Prove f(x) has a zero (i.e., a point where f(p)=0) on each interval. You can assert that the functions are continuous on the relevant intervals (i.e., a rigor- ous proof that f(x) is continuous on the given interval is not needed). f (x) = (x² + 3x – 2)ln(x² + 4); on [0, 1] -
Prove f(x) has a zero (i.e., a point where f(p)=0) on each interval. You can assert that the functions are continuous on the relevant intervals (i.e., a rigor- ous proof that f(x) is continuous on the given interval is not needed). f (x) = (x² + 3x – 2)ln(x² + 4); on [0, 1] -
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter5: Inverse, Exponential, And Logarithmic Functions
Section5.5: Properties Of Logarithms
Problem 68E
Related questions
Question
COURSE: Mathematical Analysis/
TOPIC: Continuity + Connectedness
![Prove f(x) has a zero (i.e., a point where f(p)=0) on each interval. You can
assert that the functions are continuous on the relevant intervals (i.e., a rigor-
ous proof that f(x) is continuous on the given interval is not needed).
f (x) = (x² + 3x – 2)ln(x² + 4); on [0, 1]
-](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fbaa9c753-6b68-41b4-8837-61aa8aa0a19b%2F0be19135-d025-4d90-aa32-4f28c58fd81b%2Fldwkj0l_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Prove f(x) has a zero (i.e., a point where f(p)=0) on each interval. You can
assert that the functions are continuous on the relevant intervals (i.e., a rigor-
ous proof that f(x) is continuous on the given interval is not needed).
f (x) = (x² + 3x – 2)ln(x² + 4); on [0, 1]
-
Expert Solution
Step 1
According to the given information, it is required to prove that f(x) has a zero.
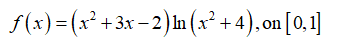
Step 2
Use the below theorem to show that f(x) has zero.
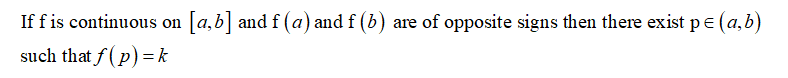
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage
