Problem 2: The slotted bar shown below is pinned at O. It has a constant angular velocity of 0 = 3 rad/s and drives the pin, P, counterclockwise through the curved guide. The shape of the guide is defined by the equation (0.40) m, where 0 is in radians and lies in the horizontal plane. If the pin has a mass of 0.2 kg, determine: r =
Problem 2: The slotted bar shown below is pinned at O. It has a constant angular velocity of 0 = 3 rad/s and drives the pin, P, counterclockwise through the curved guide. The shape of the guide is defined by the equation (0.40) m, where 0 is in radians and lies in the horizontal plane. If the pin has a mass of 0.2 kg, determine: r =
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Chapter1: Introduction To Statics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.47P: A rifle at A is fired at a target at B. If the speed of the bullet is 1400 ft/s, determine the...
Related questions
Question
Only c & d
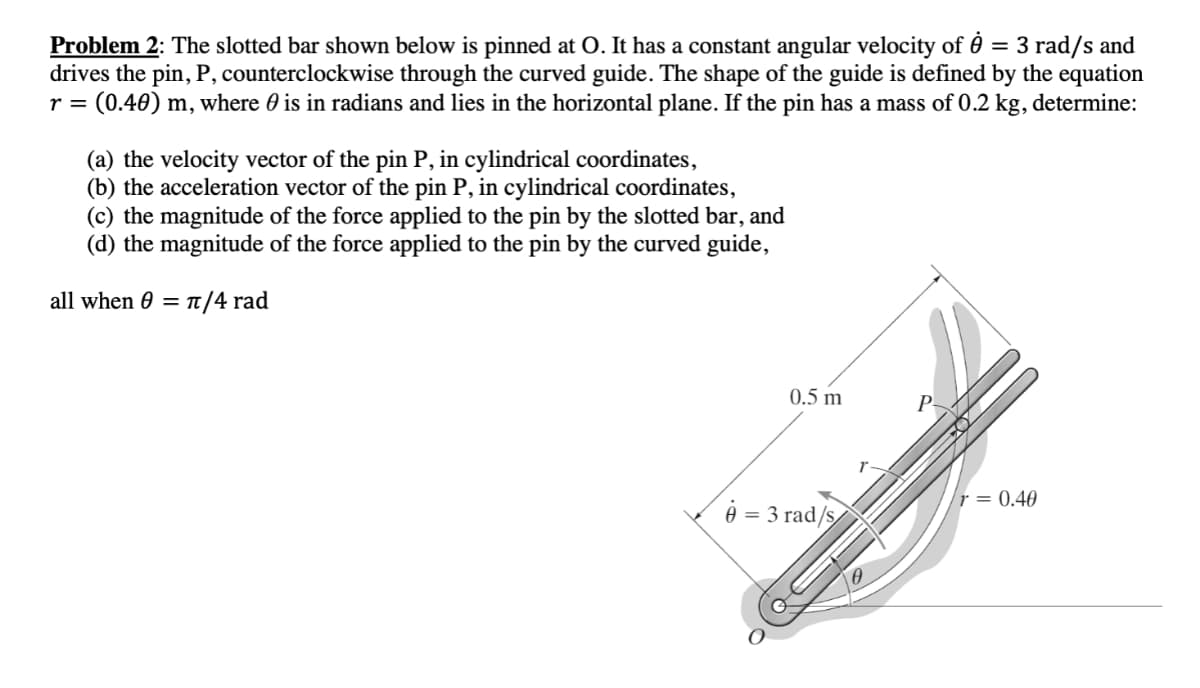
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 2: The slotted bar shown below is pinned at O. It has a constant angular velocity of 0 = 3 rad/s and
drives the pin, P, counterclockwise through the curved guide. The shape of the guide is defined by the equation
r = (0.40) m, where 0 is in radians and lies in the horizontal plane. If the pin has a mass of 0.2 kg, determine:
(a) the velocity vector of the pin P, in cylindrical coordinates,
(b) the acceleration vector of the pin P, in cylindrical coordinates,
(c) the magnitude of the force applied to the pin by the slotted bar, and
(d) the magnitude of the force applied to the pin by the curved guide,
all when 0 = 1/4 rad
0.5 m
r = 0.40
ė
= 3 rad/s
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L