addition of the base.
Express the pH numerically to three decimal places.
• View Available Hint(s)
pH =
Submit
![Part A
When a solution contains a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak
base and its conjugate acid, it will be a buffer solution. Buffers resist change
in pH following the addition of acid or base. A buffer solution prepared from a
weak acid (HA) and its conjugate base (A) is represented as
What is the pH of a buffer prepared by adding 0.708 mol of the weak acid HA to 0.507 mol of NaA in 2.00 L of solution? The dissociation constant K of HA is 5.66 x 10-7.
Express the pH numerically to three decimal places.
HA(aq) = H+ (aq) + A-(aq)
• View Available Hint(s)
The buffer will follow Le Châtelier's principle. If acid is added, the reaction
shifts to consume the added H+, forming more HA. When base
the base will react with Ht, reducing its concentration. The reaction then
shifts to replace H+ through the dissociation of HA into H+ and A. In
both instances, H+] tends to remain constant.
added,
V AZO
The pH of a buffer is calculated by using the Henderson-Hasselbalch
pH =
equation:
pH = pK, + log-
[A]
HA]
Submit
Part B
What is the pH after 0.150 mol of HCl is added to the buffer from Part A? Assume no volume change on the addition of the acid.
Express the pH numerically to three decimal places.
• View Available Hint(s)
?
pH =
Submit](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F983f8bb4-8f07-4098-8306-e588c6bd6c5d%2Fe80a8143-d0fe-41f9-ac4b-2a136f94aa28%2F9kbomo_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
When a solution contains a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak
base and its conjugate acid, it will be a buffer solution. Buffers resist change
in pH following the addition of acid or base. A buffer solution prepared from a
weak acid (HA) and its conjugate base (A) is represented as
What is the pH of a buffer prepared by adding 0.708 mol of the weak acid HA to 0.507 mol of NaA in 2.00 L of solution? The dissociation constant K of HA is 5.66 x 10-7.
Express the pH numerically to three decimal places.
HA(aq) = H+ (aq) + A-(aq)
• View Available Hint(s)
The buffer will follow Le Châtelier's principle. If acid is added, the reaction
shifts to consume the added H+, forming more HA. When base
the base will react with Ht, reducing its concentration. The reaction then
shifts to replace H+ through the dissociation of HA into H+ and A. In
both instances, H+] tends to remain constant.
added,
V AZO
The pH of a buffer is calculated by using the Henderson-Hasselbalch
pH =
equation:
pH = pK, + log-
[A]
HA]
Submit
Part B
What is the pH after 0.150 mol of HCl is added to the buffer from Part A? Assume no volume change on the addition of the acid.
Express the pH numerically to three decimal places.
• View Available Hint(s)
?
pH =
Submit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
