Problem 2.5 Mail Order House A mail order house uses 18,000 boxes per year. Carrying costs are $0.60 per box per year. Ordering costs are $96. The following price schedule applies. Number of boxes 1,000 to 1,999 Price per box $1.25 $1.20 $1.15 $1.10 2,000 to 4,999 5,000 to 9,999 10,000 or more EOQ = SQRT(2DS/H) Common minimum Q = SQRT((2*18000*96/.6)= a. Find the optimal order quanity. 2400 boxes Total Cost at 2400 = Carrying Cost+Order Cost+Purchase Cost (Q/2)H + (D/Q)S + PD (2400/2)*.6+(18000/2400)*96+1.20*18000 $23,040 Total Cost at 5000 = Total Cost at 10,000 = b. Number of orders per year.
Problem 2.5 Mail Order House A mail order house uses 18,000 boxes per year. Carrying costs are $0.60 per box per year. Ordering costs are $96. The following price schedule applies. Number of boxes 1,000 to 1,999 Price per box $1.25 $1.20 $1.15 $1.10 2,000 to 4,999 5,000 to 9,999 10,000 or more EOQ = SQRT(2DS/H) Common minimum Q = SQRT((2*18000*96/.6)= a. Find the optimal order quanity. 2400 boxes Total Cost at 2400 = Carrying Cost+Order Cost+Purchase Cost (Q/2)H + (D/Q)S + PD (2400/2)*.6+(18000/2400)*96+1.20*18000 $23,040 Total Cost at 5000 = Total Cost at 10,000 = b. Number of orders per year.
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter2: Introduction To Spreadsheet Modeling
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20P: Julie James is opening a lemonade stand. She believes the fixed cost per week of running the stand...
Related questions
Question
supply chain questions
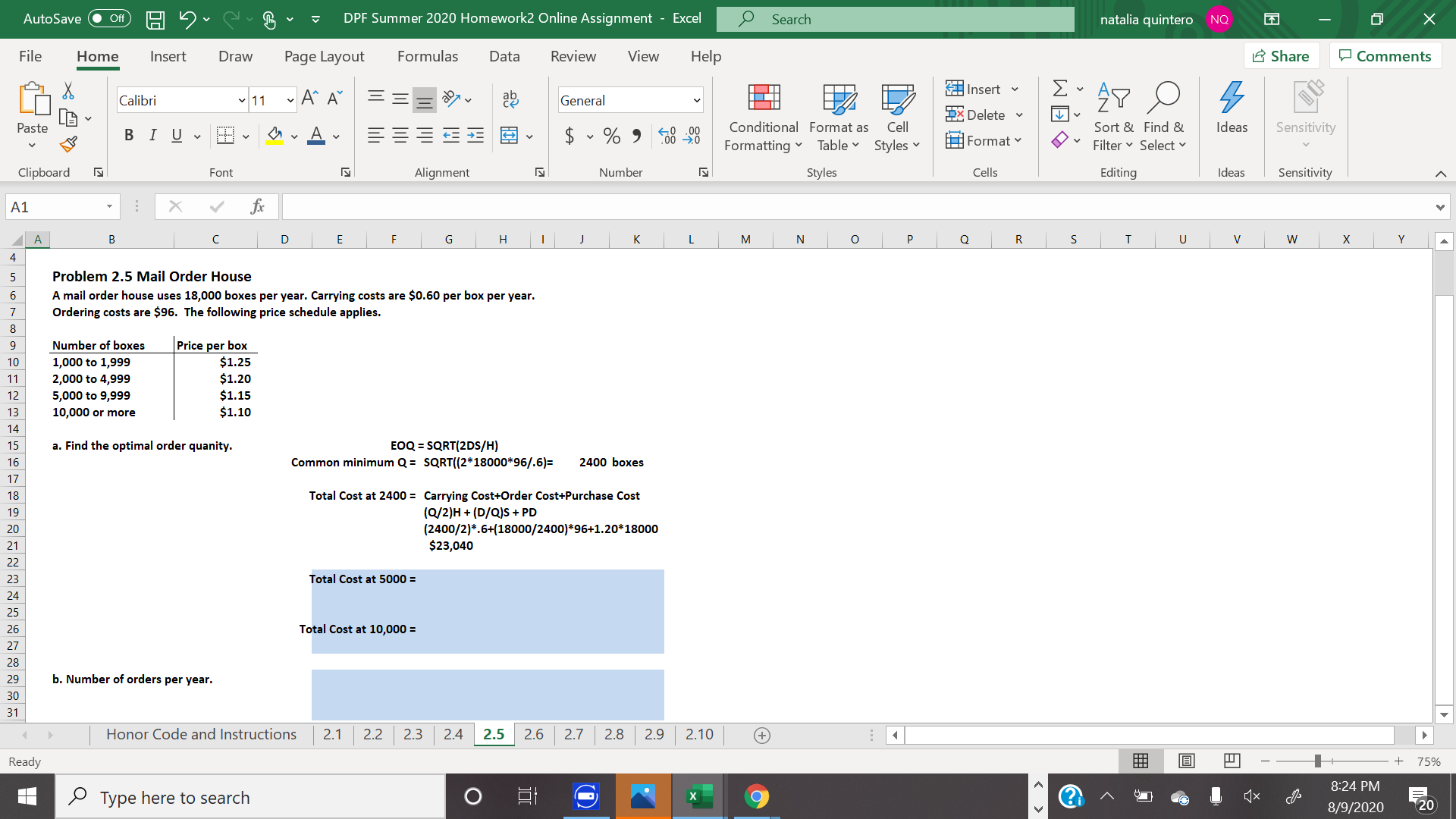
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 2.5 Mail Order House
A mail order house uses 18,000 boxes per year. Carrying costs are $0.60 per box per year.
Ordering costs are $96. The following price schedule applies.
Number of boxes
1,000 to 1,999
Price per box
$1.25
$1.20
$1.15
$1.10
2,000 to 4,999
5,000 to 9,999
10,000 or more
EOQ = SQRT(2DS/H)
Common minimum Q = SQRT((2*18000*96/.6)=
a. Find the optimal order quanity.
2400 boxes
Total Cost at 2400 = Carrying Cost+Order Cost+Purchase Cost
(Q/2)H + (D/Q)S + PD
(2400/2)*.6+(18000/2400)*96+1.20*18000
$23,040
Total Cost at 5000 =
Total Cost at 10,000 =
b. Number of orders per year.

Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, operations-management and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259667473
Author:
William J Stevenson
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259666100
Author:
F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259667473
Author:
William J Stevenson
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259666100
Author:
F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781285869681
Author:
Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. Patterson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781478623069
Author:
Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon Olsen
Publisher:
Waveland Press, Inc.