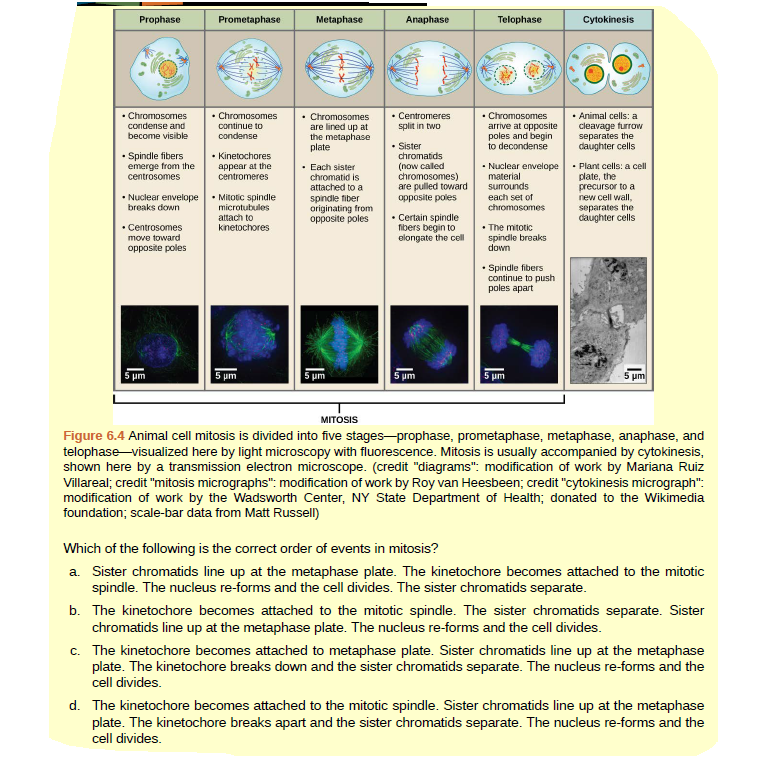
Prophase Prometaphase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis • Chromosomes continue to condense • Chromosomes are lined up at the metaphase plate • Centromeres split in two Chromosomes condense and become visible • Animal cells: a cleavage furrow separates the daughter cells Chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and begin to decondense • Sister chromatids • Spindle fibers emerge from the centrosomes • Kinetochores appear at the centromeres · Each sister chromatid is attached to a (now called chromosomes) are pulled toward opposite poles • Nuclear envelope material surrounds • Plant cells: a cell plate, the precursor to a new cell wall, • Mitotic spindle microtubules attach to kinetochores • Nuclear envelope breaks down spindle fiber originating from opposite poles each set of chromosomes separates the daughter cells • Centrosomes move toward • Certain spindle fibers begin to elongate the cell • The mitotic spindle breaks down opposite poles • Spindle fibers continue to push poles apart 5 pm 5 μm pm 5 um 5 pm 5 um MITOSIS Figure 6.4 Animal cell mitosis is divided into five stages-prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase -visualized here by light microscopy with fluorescence. Mitosis is usually accompanied by cytokinesis, shown here by a transmission electron microscope. (credit "diagrams": modification of work by Mariana Ruiz Villareal; credit "mitosis micrographs": modification of work by Roy van Heesbeen; credit "cytokinesis micrograph": modification of work by the Wadsworth Center, NY State Department of Health; donated to the Wikimedia foundation; scale-bar data from Matt Russell) Which of the following is the correct order of events in mitosis? a. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides. The sister chromatids separate. b. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. The sister chromatids separate. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides. c. The kinetochore becomes attached to metaphase plate. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore breaks down and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides. d. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore breaks apart and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides.
Oogenesis
The formation of the ovum (mature female gamete) from undifferentiated germ cells is called oogenesis. This process takes place in the ovaries (female gonads). Oogenesis consists of three stages known as the multiplication phase, growth phase, and maturation phase.
Cell Division
Cell division involves the formation of new daughter cells from the parent cells. It is a part of the cell cycle that takes place in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. Cell division is required for three main reasons:
Figure 6.4 Which of the following is the correct order of events in mitosis?
a. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides. The sister chromatids separate.
b. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. The sister chromatids separate. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides.
c. The kinetochore becomes attached to metaphase plate. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore breaks down and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides.
d. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore breaks apart and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images







