Preparing for Automation The possibility of having robots or mechanical assistants completing our laborious, dangerous, or repetitive day-to-day tasks has long been a dream of humanity. Now, as Robotic Process Automation (RPA) becomes commonplace, this dream or concern, depending on viewpoint - is getting closer. RPA, far from the walking, talking android commonly found in science fiction series, can be thought of as a programmable piece of software which, through using a series of rules, will complete repetitive tasks with a lower error rate and less interruption than a human completing the same tasks. The aim of RPA, beyond improving efficiency, is to free up humans from the monotony of roles like data entry, stock management and predictable physical work, to focus on more critical, unpredictable tasks such as decision making, interpreting, and delivering insight to customers. Ask any expert and you can almost guarantee that they will inform you that years of data reliably point to the conclusion that automation has always created more jobs than it has removed. The invention of the plough has allowed us to stop working on farms and technology has continued in this fashion, boosting productivity and, in turn, providing greater work satisfaction and improved living standards. It is currently estimated that 3% of roles could be entirely automated using the technology we have available to us now. By 2025 this will have risen to around 35%, by 2030 it will be at 50% and by 2080 scientists are predicting advanced artificial intelligence (Al) technologies will have replaced 85% of current jobs. A more astonishing figure is the 42% of roles which could be made more efficient, more productive, and more enjoyable through automating individual tasks within the wider role. This is not spread evenly across industries, however certain industries like waste management, an industry with a CHF 48 billion salary bill in Switzerland, where many humans are currently paid 'hazard pay' to do dangerous but repetitive tasks, is the industry in Switzerland with the highest potential for automation. As we begin to enter this Fourth Industrial Revolution, it is becoming apparent that there is a separation of organisations into two clear groups: those who are using basic digitisation to support their business, and those who have re-examined the way they do business and integrated combinations of technologies, including RPA, to great effect. So, should we run for the hills or turn and embrace RPA? The answer is not clear but, looking at those who have benefitted from this technology already, preparation for automation will be key. "By 2080 scientists are predicting advanced artificial intelligence (Al) technologies will have replaced 85% of current jobs" Transcribed Image Text:Likelihood of industries becoming automated in the future Proportion of jobs and their risk of automation. Note: the graph shows a linear decrease in the proportion of jobs at risk of full automation. 60% 55% 50% 45% 40% 35% 30% 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% 0% Waste Management Transportation and Retail Value Proportion of Jobs at Risk of Full Automation 41% Employment Share of Total Jobs Series Manufacturing H Retail 19% Administration Finance and Insurance LI Electricity and Gas Other
Preparing for Automation The possibility of having robots or mechanical assistants completing our laborious, dangerous, or repetitive day-to-day tasks has long been a dream of humanity. Now, as Robotic Process Automation (RPA) becomes commonplace, this dream or concern, depending on viewpoint - is getting closer. RPA, far from the walking, talking android commonly found in science fiction series, can be thought of as a programmable piece of software which, through using a series of rules, will complete repetitive tasks with a lower error rate and less interruption than a human completing the same tasks. The aim of RPA, beyond improving efficiency, is to free up humans from the monotony of roles like data entry, stock management and predictable physical work, to focus on more critical, unpredictable tasks such as decision making, interpreting, and delivering insight to customers. Ask any expert and you can almost guarantee that they will inform you that years of data reliably point to the conclusion that automation has always created more jobs than it has removed. The invention of the plough has allowed us to stop working on farms and technology has continued in this fashion, boosting productivity and, in turn, providing greater work satisfaction and improved living standards. It is currently estimated that 3% of roles could be entirely automated using the technology we have available to us now. By 2025 this will have risen to around 35%, by 2030 it will be at 50% and by 2080 scientists are predicting advanced artificial intelligence (Al) technologies will have replaced 85% of current jobs. A more astonishing figure is the 42% of roles which could be made more efficient, more productive, and more enjoyable through automating individual tasks within the wider role. This is not spread evenly across industries, however certain industries like waste management, an industry with a CHF 48 billion salary bill in Switzerland, where many humans are currently paid 'hazard pay' to do dangerous but repetitive tasks, is the industry in Switzerland with the highest potential for automation. As we begin to enter this Fourth Industrial Revolution, it is becoming apparent that there is a separation of organisations into two clear groups: those who are using basic digitisation to support their business, and those who have re-examined the way they do business and integrated combinations of technologies, including RPA, to great effect. So, should we run for the hills or turn and embrace RPA? The answer is not clear but, looking at those who have benefitted from this technology already, preparation for automation will be key. "By 2080 scientists are predicting advanced artificial intelligence (Al) technologies will have replaced 85% of current jobs" Transcribed Image Text:Likelihood of industries becoming automated in the future Proportion of jobs and their risk of automation. Note: the graph shows a linear decrease in the proportion of jobs at risk of full automation. 60% 55% 50% 45% 40% 35% 30% 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% 0% Waste Management Transportation and Retail Value Proportion of Jobs at Risk of Full Automation 41% Employment Share of Total Jobs Series Manufacturing H Retail 19% Administration Finance and Insurance LI Electricity and Gas Other
Algebra for College Students
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285195780
Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Chapter11: Systems Of Equations
Section11.CT: Test
Problem 24CT
Related questions
Question
Which of the following is the largest number of jobs that could theoretically be within the software industry at present, based on the information available?
