Prompt: Explore the applet. In the applet above, a solid object is displayed. You can make the object appear "see though" using the "Filling" slider. Make the object completely see-through. The xy-plan is shown using the red and green arrows. You can click on the image of the solid and drag to change the view. Click and drag the image so you can see the xy-plane in the standard orientation--the y-axis vertical and the x-axis horizontal. The upper and lower curves mark the top and the bottom of the solid. the left and right sides of the solid are set by boundaries in x. The solid has a cross-section of a square. The 4 sides of the square are determined by the distance between the upper and the lower functions. If we can write an expression that represents the area of the square cross-section, then we can integrate over the x axis from a to be to calculate the volume! Answer the following auestions: 1. The upper and lower functions are graphed in the xy-plane. The top of the solid is determined by the top left and right corners of the square. Why does the square size change? What determines the size of the square?
Prompt: Explore the applet. In the applet above, a solid object is displayed. You can make the object appear "see though" using the "Filling" slider. Make the object completely see-through. The xy-plan is shown using the red and green arrows. You can click on the image of the solid and drag to change the view. Click and drag the image so you can see the xy-plane in the standard orientation--the y-axis vertical and the x-axis horizontal. The upper and lower curves mark the top and the bottom of the solid. the left and right sides of the solid are set by boundaries in x. The solid has a cross-section of a square. The 4 sides of the square are determined by the distance between the upper and the lower functions. If we can write an expression that represents the area of the square cross-section, then we can integrate over the x axis from a to be to calculate the volume! Answer the following auestions: 1. The upper and lower functions are graphed in the xy-plane. The top of the solid is determined by the top left and right corners of the square. Why does the square size change? What determines the size of the square?
Algebra for College Students
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285195780
Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Chapter4: Rational Expressions
Section4.CM: Cumulative Review Problem Set
Problem 55CM
Related questions
Question
1

Transcribed Image Text:Prompt:
Explore the applet.
In the applet above, a solid object is displayed. You can make the object appear "see though" using the
"Filling" slider. Make the object completely see-through.
The xy-plan is shown using the red and green arrows. You can click on the image of the solid and drag to
change the view. Click and drag the image so you can see the xy-plane in the standard orientation--the
y-axis vertical and the x-axis horizontal.
The upper and lower curves mark the top and the bottom of the solid. the left and right sides of the
solid are set by boundaries in x.
The solid has a cross-section of a square. The 4 sides of the square are determined by the distance
between the upper and the lower functions.
If we can write an expression that represents the area of the square cross-section, then we can integrate
over the x axis from a to be to calculate the volume!
Anşwer the following questions:
1. The upper and lower functions are graphed in the xy-plane. The top of the solid is determined by the
top left and right corners of the square. Why does the square size change? What determines the size
of the square?
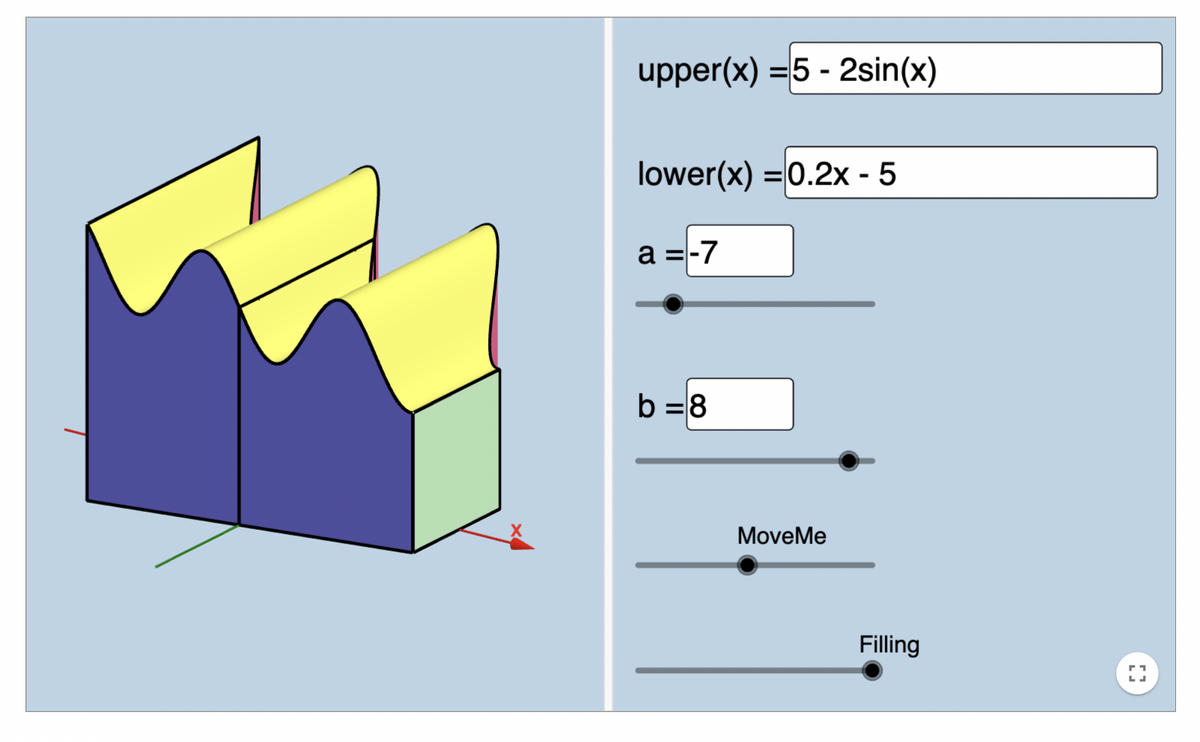
Transcribed Image Text:upper(x) =5 - 2sin(x)
lower(x) =0.2x - 5
a =-7
%3D
b =8
MoveMe
Filling
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra for College Students
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195780
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195728
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra for College Students
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195780
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195728
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage