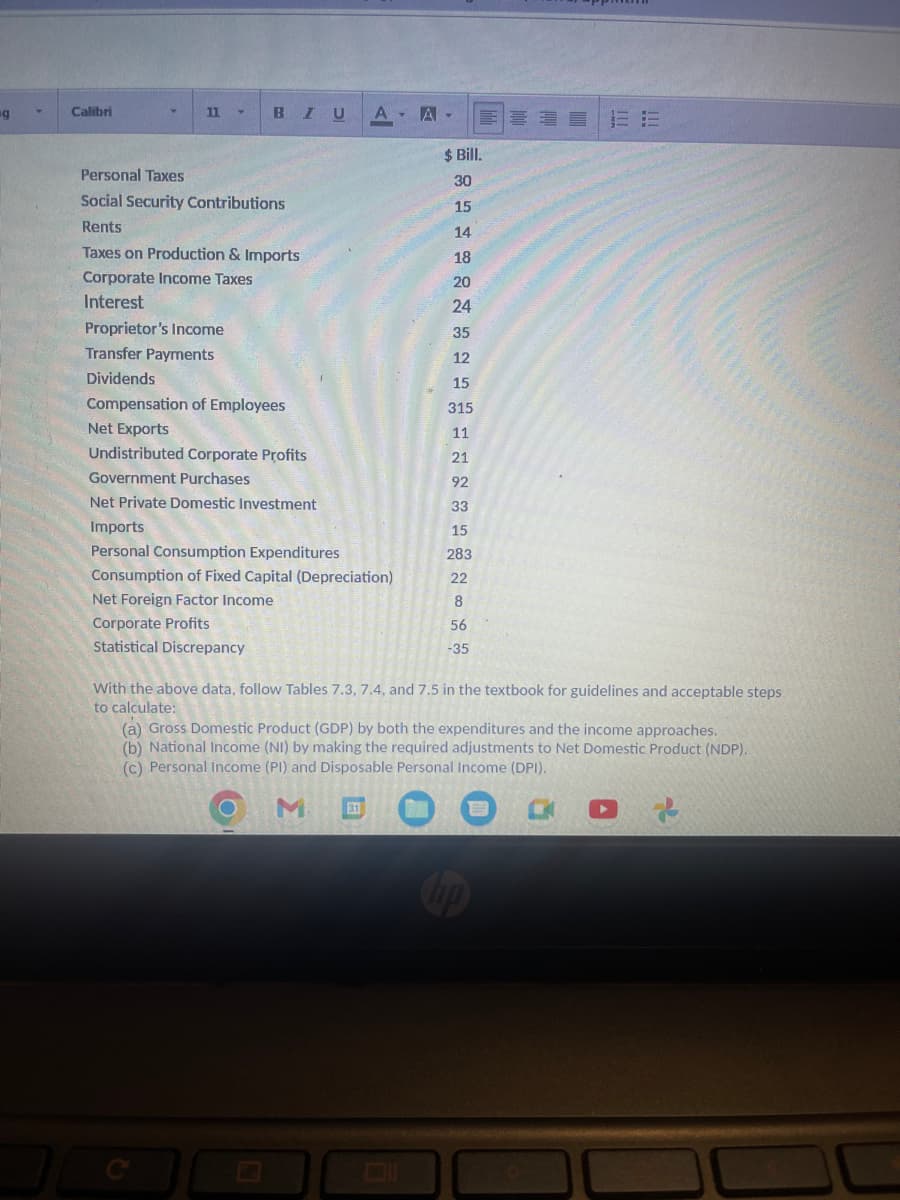
Personal Taxes Social Security Contributions Rents Taxes on Production & Imports Corporate Income Taxes Interest Proprietor's Income Transfer Payments Dividends Compensation of Employees Net Exports Undistributed Corporate Profits Government Purchases Net Private Domestic Investment Imports Personal Consumption Expenditures Consumption of Fixed Capital (Depreciation) Net Foreign Factor Income Corporate Profits Statistical Discrepancy $Bill. 30 15 14 18 20 24 35 12 15 315 11 21 92 33 15 283 22 8 56 -35 With the above data, follow Tables 7.3, 7.4, and 7.5 in the textbook for guidelines and acceptable steps to calculate: (a) Gross Domestic Product (GDP) by both the expenditures and the income approaches. (b) National Income (NI) by making the required adjustments to Net Domestic Product (NDP). (c) Personal Income (PI) and Disposable Personal Income (DPI).
Personal Taxes Social Security Contributions Rents Taxes on Production & Imports Corporate Income Taxes Interest Proprietor's Income Transfer Payments Dividends Compensation of Employees Net Exports Undistributed Corporate Profits Government Purchases Net Private Domestic Investment Imports Personal Consumption Expenditures Consumption of Fixed Capital (Depreciation) Net Foreign Factor Income Corporate Profits Statistical Discrepancy $Bill. 30 15 14 18 20 24 35 12 15 315 11 21 92 33 15 283 22 8 56 -35 With the above data, follow Tables 7.3, 7.4, and 7.5 in the textbook for guidelines and acceptable steps to calculate: (a) Gross Domestic Product (GDP) by both the expenditures and the income approaches. (b) National Income (NI) by making the required adjustments to Net Domestic Product (NDP). (c) Personal Income (PI) and Disposable Personal Income (DPI).