A) 1,4 million
B) 2,4 million
C) 4 million
D) 8 million
E) 10 million
Transcribed Image Text:Preparing for Automation The possibility of having robots or mechanical assistants completing our laborious, dangerous, or repetitive day-to-day tasks has long been a dream of humanity. Now, as Robotic Process Automation (RPA) becomes commonplace, this dream or concern, depending on viewpoint - is getting closer. RPA, far from the walking, talking android commonly found in science fiction series, can be thought of as a programmable piece of software which, through using a series of rules, will complete repetitive tasks with a lower error rate and less interruption than a human completing the same tasks. The aim of RPA, beyond improving efficiency, is to free up humans from the monotony of roles like data entry, stock management and predictable physical work, to focus on more critical, unpredictable tasks such as decision making, interpreting, and delivering insight to customers. Ask any expert and you can almost guarantee that they will inform you that years of data reliably point to the conclusion that automation has always created more jobs than it has removed. The invention of the plough has allowed us to stop working on farms and technology has continued in this fashion, boosting productivity and, in turn, providing greater work satisfaction and improved living standards. It is currently estimated that 3% of roles could be entirely automated using the technology we have available to us now. By 2025 this will have risen to around 35%, by 2030 it will be at 50% and by 2080 scientists are predicting advanced artificial intelligence (Al) technologies will have replaced 85% of current jobs. A more astonishing figure is the 42% of roles which could be made more efficient, more productive, and more enjoyable through automating individual tasks within the wider role. This is not spread evenly across industries, however certain industries like waste management, an industry with a CHF 48 billion salary bill in Switzerland, where many humans are currently paid 'hazard pay' to do dangerous but repetitive tasks, is the industry in Switzerland with the highest potential for automation. As we begin to enter this Fourth Industrial Revolution, it is becoming apparent that there is a separation of organisations into two clear groups: those who are using basic digitisation to support their business, and those who have re-examined the way they do business and integrated combinations of technologies, including RPA, to great effect. So, should we run for the hills or turn and embrace RPA? The answer is not clear but, looking at those who have benefitted from this technology already, preparation for automation will be key. "By 2080 scientists are predicting advanced artificial intelligence (Al) technologies will have replaced 85% of current jobs"
Transcribed Image Text:Likelihood of industries becoming automated in the future Proportion of jobs and their risk of automation. Note: the graph shows a linear decrease in the proportion of jobs at risk of full automation. 60% 55% 50% 45% 40% 35% 30% 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% 0% Waste Management Transportation and Retail Value Proportion of Jobs at Risk of Full Automation 41% Employment Share of Total Jobs Series Manufacturing H Retail 19% Administration Finance and Insurance LI Electricity and Gas Other

Transcribed Image Text:Preparing
for Automation
The possibility of having robots or
mechanical assistants completing our
laborious, dangerous, or repetitive
day-to-day tasks has long been a
dream of humanity. Now, as Robotic
Process Automation (RPA) becomes
commonplace, this dream - or
concern, depending on viewpoint -
is getting closer.
