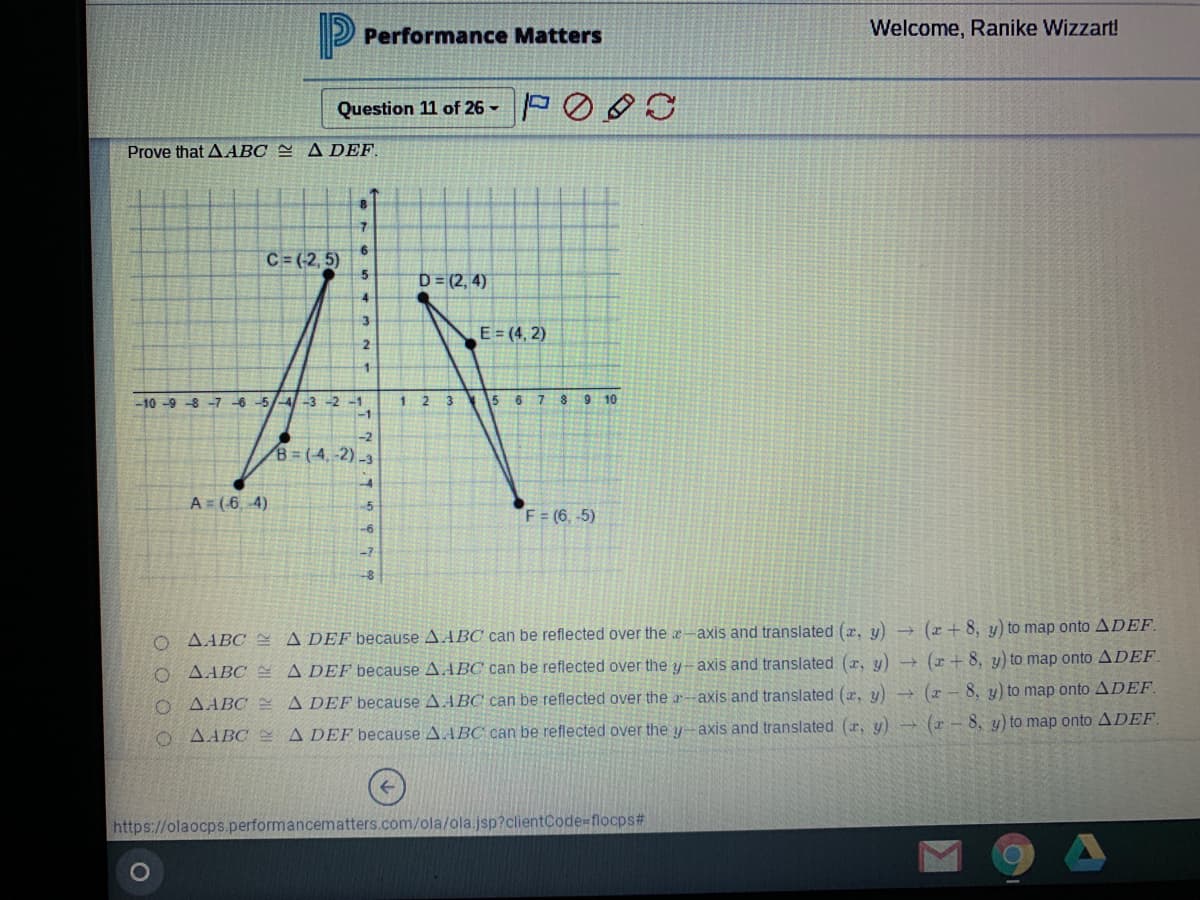
Prove that AABC = A DEF. 7 6. C=(2, 5) D= (2, 4) 4. 3. E = (4, 2) 8 9 10 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5/-4-3 -2 -1 -1 23 5 6 7 B (4,-2) -3 A= (6, 4) F= (6, -5) O AABC A DEF because AABC can be reflected over the a-axis and translated (z, y) - (z+ 8, y) to map onto ADEF. O AABC E A DEF because AABC can be reflected over the y-axis and translated (r, y) (I+ 8, y) to map onto ADEF. O AABC A DEFbecause A.ABC can be reflected over the r-axis and translated (z, y) - (r - 8, y) to map onto ADEF. O AABC E A DEF because A.ABC can be reflected over the y-axis and translated (r, y) - (r - 8, y) to map onto ADEF.
Prove that AABC = A DEF. 7 6. C=(2, 5) D= (2, 4) 4. 3. E = (4, 2) 8 9 10 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5/-4-3 -2 -1 -1 23 5 6 7 B (4,-2) -3 A= (6, 4) F= (6, -5) O AABC A DEF because AABC can be reflected over the a-axis and translated (z, y) - (z+ 8, y) to map onto ADEF. O AABC E A DEF because AABC can be reflected over the y-axis and translated (r, y) (I+ 8, y) to map onto ADEF. O AABC A DEFbecause A.ABC can be reflected over the r-axis and translated (z, y) - (r - 8, y) to map onto ADEF. O AABC E A DEF because A.ABC can be reflected over the y-axis and translated (r, y) - (r - 8, y) to map onto ADEF.
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305652224
Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Chapter8: Complex Numbers And Polarcoordinates
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2RP: A Bitter Dispute With the publication of Ars Magna, a dispute intensified between Jerome Cardan and...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Performance Matters
Welcome, Ranike Wizzart!
Question 11 of 26 - PO0
Prove that AABC = A DEF.
6.
C=(-2, 5)
D = (2, 4)
E= (4, 2)
2
-1
7 8 9 10
-10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5/-4-3 -2 -1
-1
2 3
15
-2
B (4,-2) -3
A= (6. 4)
F = (6, -5)
-6
-7
O AABC A DEF because AABC can be reflected over the a-axis and translated (x, y) → (x+ 8, y) to map onto ADEF.
AABC A DEF because A.ABC can be reflected over the y-axis and translated (r, y) + (r + 8, y) to map onto ADEF.
AABC A DEF because AABC can be reflected over the a-axis and translated (x, y) (x - 8, y) to map onto ADEF.
O AABC E A DEF because A.ABC can be reflected over the y-axis and translated (r, y) - (r - 8, y) to map onto ADEF.
https://olaocps.performancematters.com/ola/ola.jsp?clientCode=flocps#
O O O O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, geometry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781305652224
Author:
Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781305652224
Author:
Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage