Phosphorus pentachloride decomposes at higher temperatures. PCl5(g) ⇄ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) An equilibrium mixture at some temperature consists of 4.75 g PCl5, 208.23 g/mol 4.86 g PCl3, 137.33 g/mol 3.59 g Cl2, 70.91 g/mol in a 1.00-L flask. If you add 1.31 g of Cl2, how will the equilibrium be affected and what will the concentration of PCl5 be when equilibrium is reestablished?
Phosphorus pentachloride decomposes at higher temperatures.
PCl5(g) ⇄ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
An equilibrium mixture at some temperature consists of
4.75 g PCl5, 208.23 g/mol
4.86 g PCl3, 137.33 g/mol
3.59 g Cl2, 70.91 g/mol
in a 1.00-L flask.
If you add 1.31 g of Cl2, how will the equilibrium be affected and what will the concentration of PCl5 be when equilibrium is reestablished?
The given equilibrium reaction is

The equilibrium amounts in grams are given. Hence, we can calculate the equilibrium number of moles as follows:
n PCl5 = 4.75/208.23 = 0.0228 mol
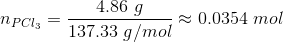
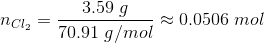
Since the volume of the container is 1.00 L, the number of moles at equilibrium are equal to the molar concentrations.
[PCl5] = 0.0228 M

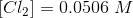
Hence, we can calculate the value of equilibrium constant Kc for the reaction as follows:
Kc = PCl3×Cl2 / PCl5 = 0.0354× 0.0506 / 0.0228= 0.0785
Now, the equilibrium is disturbed by addition of 1.31 g of Cl2.
Note that Cl2 is a product in the reaction. Hence, addition of a product to the equilibrium mixture will result in shift of the equilibrium towards the reactants (i.e. towards left) according to Le Chateliers principle.
Hence, the equilibrium will shift towards left.
Now, number of moles of Cl2 added is
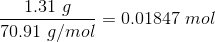
Hence, the new initial concentration of Cl2 is
![C12] = 0.0506 mol + 0.01847 mol 1.00 L 0.0691 M](https://ci4.googleusercontent.com/proxy/kEeBpXvYB5InWo08Su-fv1dPyOZFnLiEjRaSOdWOwUXQWUROPfDbasMF7shxSuIeiiYZ7CC57WoewznqwzQ8LZKfkroF0Rz9_lozni4Rp_LqyXbrz0LBtJX9LLD_7DuAlll_dV_zMfpCPvibwACfnFbG_YI1cOFOUsZ2rq1MnJaKIMh_iA=s0-d-e1-ft#https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/aef/aef140e6-4214-4407-97bf-67b7d76b3040/f36aa5e0-be97-4a4b-a47b-d2a3b3d43889.png)
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 10 images