Chapter8: Aggregate Demand And The Powerful Consumer
Section8.A: National Income Accounting
Problem 3TY
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:ig
Y
Calibri
Y
11 -
Personal Taxes
Social Security Contributions
Rents
BIU A A-
Taxes on Production & Imports
Corporate Income Taxes
Interest
Proprietor's Income
Transfer Payments
Dividends
Compensation of Employees
Net Exports
Undistributed Corporate Profits
Government Purchases
Net Private Domestic Investment
Imports
Personal Consumption Expenditures
Consumption of Fixed Capital (Depreciation)
Net Foreign Factor Income
Corporate Profits
Statistical Discrepancy
C
$ Bill.
30
15
14
18
20
24
35
12
15
315
11
21
92
33
15
283
31
22
8
56
-35
With the above data, follow Tables 7.3, 7.4, and 7.5 in the textbook for guidelines and acceptable steps
to calculate:
(a) Gross Domestic Product (GDP) by both the expenditures and the income approaches.
(b) National Income (NI) by making the required adjustments to Net Domestic Product (NDP).
(c) Personal Income (PI) and Disposable Personal Income (DPI).
M
B
EE
Chp
Transcribed Image Text:Sheets & Slides| chrome-extension://bpmcpldpdmajfigpchkicefoigmkfalc/views/app.html
cing
Calibri
11
▾
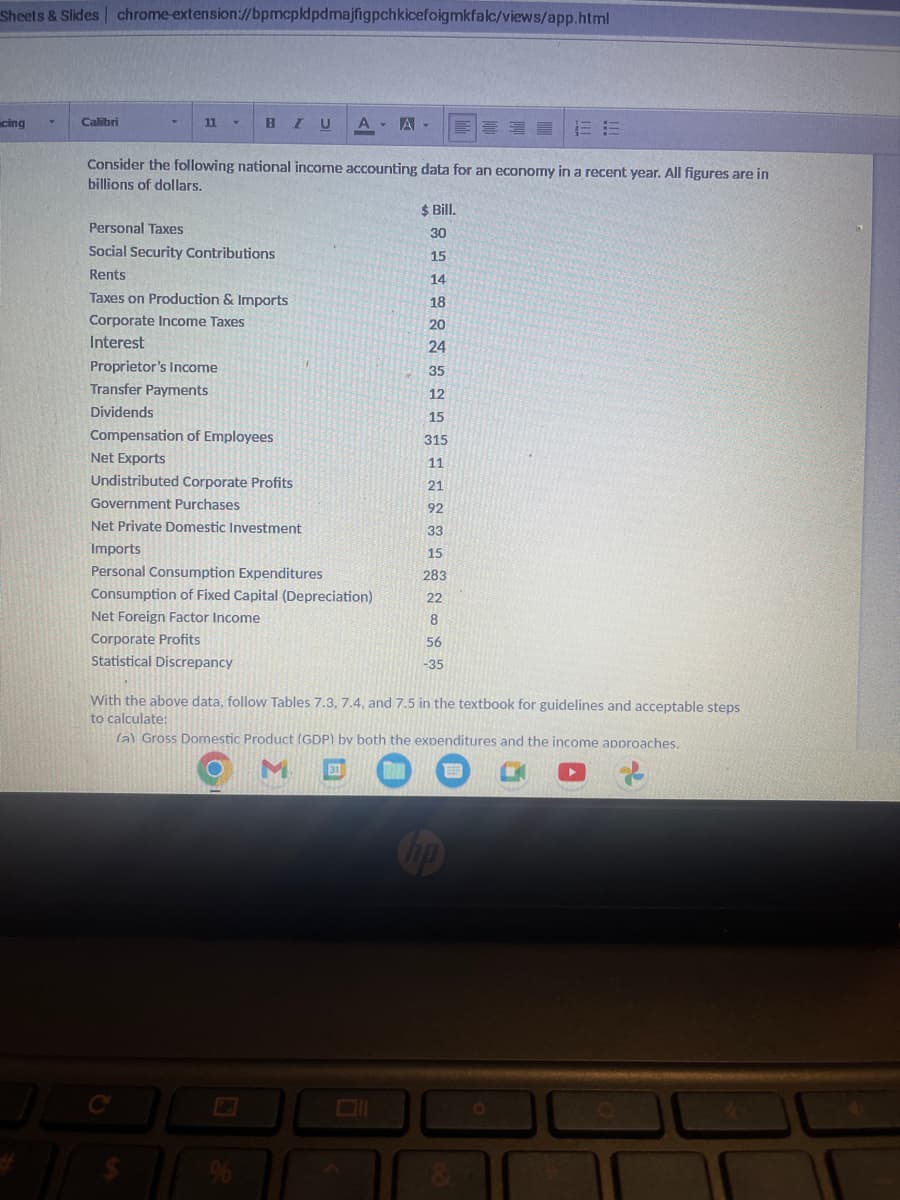
Consider the following national income accounting data for an economy in a recent year. All figures are in
billions of dollars.
Proprietor's Income
Transfer Payments
Dividends
Personal Taxes
Social Security Contributions
Rents
Taxes on Production & Imports
Corporate Income Taxes
Interest
BIU A A-
Compensation of Employees
Net Exports
Undistributed Corporate Profits
Government Purchases
Net Private Domestic Investment
C
Imports
Personal Consumption Expenditures
Consumption of Fixed Capital (Depreciation)
Net Foreign Factor Income
Corporate Profits
Statistical Discrepancy
With the above data, follow Tables 7.3, 7.4, and 7.5 in the textbook for guidelines and acceptable steps
to calculate:
(a) Gross Domestic Product (GDP) by both the expenditures and the income approaches.
M 31
A
%
$ Bill.
30
15
14
18
20
24
35
12
15
315
11
21
92
33
15
283
22
8
56
-35
hp
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