RPA, far from the walking, talking android
commonly found in science fiction series,
can be thought of as a programmable
piece of software which, through using
a series of rules, will complete repetitive
task with a lower error rate and less
interruption than a human completing
the same tasks. The aim of RPA, beyond
improving efficiency, is to free up
humans from the monotony of roles
like data entry, stock management and
predictable physical work, to focus on
more critical, unpredictable tasks such
as decision making, interpreting, and
delivering insight to customers.
Ask any expert and you can almost
guarantee that they will inform you
that years of data reliably point to
the conclusion that automation has
always created more jobs than it has
removed. The invention of the plough
has allowed us to stop working on farms
and technology has continued in this
fashion, boosting productivity and, in
turn, providing greater work satisfaction
and improved living standards.
It is currently estimated that 3% of roles
could be entirely automated using the
technology we have available to us now.
By 2025 this will have risen to around
35%, by 2030 it will be at 50% and by
2080 scientists are predicting advanced
artificial intelligence (Al) technologies
will have replaced 85% of current jobs.
A more astonishing figure is the
of roles which could be made more
efficient, more productive, and more
enjoyable through automating individual
tasks within the wider role. This is
not spread evenly across industries,
however certain industries like waste
management, an industry with a CHF 48
billion salary bill in Switzerland, where
many humans are currently paid 'hazard
pay' to do dangerous but repetitive
tasks, is the industry in Switzerland with
the highest potential for automation.
As we begin to enter this Fourth
Industrial Revolution, it is becoming
apparent that there is a separation of
organisations into two clear groups:
those who are using basic digitisation
to support their business, and those
who have re-examined the way they do
business and integrated combinations.
of technologies, including RPA, to great
effect.
So, should we run for the hills or turn
and embrace RPA? The answer is not
clear but, looking at those who have
benefitted from this technology already,
preparation for automation will be key.
"By 2080 scientists are predicting
advanced artificial intelligence
(Al) technologies will have
replaced 85% of current jobs"
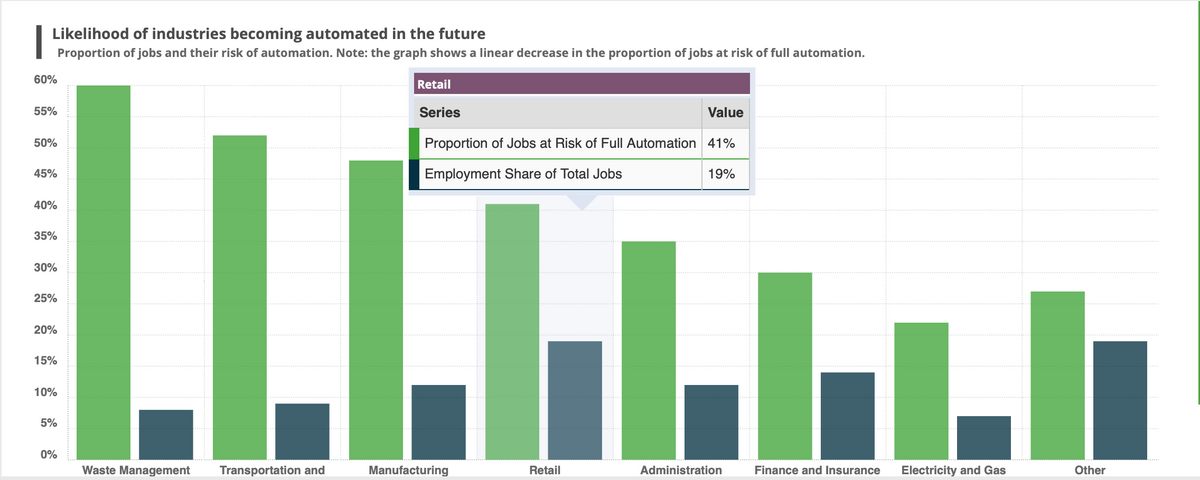
Transcribed Image Text:Likelihood of industries becoming automated in the future
Proportion of jobs and their risk of automation. Note: the graph shows a linear decrease in the proportion of jobs at risk of full automation.
60%
55%
50%
45%
40%
35%
30%
25%
20%
15%
10%
5%
0%
Waste Management Transportation and
Retail
Series
Value
Proportion of Jobs at Risk of Full Automation 41%
Employment Share of Total Jobs
19%
Manufacturing
Retail
Administration
Finance and Insurance Electricity and Gas
Other
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra for College Students
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195780
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra for College Students
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195780
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning