Problem 24. The thermodynamics of decomposition reactions The thermodynamic data of the species involved in the reactions are listed in the table below: Ag₂CO3(s) Ag₂O(s) CO₂(g) AH (298K) (kJ mol-¹) -501.66 -30.58 -393.51 S (298K) (J mol-¹ K-¹) 167.4 121.8 213.8 m Cpm (J mol-¹ K-¹) 109.6 65.7 37.6 24-1 The decomposition of Ag2CO3 proceeds with the chemical equation: Ag2CO3(s) →Ag2O(s) + CO₂(g). Calculate the standard equilibrium constant, K (298 K), of the reaction at 298 K. 24-2 The enthalpy and entropy changes with temperature are given by the equations: AH (T₂)=AH (T) +AC (T₂-T₂) AS (T₂)=4,S (T₂)+A,C in ¹2 T₁ In order to dry Ag2CO3(s) with a hot air flow under a constant pressure of 105 Pa and a constant temperature of 383 K, calculate the minimum partial pressure of CO2(g) needed in the air flow to avoid the decomposition of Ag2CO3(s).
Problem 24. The thermodynamics of decomposition reactions The thermodynamic data of the species involved in the reactions are listed in the table below: Ag₂CO3(s) Ag₂O(s) CO₂(g) AH (298K) (kJ mol-¹) -501.66 -30.58 -393.51 S (298K) (J mol-¹ K-¹) 167.4 121.8 213.8 m Cpm (J mol-¹ K-¹) 109.6 65.7 37.6 24-1 The decomposition of Ag2CO3 proceeds with the chemical equation: Ag2CO3(s) →Ag2O(s) + CO₂(g). Calculate the standard equilibrium constant, K (298 K), of the reaction at 298 K. 24-2 The enthalpy and entropy changes with temperature are given by the equations: AH (T₂)=AH (T) +AC (T₂-T₂) AS (T₂)=4,S (T₂)+A,C in ¹2 T₁ In order to dry Ag2CO3(s) with a hot air flow under a constant pressure of 105 Pa and a constant temperature of 383 K, calculate the minimum partial pressure of CO2(g) needed in the air flow to avoid the decomposition of Ag2CO3(s).
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter18: Electrochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9RQ: What characterizes an electrolytic cell? What is an ampere? When the current applied to an...
Related questions
Question
5
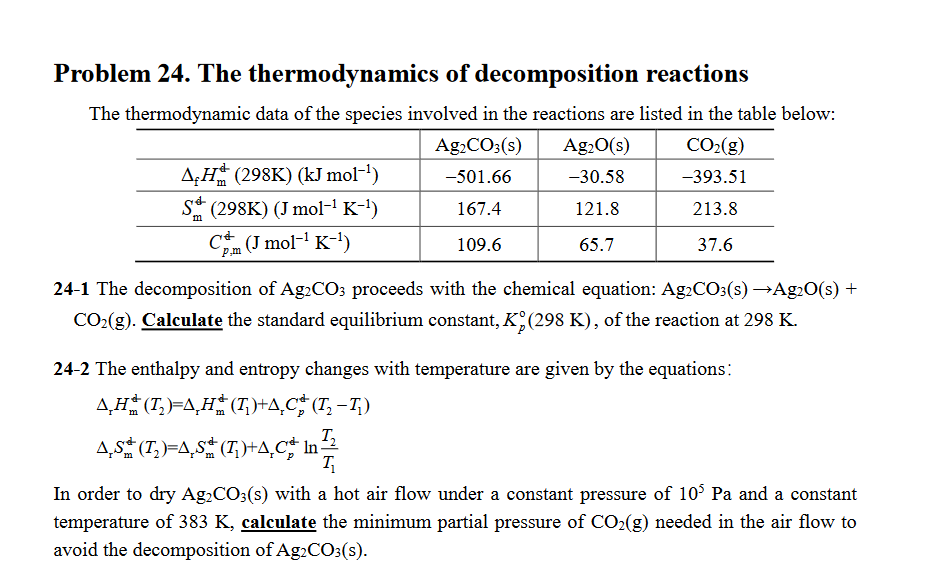
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 24. The thermodynamics of decomposition reactions
The thermodynamic data of the species involved in the reactions are listed in the table below:
Ag₂CO3(s)
Ag₂O(s)
CO₂(g)
AH (298K) (kJ mol-¹)
-501.66
-30.58
-393.51
S (298K) (J mol-¹ K-¹)
167.4
121.8
213.8
m
C (J mol-¹ K-¹)
109.6
65.7
37.6
24-1 The decomposition of Ag2CO3 proceeds with the chemical equation: Ag2CO3(s) →Ag₂O(s) +
CO₂(g). Calculate the standard equilibrium constant, K (298 K), of the reaction at 298 K.
24-2 The enthalpy and entropy changes with temperature are given by the equations:
A₂H (T₂)=AH (T₂)+A,C# (T₂ −T₂)
AS✯ (T₂)=øSª (T₁)+øCº In
T₂
T₁
In order to dry Ag₂CO3(s) with a hot air flow under a constant pressure of 105 Pa and a constant
temperature of 383 K, calculate the minimum partial pressure of CO₂(g) needed in the air flow to
avoid the decomposition of Ag2CO3(s).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
